This could open doors to technologies we thought were impossible.


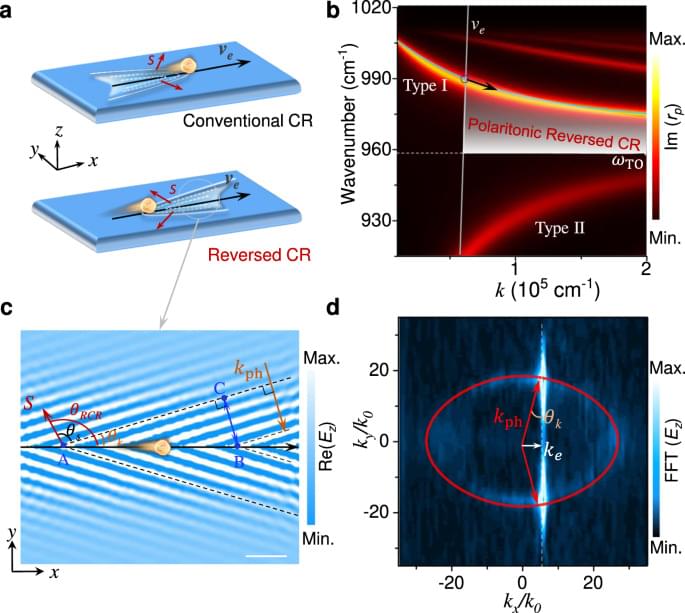
A new study led by Vinod M. Menon and his group at the City College of New York shows that trapping light inside magnetic materials may dramatically enhance their intrinsic properties. Strong optical responses of magnets are important for the development of magnetic lasers and magneto-optical memory devices, as well as for emerging quantum transduction applications.
In their new article in Nature, Menon and his team report the properties of a layered magnet that hosts strongly bound excitons—quasiparticles with particularly strong optical interactions. Because of that, the material is capable of trapping light—all by itself.
As their experiments show, the optical responses of this material to magnetic phenomena are orders of magnitude stronger than those in typical magnets. “Since the light bounces back and forth inside the magnet, interactions are genuinely enhanced,” said Dr. Florian Dirnberger, the lead-author of the study.


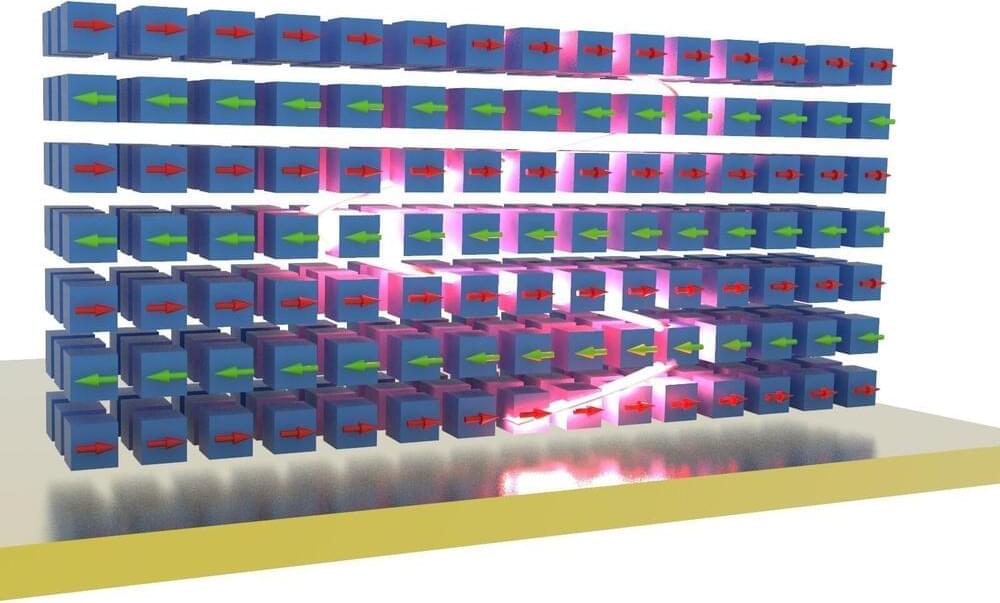
Research is underway around the world to find alternatives to our current electronic computing technology, as great, electron-based systems have limitations. A new way of transmitting information is emerging from the field of magnonics. Instead of electron exchange, the waves generated in magnetic media could be used for transmission, but magnonics-based computing has been (too) slow to date.
Scientists at the University of Vienna have now discovered a significant new method. When the intensity is increased, the spin waves become shorter and faster—another step towards magnon computing. The results are published in the journal Science Advances.
Magnonics is a relatively new field of research in magnetism in which spin waves play a central role. A local disturbance in the magnetic order of a magnet can propagate as waves through a material. These waves are called spin waves, and the associated quasiparticles are called magnons. They carry information in the form of angular momentum pulses. Because of this property, they can be used as low-power data carriers in smaller and more energy-efficient computers of the future.
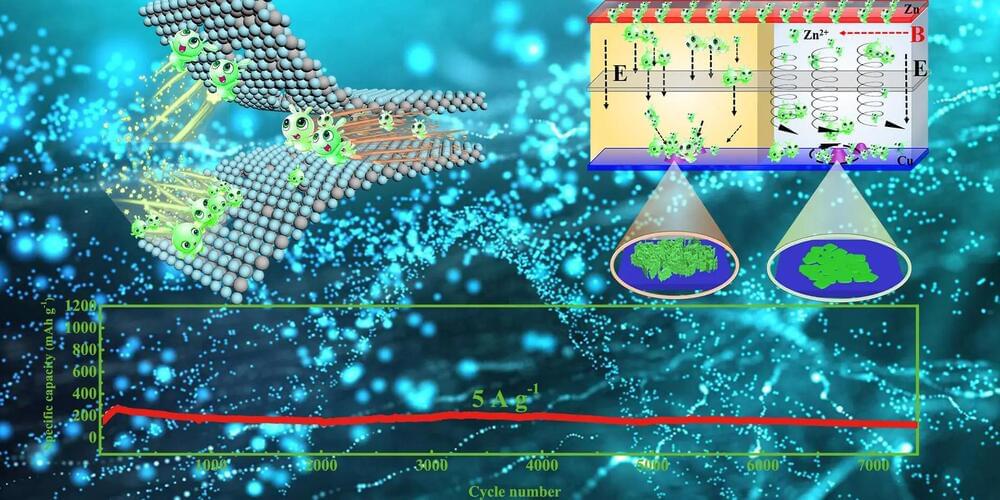
A research team has developed an advanced aqueous zinc-ion battery with an enhanced cycle lifespan using a weak magnetic field and a new VS2 material. The breakthrough addresses the challenges of zinc dendrite growth and cathode material limitations. Credit: Mao Yunjie.
A research team at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), led by Prof. Zhao Bangchuan, developed a high-performance aqueous zinc-ion battery with ultralong cycle lifespan in a weak magnetic field.
The findings were recently published in the journal Materials Horizons.
A team of mechanical engineers from Chung-Ang University, Massachusetts General Hospital, LS Materials and Yonsei University has found that a hand-held cylinder containing crumpled aluminum foil balls is capable of producing enough electricity when shaken to light a small LED grid. In their paper published in the journal Advanced Science, the group describes other materials used in the cylinder and possible uses for such a device.
Prior research has shown that a wide variety of materials can be used to generate static electricity, and that some constructions can capture that electricity. Researchers have suggested such devices could be useful as the power needs of personal electronics decrease. In this new effort, the researchers have looked to aluminum foil as a material for generating static electricity and capturing it to power an external device.
The device the team built is shaped as a cylinder with a cap on the top and bottom—about the size of a Pringle’s can. The tube was made using an acrylic substrate covered with a polytetrafluoroethylene layer. The caps, which serve as electrodes, were made of aluminum. The team then crumpled three wads of aluminum foil into balls and placed them inside the tube.
Rutgers University scientists have devised a highly accurate method for creating coatings of biologically active materials for a variety of medical products. Such a technique could pave the way for a new era of transdermal medication, including shot-free vaccinations, the researchers said.
Writing in Nature Communications, the researchers described a new approach to electrospray deposition, an industrial spray-coating process. Essentially, the team developed a way to better control the target region within a spray zone as well as the electrical properties of microscopic particles that are being deposited. The greater command of those two properties means that more of the spray is likely to hit its microscopic target.
In electrospray deposition, manufacturers apply a high voltage to a flowing liquid, such as a biopharmaceutical, converting it into fine particles. Each of those droplets evaporates as it travels to a target area, depositing a solid precipitate from the original solution.

Scientists led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) investigators have made a significant advance in developing alternative materials for the high-speed memory chips that let computers access information quickly and that bypass the limitations of existing materials.
They have discovered a way that allows them to make sense of previously hard-to-read data stored in these alternative materials, known as antiferromagnets.
Researchers consider antiferromagnets to be attractive materials for making computer memory chips because they are potentially more energy efficient than traditional ones made of silicon. Memory chips made of antiferromagnets are not subject to the size and speed constraints nor corruption issues that are inherent to chips made with certain magnetic materials.