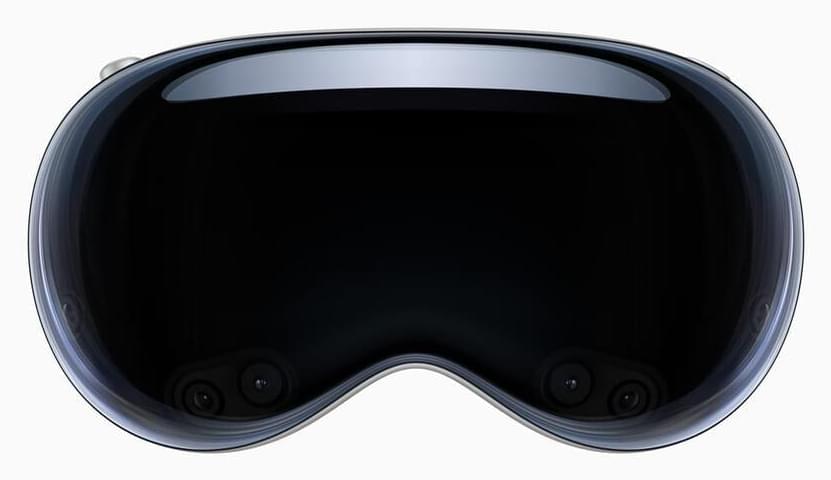
“Apple today unveiled Apple Vision Pro, a revolutionary spatial computer that seamlessly blends digital content with the physical world, while allowing users to stay present and connected to others. Vision Pro creates an infinite canvas for apps that scales beyond the boundaries of a traditional display and introduces a fully three-dimensional user interface controlled by the most natural and intuitive inputs possible — a user’s eyes, hands, and voice.”
CUPERTINO, CALIFORNIA Apple today unveiled Apple Vision Pro, a revolutionary spatial computer that seamlessly blends digital content with the physical world, while allowing users to stay present and connected to others. Vision Pro creates an infinite canvas for apps that scales beyond the boundaries of a traditional display and introduces a fully three-dimensional user interface controlled by the most natural and intuitive inputs possible — a user’s eyes, hands, and voice. Featuring visionOS, the world’s first spatial operating system, Vision Pro lets users interact with digital content in a way that feels like it is physically present in their space. The breakthrough design of Vision Pro features an ultra-high-resolution display system that packs 23 million pixels across two displays, and custom Apple silicon in a unique dual-chip design to ensure every experience feels like it’s taking place in front of the user’s eyes in real time.
“Today marks the beginning of a new era for computing,” said Tim Cook, Apple’s CEO. “Just as the Mac introduced us to personal computing, and iPhone introduced us to mobile computing, Apple Vision Pro introduces us to spatial computing. Built upon decades of Apple innovation, Vision Pro is years ahead and unlike anything created before — with a revolutionary new input system and thousands of groundbreaking innovations. It unlocks incredible experiences for our users and exciting new opportunities for our developers.”
“Creating our first spatial computer required invention across nearly every facet of the system,” said Mike Rockwell, Apple’s vice president of the Technology Development Group. “Through a tight integration of hardware and software, we designed a standalone spatial computer in a compact wearable form factor that is the most advanced personal electronics device ever.”