A dry material makes a great fire starter, and a soft material lends itself to a sweater. Batteries require materials that can store lots of energy, and microchips need components that can turn the flow of electricity on and off.
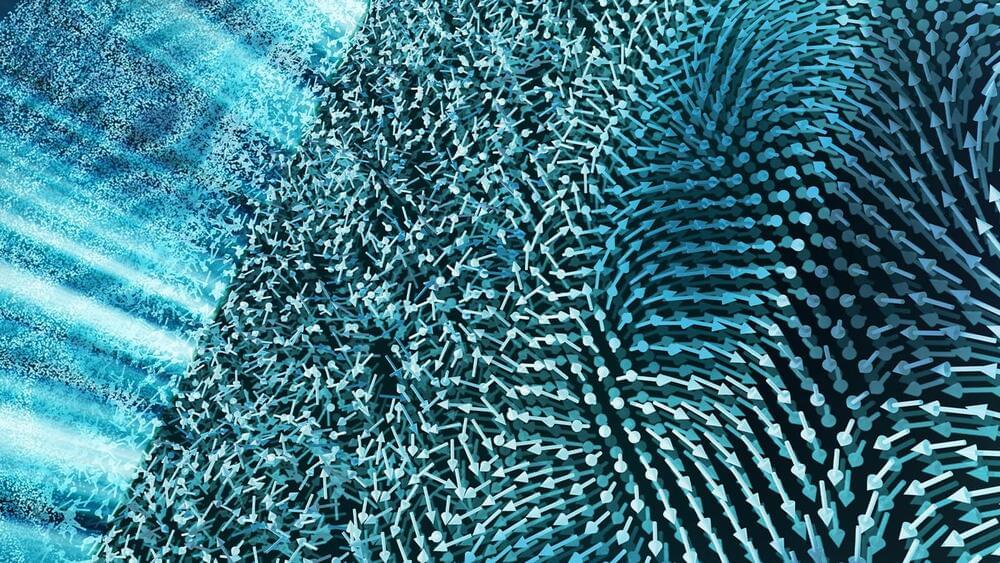
Each material’s properties are a result of what’s happening internally. The structure of a material’s atomic scaffolding can take many forms and is often a complex combination of competing patterns. This atomic and electronic landscape determines how a material will interact with the rest of the world, including other materials, electric and magnetic fields, and light.
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory, as part of a multi-institutional team of universities and national laboratories, are investigating a material with a highly unusual structure—one that changes dramatically when exposed to an ultrafast pulse of light from a laser.