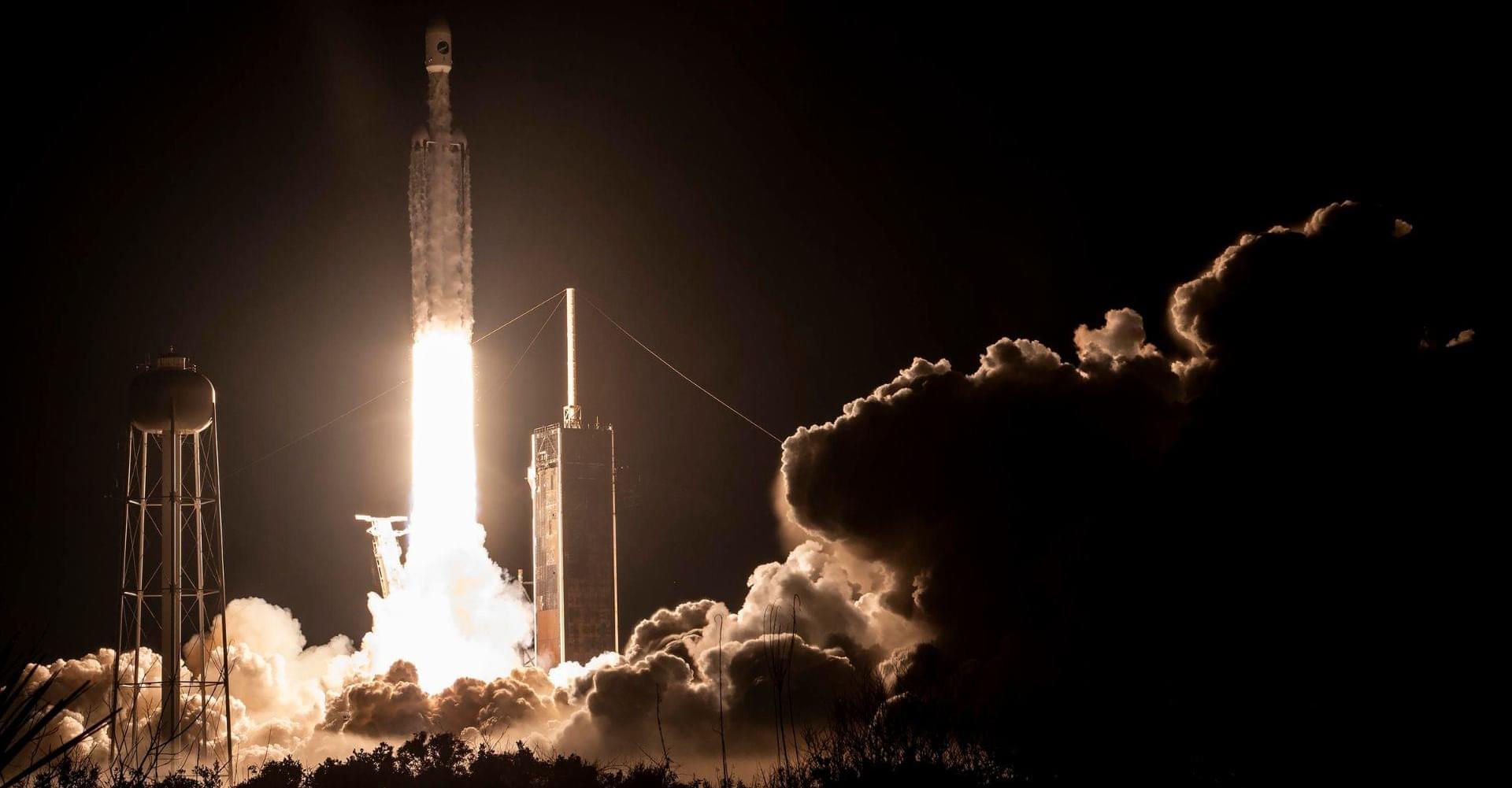
Mysterious US military space plane launches on 8th secret mission with SpaceX.
SpaceX has teamed up with the US Space Force to launch X-37B for testing sensors and technology in earth’s lower orbit.
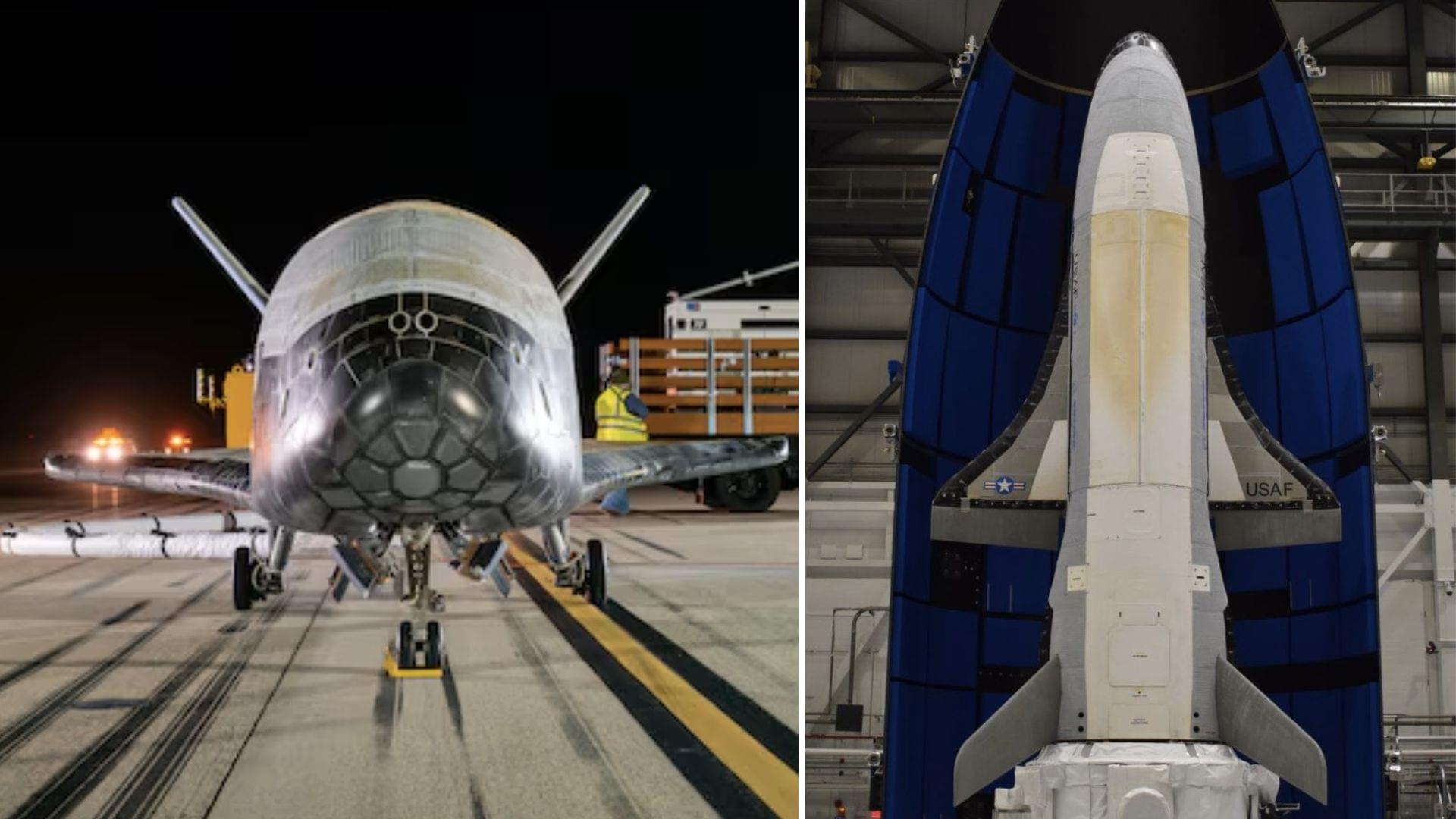


US secret military space plane to embark on new mission with undisclosed goal.
Developed by Boeing, the uncrewed spacecraft is used by the U.S. military to conduct experiments in high and low Earth orbits.
Boeing earlier claimed that the space plane is equipped with state-of-the-art technologies that provide exceptional performance and durability. Its modular design allows for a wide range of experiments and missions, making it a versatile and valuable asset in space exploration.
While it looks like a smaller version of the now-retired space shuttle, the X-37B can’t get into orbit without a boost. For this upcoming mission, it’s hitching a ride on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket inside the rocket’s fairing, a protective enclosure made of carbon composite that keeps it safe during the launch until it’s ready to be released into orbit, reported ABC News.
Inside Beijing’s Crisis: Tanks, Fear, and a Nation on Edge reveals the shocking truth behind China’s escalating turmoil in 2025. From military convoys flooding the capital to social unrest, epidemics, and economic collapse, discover how Beijing has become the symbol of a nation on the brink.
#chinanews #chinacrisis #chinadisasters
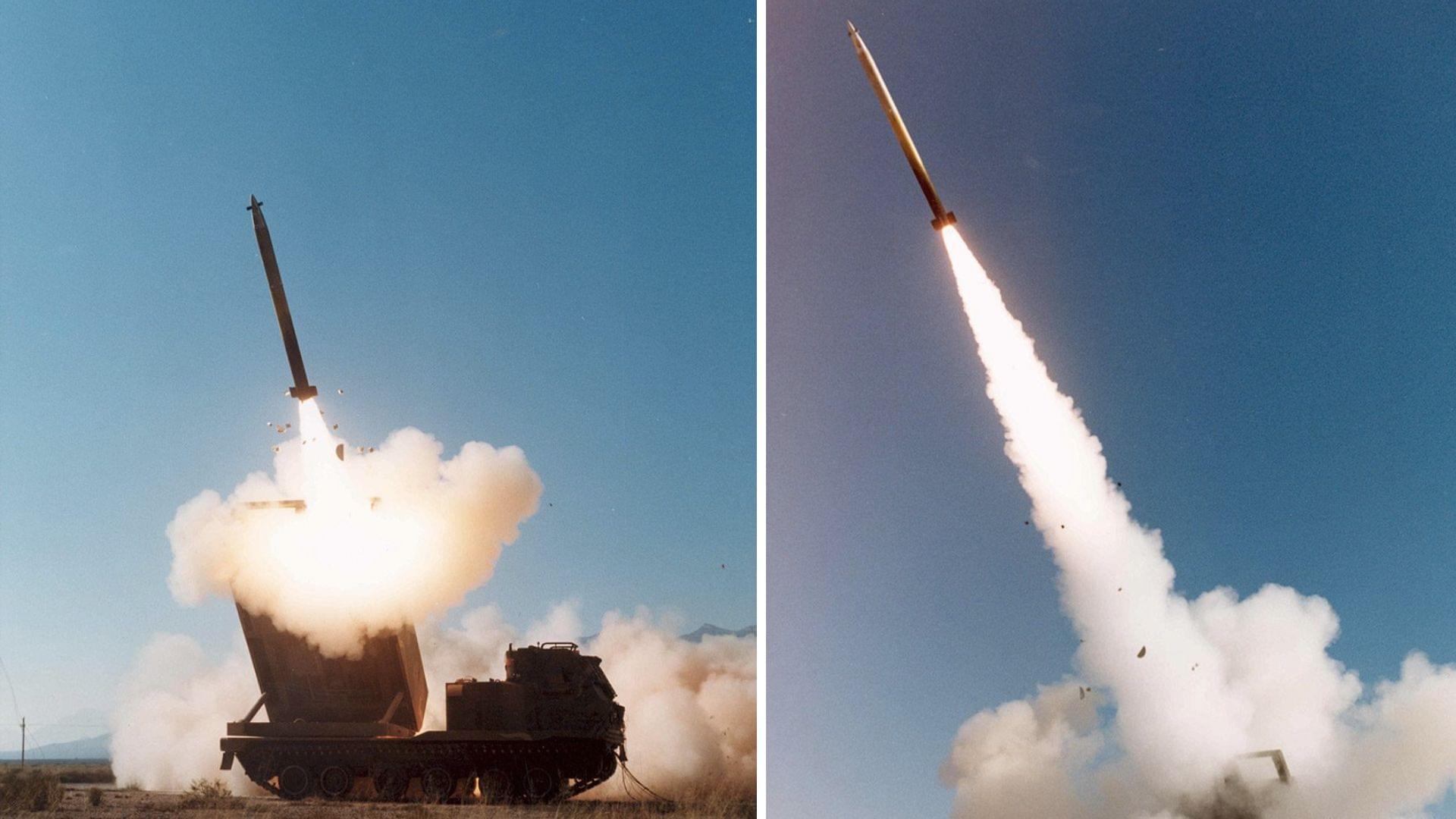

98% reliable, guided rocket that hits target with perfection to get production boost.
GMLRS, also known as the “70-kilometer sniper rifle”, is an all-weather, precision-guided rocket. The system offers higher accuracy, reducing the number of rockets needed to defeat targets.
Lockheed Martin claims that the MLRS Family of Munitions (MFOM) includes a variety of precision-strike rockets and missiles, with on-going evolutionary development to meet the needs of the warfighter. These combat-proven low-cost, low-risk rounds greatly reduce collateral damage and provide tremendous capability and flexibility in addressing today’s threats.
There are multiple GMLRS variants, according to the company. Its GMLRS Unitary round integrates a 200-pound unitary warhead, providing precision strike for point targets. The Unitary variant has a range exceeding 70 kilometers.
Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland, have demonstrated that a quantum algorithm can be used to speed up an information analysis task that classical computers struggle to perform.
The innovation tackles a key element of information operations: tracking and attributing topics and narratives as they emerge and evolve online, which can help analysts spot indications of potential terrorist acts, for example. This involves using computers to perform what’s known as semantic text similarity analysis, or comparing the similarities within a textual dataset — not just the similarity of the words, but the meaning behind them, which makes it possible to identify related texts even if they don’t share any common keywords.
“The amount of open-source text data online — on social media platforms especially — is growing dramatically, and our ability to analyze all of that data has not kept pace with our ability to collect it,” said Roxy Holden, a mathematician at APL and principal investigator of this effort. “Intelligence analysts have limited resources, so finding better ways to automate this kind of analysis is critical for the military and the intelligence community.”
APL researchers have demonstrated that a quantum algorithm can be used to speed up an information analysis task that classical computers struggle to perform.
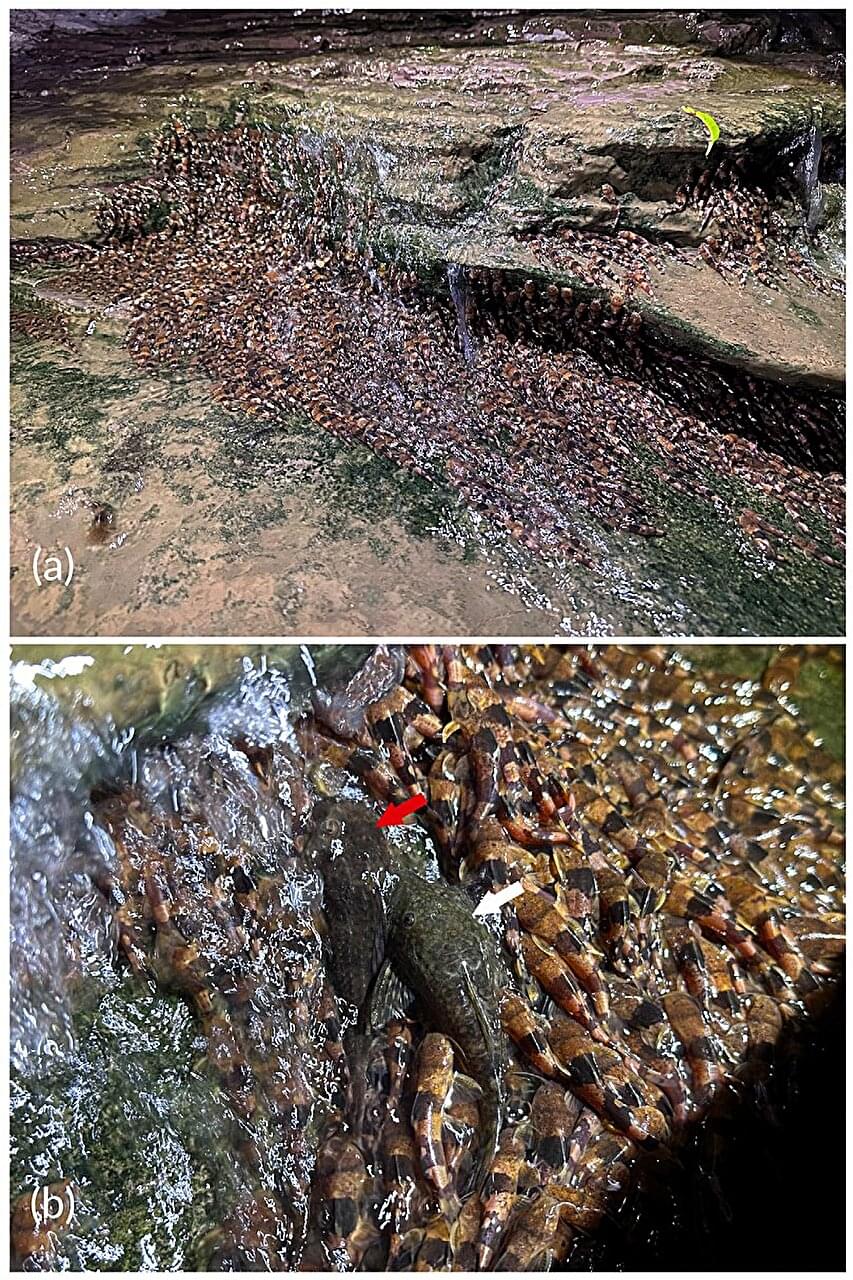

Nature often puts on incredible displays. A recent example caught on camera shows thousands of bumblebee catfish (Rhyacoglanis paranensis) climbing waterfalls in southern Brazil. This is the first time the species has been observed in such a large group and climbing, according to a study published in the Journal of Fish Biology describing the spectacle.
Environmental Military Police from Mato Grosso do Sul State spotted the catfish scaling slippery rocks between one and four meters high behind waterfalls on the Aquidauana River. The sighting occurred in November 2024 at the beginning of the rainy season, and a week later, a team of Brazilian scientists arrived to document the event.
They observed that the catfish’s climbing behavior depended on the time of day. During the hot afternoons, the fish sheltered under rocks and in shaded areas. They began climbing in the early evening as the sun was setting. The researchers also studied how the fish are able to climb. They keep their paired fins wide open and use lateral and caudal movements to push themselves forward. Scientists believe this is also aided by a suction mechanism that helps them stick to flat surfaces.
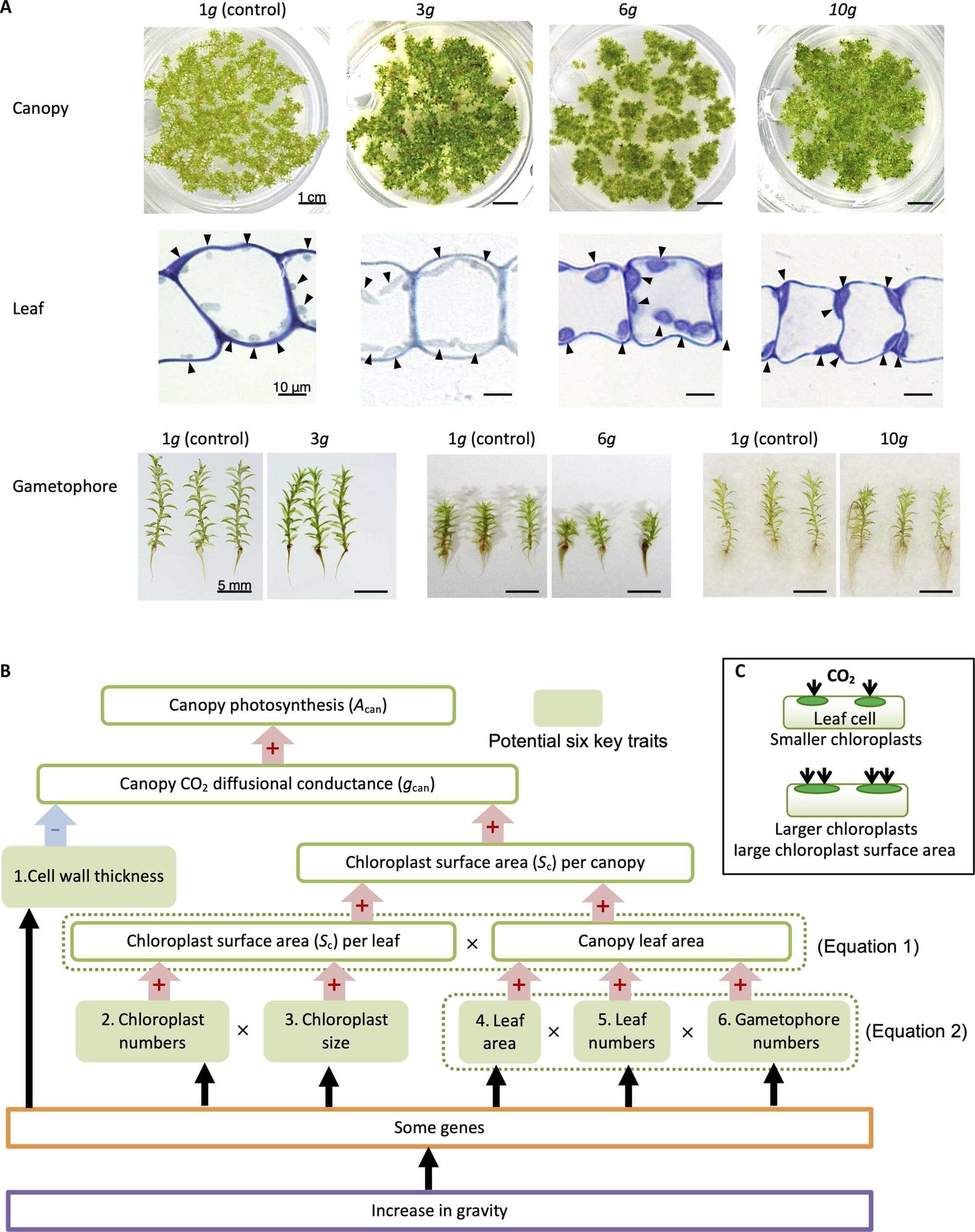
Unless one is a trained fighter jet pilot, or a Formula 1 driver, humans tend not to do well at higher gravity, but tiny green moss plants seem to thrive under such conditions.
A team from Japan found that moss (Physcomitrium patens) exhibited increased photosynthesis under hypergravity conditions (six and 10 times Earth’s gravity) due to enhanced carbon dioxide (CO2) diffusion from the atmosphere into the chloroplasts within the plant leaves.
The plants adapt to the increased gravity by increasing the size of their chloroplasts and the number of leafy shoots of the moss (gametophores). Researchers identified for the first time the gene factor responsible for this response. They named the factor ISSUNBOSHI1 or IBSH1, a namesake of an inch-high, warrior boy from a beloved Japanese fairytale.
The People’s Liberation Army has released rare footage showing its reconnaissance drones tracking a ‘hostile warship,’ highlighting China’s increasing integration of unmanned systems with intelligence operations.
The video, aired in Forging Ahead, the PLA’s latest military documentary, depicts a coordinated mission involving the WZ-7 and WZ-10 unmanned aerial vehicles. Both are high-altitude, long-endurance platforms built by the Aviation Industry Corp (AVIC) of China for surveillance missions.

The US Air Force could soon add a new tool to its arsenal of training aids: a full-scale replica of China’s HQ-22 surface-to-air missile system.
The decoy, developed by US defense contractor Torch Technologies at its Integration and Prototyping Center in Huntsville, Alabama, is designed to mimic the real Chinese air defense weapon’s look, radar signature, and battlefield behavior.
The company said such surrogates are critical for preparing aircrews to face modern anti-aircraft threats in potential high-intensity conflicts.
