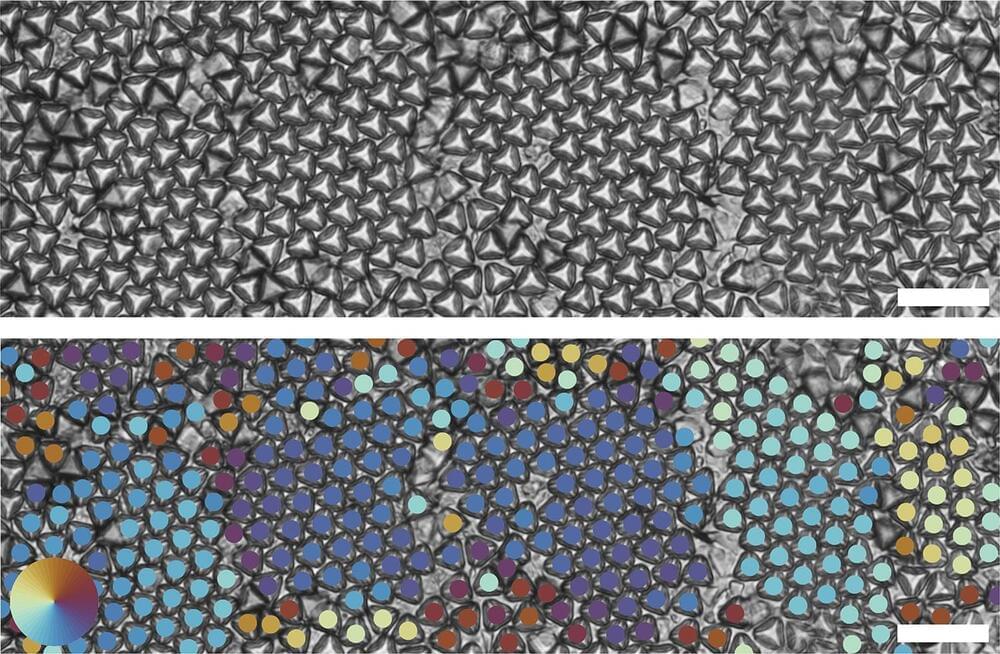
When we take a stroll on the beach, we walk on the sand without any trouble. The sand appears solid and is difficult to compress. When we put the same sand grains in an hourglass, they behave very differently: the sand flows like a liquid.

Year 2023 face_with_colon_three
The new manufacturing method deals with the packaging substrate, the material to which chip dies are bonded. Intel and others have long used plastic (also known as organic) substrates, but the material can shrink or warp during the chip-making process, leading to defects.
Intel notes the warping risk grows as more silicon is placed on the substrate. “As the demand for data-centric, AI-centric compute increases, we are seeing an increasing amount of silicon being packed onto the package substrate, which organic packages have come to some kind of limitation in terms of handling it,” Manepalli added.
The company found a solution in glass, a homogenous substance that can remain rigid under a higher chip load. “Compared to today’s organic substrates, glass offers distinctive properties such as ultra-low flatness and better thermal and mechanical stability, resulting in much higher interconnect density in a substrate,” Intel said in its announcement.
Thesis:
Part I: It has been proven that the human mind cannot be analogous to an electronic (or any other type of) computer, and the functioning of an intellective mind cannot be reproduced (though it can certainly be simulated) by any type of mechanical device, including modern artificial intelligence systems.
Part II: It is further impossible that the human mind is a purely material thing (including some “emergent property” of matter).
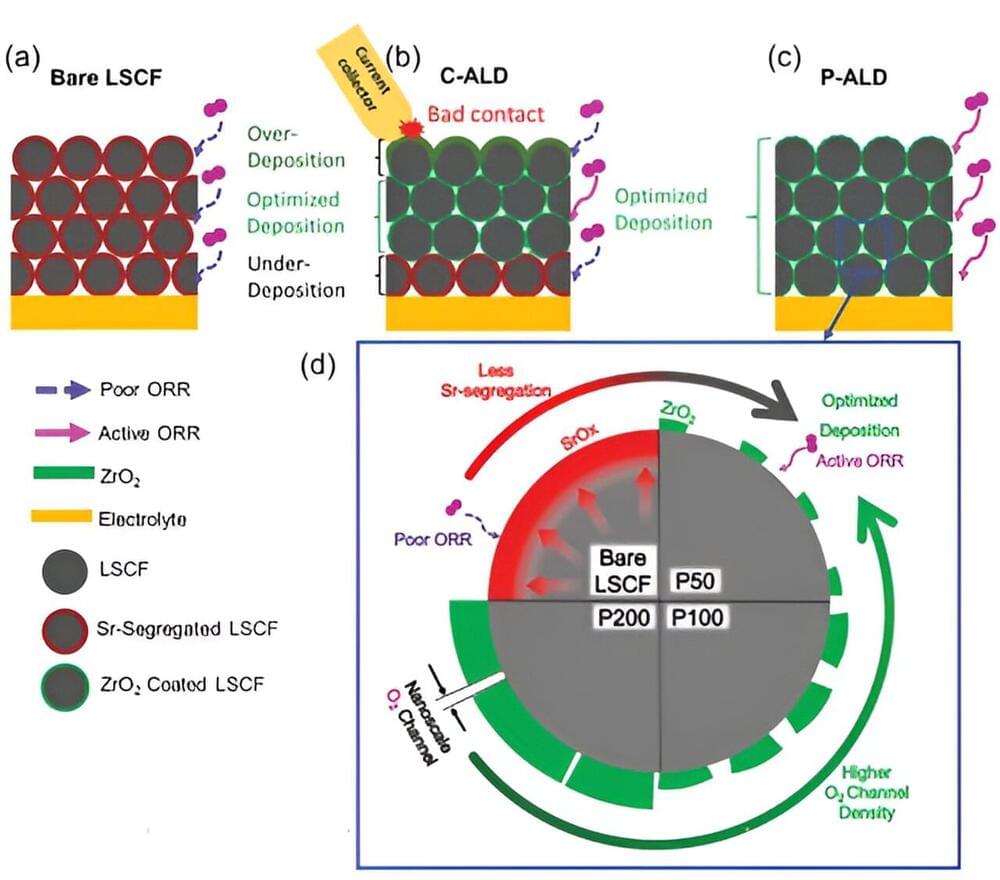
To enhance this efficiency, there is a requirement to fabricate electrodes with a porous structure. Unfortunately, existing technologies face challenges in achieving a uniform coating of ceramic materials within electrodes possessing intricate porous structures.
A collaborative research team, comprising Professor Jihwan An and Ph.D. candidate Sung Eun Jo from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), and others, has successfully produced porous electrodes for SOFCs using latest semiconductor processes. This research has been featured as a back cover article in Small Methods.
The process of atomic layer deposition (ALD) involves depositing gaseous materials onto a substrate surface in thin, uniform atomic layers. In a recent study, Professor Jihwan An’s team, known for their prior work in enhancing the efficiency of SOFCs using ALD, developed and applied a powder ALD process and equipment. This enabled them to precisely coat nano-thin films on fine powders.
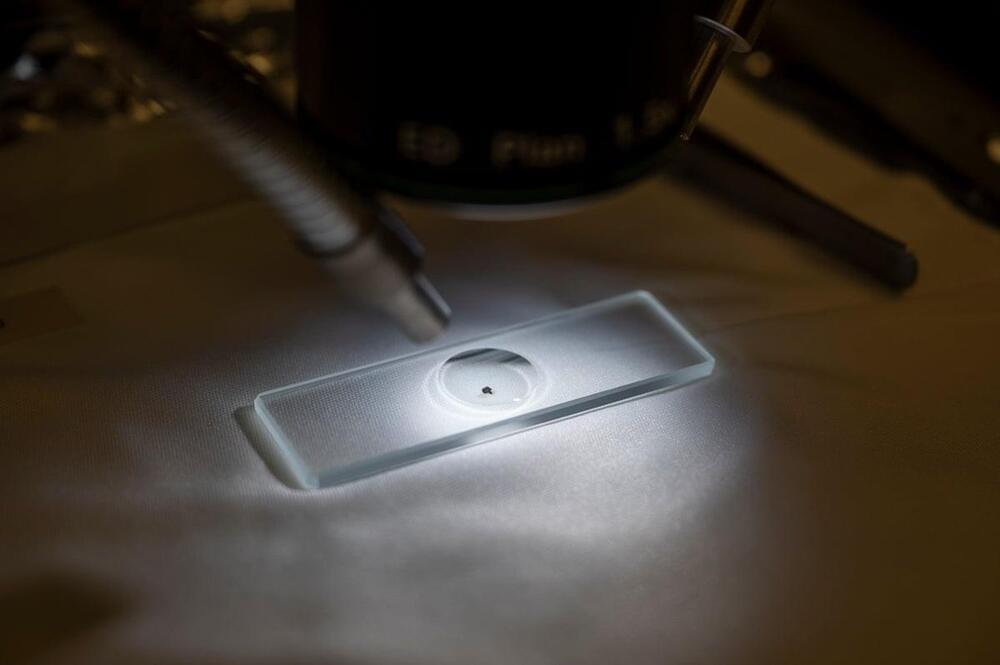

Scientists have scarcely begun studying pristine material from asteroid Bennu brought back to Earth by the OSIRIS-REx mission, but have already found several surprises.