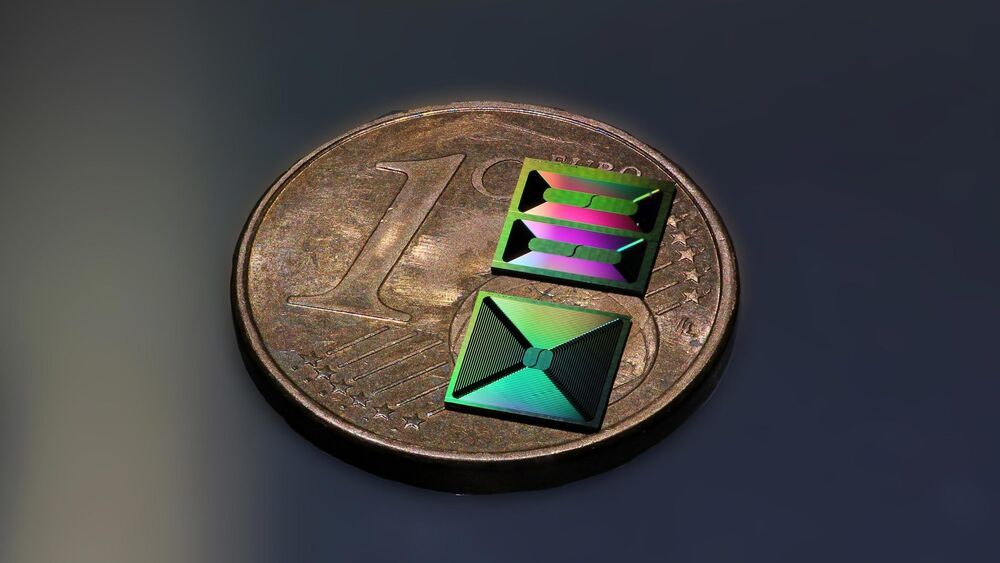
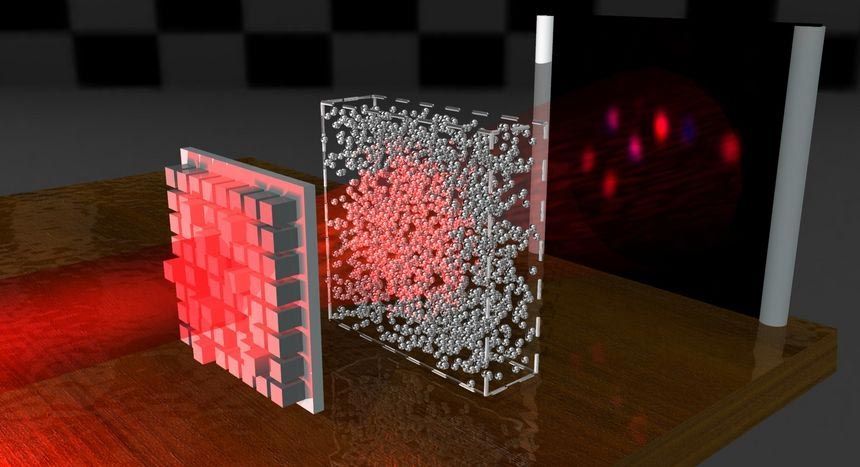
The second-generation of their implantable scaffold takes the shape of an ice cube tray, and can hold three times as many photoreceptor cells — 300000 of them in all — and features cylindrical holes on the underside so these cells can connect with the patient’s retinal tissue as they mature. It is made from a biocompatible material called poly(glycerol-sebacate) that offers the necessary mechanical strength, but is safely metabolized by the body after it serves its purpose.
One of the main causes of vision loss in adults is deteriorative disorders of the retina, like macular degeneration, that are characterized by the death of the eye’s photoreceptor cells. Scientists are therefore focusing a lot of attention on coming up with ways to regenerate these cells, and a team at the University of Wisconsin-Madison (UW-Madison) has engineered a novel type of scaffold that could give these efforts a boost, by improving the precision with which replacement photoreceptor cells can be delivered into the eye.
Way back in 2012, we looked at research in which UW-Madison scientists demonstrated how pluripotent stem cells could be used to grow retinal tissue in the lab. This tissue featured many of the hallmarks of real retinal tissue, including photoreceptor cells, and raised the prospect of harnessing this technique to grow replacement tissue in place within a damaged or diseased eye to restore vision.
“While it was a breakthrough to be able to make the spare parts – these photoreceptors – it’s still necessary to get them to the right spot so they can effectively reconstruct the retina,” says professor of ophthalmology and visual sciences David Gamm. “So, we started thinking, ‘How can we deliver these cells in a more intelligent way?’ That’s when we reached out to our world-class engineers at UW–Madison.”