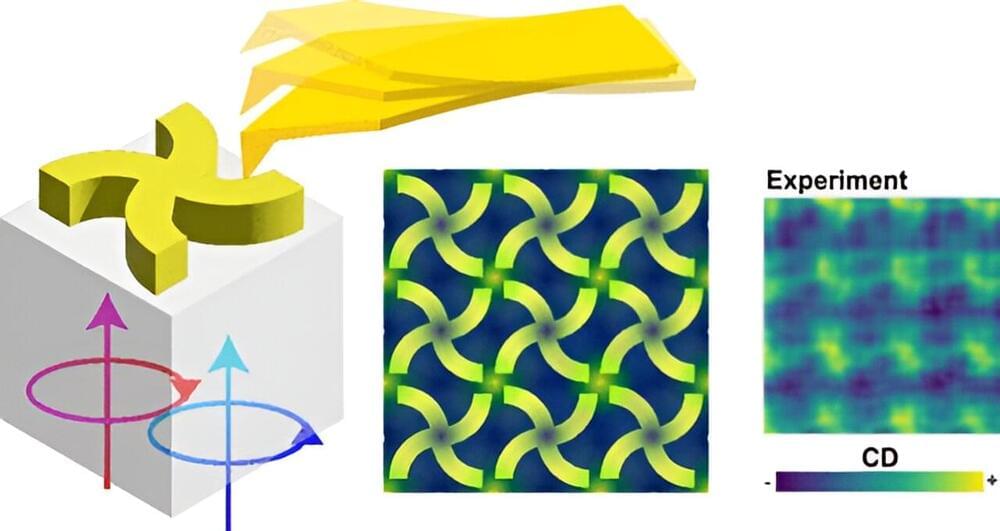
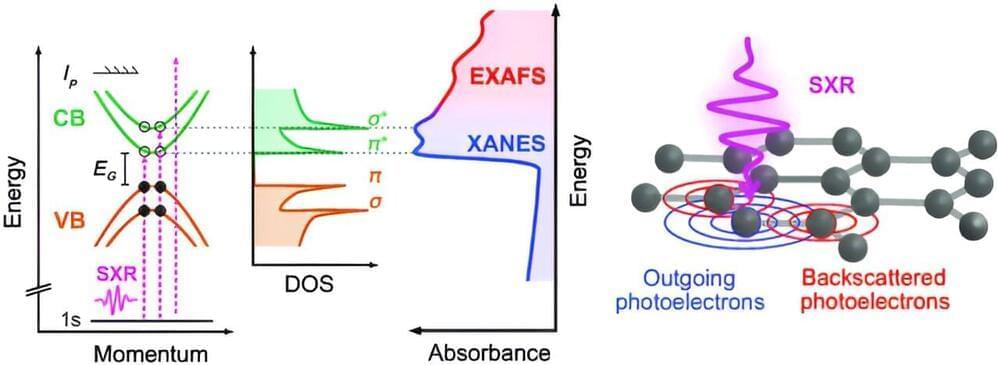
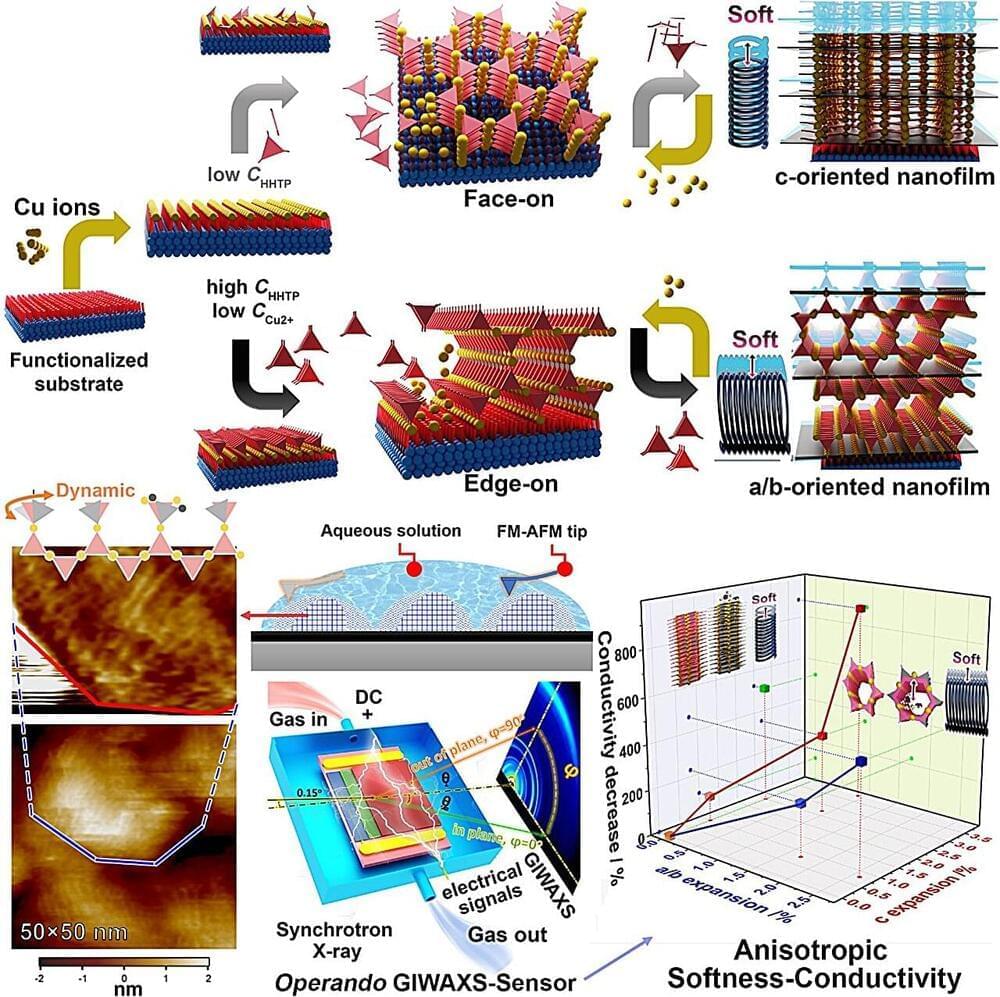
A research group at the Institute for Molecular Science has successfully observed the left and right handedness of material structures at the nanoscale, by illuminating chiral gold nanostructures with circularly polarized light and detecting the optical force acting on a probe near the nanostructures. This result demonstrated that it is possible to analyze the chiral structure of matter at the nanoscale using light.
Chirality describes the property of a material structure not being superimposable onto its mirror image. Since the left and right hands, which are mirror images of each other, do not coincide (they are not the same), they are chiral.
Chiral objects can be distinguished to right-or left-handedness. Many substances that constitute life are chiral, and often only one of either the right-or left-handedness naturally exists. Also, in new functional materials, their chiral nature often plays an important role for the functions.