Longevity is becoming mainstream. A central player has become hormones who hold the power to radically transform our well-being.

Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/
The United States Food and Drug Administration has just approved the first-ever clinical trial that uses CRISPR-Cas13 RNA editing. Its aim is to treat an eye disease called wet age-related macular degeneration that causes vision loss in millions of older people worldwide.
This trial marks a new frontier in gene therapy —the process of treating or curing medical conditions by changing a person’s genes.
What makes it special is the fact the therapy targets RNA, instead of DNA. So, what does that mean, and why should we be excited?

Please consider adding this book to your collection. The more places wisdom is preserved, the better!
https://www.amazon.com/Why-We-Die-Sci?tag=lifeboatfound-20…
Death — the ultimate enigma that has haunted humanity since the dawn of consciousness. In \.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/
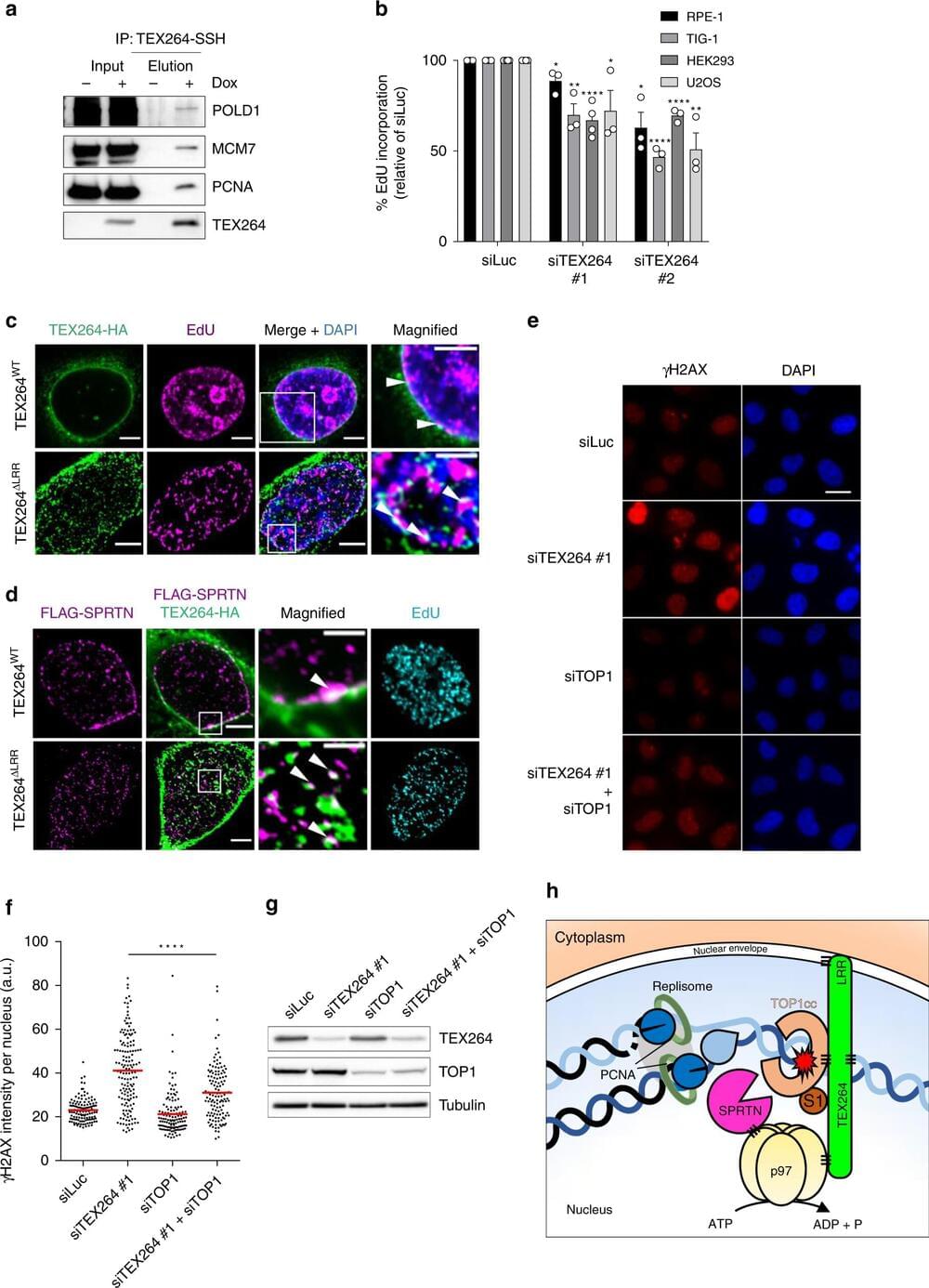
A new “toolkit” to repair damaged DNA that can lead to aging, cancer and motor neuron disease (MND) has been discovered by scientists at the Universities of Sheffield and Oxford.
Published in Nature Communications, the research shows that a protein called TEX264, together with other enzymes, is able to recognize and “eat” toxic proteins that can stick to DNA and cause it to become damaged. An accumulation of broken, damaged DNA can cause cellular aging, cancer and neurological diseases such as MND.
Until now, ways of repairing this sort of DNA damage have been poorly understood, but scientists hope to exploit this novel repair toolkit of proteins to protect us from aging, cancer and neurological disease.
Lykke Sylow, University of Copenhagen, Denmark, presents at the 11th Aging Research and Drug Discovery meeting: Preserving muscle mass for healthy aging: Old tricks and new targets.

This age-related deterioration affects both innate and adaptive immunity, compromising immune function and leading to chronic inflammation that accelerates aging. Immunosenescence is characterized by alterations in immune cell populations and impaired functionality, resulting in increased susceptibility to infections, diminished vaccine efficacy, and higher prevalence of age-related diseases. Chronic low-grade inflammation further exacerbates these issues, contributing to a decline in overall health and resilience. This review delves into the characteristics of immunosenescence and examines the various intrinsic and extrinsic factors contributing to immune aging and how the hallmarks of aging and cell fates can play a crucial role in this process. Additionally, it discusses the impact of sex, age, social determinants, and gut microbiota health on immune aging, illustrating the complex interplay of these factors in altering immune function. Furthermore, the concept of immune resilience is explored, focusing on the metrics for assessing immune health and identifying strategies to enhance immune function. These strategies include lifestyle interventions such as diet, regular physical activity, stress management, and the use of gerotherapeutics and other approaches. Understanding and mitigating the effects of immunosenescence are crucial for developing interventions that support robust immune responses in aged individuals.
The immune system plays a crucial role in protecting our bodies from harmful pathogens. It is divided into two segments: innate immunity and adaptive immunity. The innate immune system acts as an immediate but non-specific first responder to defend against pathogens, composed of phagocytic and natural killer cells. Besides innate immune cells, another important component of the innate system includes physical barriers like skin and mucous membranes. Meanwhile, adaptive immunity is more specialized and requires time to mount a high-affinity and specific response, relying on anticipatory receptors that recognize pathogen-specific antigens. The adaptive immune response is centered around B and T lymphocytes, which are produced in the bone marrow and thymus, respectively (Farber, 2020; Lam et al., 2024). With age, the ability of our immune system to mount productive and timely responses to pathogens diminishes.
#AINews #ArtificialIntelligence #MachineLearning.
Unlocking Immortality: Explore the Future of Eternal Life through Brain Uploading! 🧠💻 Embrace cutting-edge technology as we delve into the possibility of uploading our human consciousness into digital realms, paving the way for eternal existence. Join us on this mind-blowing journey where science fiction meets reality, as we discuss brain upload, digital immortality, consciousness transfer, AI advancements, and the limitless potential of our digital future. 🔬🌌 Discover the key to everlasting life and transcendence in the digital age! 🚀 #EternalLife #BrainUploading #DigitalImmortality #ConsciousnessTransfer #AIAdvancements #FutureTech #Transcendence