Here’s how a lightweight, prefabricated concrete slab is signaling a revolution in architecture.


Using an advanced microscopy technique, Texas A&M researchers have uncovered a twin boundary defect in a soft polymer that has never been observed before.
Texas A&M University scientists have for the first time revealed a single microscopic defect called a “twin” in a soft-block copolymer using an advanced electron microscopy technique. This defect may be exploited in the future to create materials with novel acoustic and photonic properties.
“This defect is like a black swan — something special going on that isn’t typical,” said Edwin Thomas, professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering. “Although we chose a certain polymer for our study, I think the twin defect will be fairly universal across a bunch of similar soft matter systems, like oils, surfactants, biological materials, and natural polymers. Therefore, our findings will be valuable to diverse research across the soft matter field.”
Discover the advantages of 3D printed jewelry, the best materials, and get inspired by the most interesting projects!
In new research, Texas A&M University scientists have for the first time revealed a single microscopic defect called a “twin” in a soft-block copolymer using an advanced electron microscopy technique. This defect may be exploited in the future to create materials with novel acoustic and photonic properties.
“This defect is like a black swan—something special going on that isn’t typical,” said Dr. Edwin Thomas, professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering. “Although we chose a certain polymer for our study, I think the twin defect will be fairly universal across a bunch of similar soft matter systems, like oils, surfactants, biological materials and natural polymers. Therefore, our findings will be valuable to diverse research across the soft matter field.”
The results of the study are detailed in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
GMG and the University of Queensland presented a graphene aluminum-ion cell that charges faster than Li-ion batteries. It also requires no cooling.


Moore’s Law, the famous prediction that the number of transistors that can be packed onto a microchip will double every couple of years, has been bumping into basic physical limits. These limits could bring decades of progress to a halt, unless new approaches are found.
One new direction being explored is the use of atomically thin materials instead of silicon as the basis for new transistors, but connecting those “2D” materials to other conventional electronic components has proved difficult.
Now researchers at MIT, the University of California at Berkeley, the Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, and elsewhere have found a new way of making those electrical connections, which could help to unleash the potential of 2D materials and further the miniaturization of components—possibly enough to extend Moore’s Law, at least for the near future, the researchers say.

To combat this, Li and his team at Harvard have designed their solid-state battery with a multilayer approach that stacks its materials of varying stabilities between the anode and cathode. Much like a sandwich. This multi-material battery sandwich helps alleviate the penetration of lithium dendrites by controlling and containing them rather than preventing them altogether.
As you can see from the image above, the Harvard team has simplified its battery design to a form that’s more our speed. In this case, a BLT sandwich. The top slice of bread represents the lithium-metal anode, followed by lettuce appropriately representing a coating of graphite. The two layers of tomatoes represent the first electrolyte, protecting the delicious middle layer of bacon as the second electrolyte. Everything sits upon the bottom slice of bread, or the cathode. Is anyone else suddenly hungry for batteries?
In this design, dendrites are able to grow through the graphite (lettuce) and first electrolyte (tomato) but are halted when they reach the second electrolyte (bacon), thus preventing the dendrites from shorting the entire battery. This multilayer approach provokes chemistry that makes the second electrolyte too tight for the dendrites to penetrate. Furthermore, the Harvard researchers say this same chemistry can backfill the holes made by dendrites, essentially making the solid-state battery self-healing. Is there anything better than a sandwich that can regenerate itself? Honestly.

After spending nearly two-and-a-half years together, a NASA spacecraft will bid farewell to its asteroid companion Monday and begin the long journey back to Earth.
The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft is NASA’s first asteroid sample return mission, and it carries a generous amount of material collected from the near-Earth asteroid Bennu.
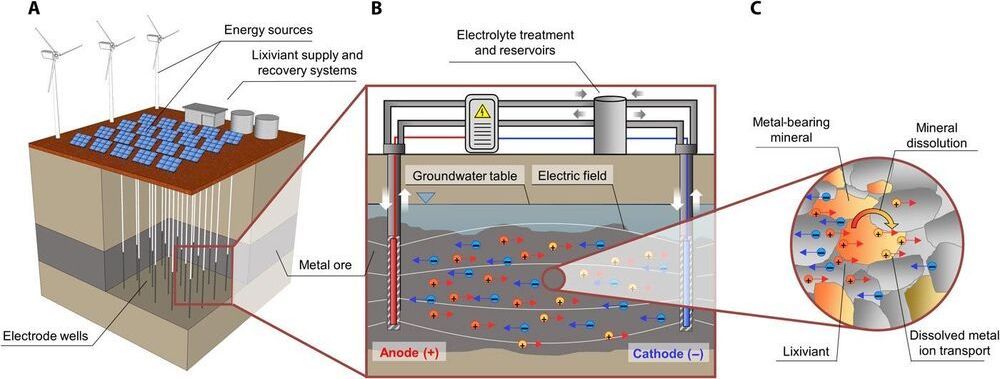
A team of international researchers, including Dr. Rich Crane from the Camborne School of Mines, University of Exeter, have developed a new method to extract metals, such as copper, from their parent ore body.
The research team has provided a proof of concept for the application of an electric field to control the movement of an acid within a low permeability copper-bearing ore deposit to selectively dissolve and recover the metal in situ.
This is in contrast to the conventional approach for the mining of such deposits where the material must be physically excavated, which requires removal of both overburden and any impurities within the ore (known as gangue material).