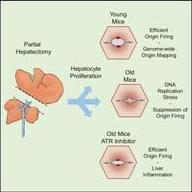
In vivo DNA replication dynamics in regenerating mouse livers unveil aging-dependent decline in replication efficiency and a crucial role of the ATR checkpoint kinase in mitigating inflammation associated with the decline.

Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.
Billionaires are backing top scientists racing to develop tech that could reverse aging. Cellular reprogramming promises to rejuvenate the body… but how does it work, and is it safe?
00:00 – Introduction.
00:55 – The Role Of Stem Cells.
02:33 – What Is Aging?
03:24 – What Is Cellular Reprogramming?
03:56 – How The Yamanaka Factors Can Rejuvenate Cells.
05:35 – Why Scientists Want To Partially Reprogram Cells.
06:28 – How Humans Could Become More Resilient To Age-Related Diseases.
07:00 – How Johnny Huard Uses Cellular Reprogramming.
08:10 – How Cellular Reprogramming Could Shape The Future.
08:38 – Amazon’s Jeff Bezos Is Investing Billions With Altos Labs.
09:02 – How Harvard Professor David Sinclair Used Cellular Reprogramming on Mice.
10:07 – ChatGPT’s Sam Altman Launched Retro. Biosciences.
10:57 – The Risks of Cellular Reprogramming, Including Cancer.
12:56 – How the Tech World Is Investing In Biotech.
13:50 – Credits.
MORE BUSINESS INSIDER EXPLAINS VIDEOS:
How Food Giants Are Jumping On The Ozempic Game With Frozen Meals | Business Insider Explains.
• How Food Giants Are Jumping On The Oz…
Here’s What Would Happen If We Raised Minimum Wage | Business Insider Explains | Business Insider.
• Here’s What Would Happen If We Raised…
The Rivalry Between Tech Billionaires Bill Gates And Steve Jobs | Business Insider Explains.
• The Rivalry Between Tech Billionaires…
#aging #health #businessinsider.
Business Insider tells you all you need to know about business, finance, tech, retail, and more.
Visit our homepage for the top stories of the day: https://www.businessinsider.com.

Researchers at Duke-NUS Medical School have identified interleukin-11 (IL11) as a key factor in the ageing process. Elevated IL11 levels lead to fat accumulation and muscle loss—two major indicators of ageing. Inhibiting IL11 could enhance healthy lifespans.
Ageing populations pose significant health and economic challenges globally. Even a one-year increase in life expectancy could be valued at $38 trillion.
In a study published in Nature, the team demonstrated that anti-IL11 therapy not only counters the harmful effects of ageing but also increases lifespan by up to 25% in preclinical models. The therapy shifts metabolism from generating harmful white fat to beneficial brown fat, which helps burn calories and maintain body temperature.

Our longevity may actually turn out to have a hard limit. In a new study this week, scientists show that the long rise in our collective life expectancy seen during the 20th century has started to slow down as of late. The findings suggest that focusing on simply expanding our lifespan might be short-sighted, the researchers say.
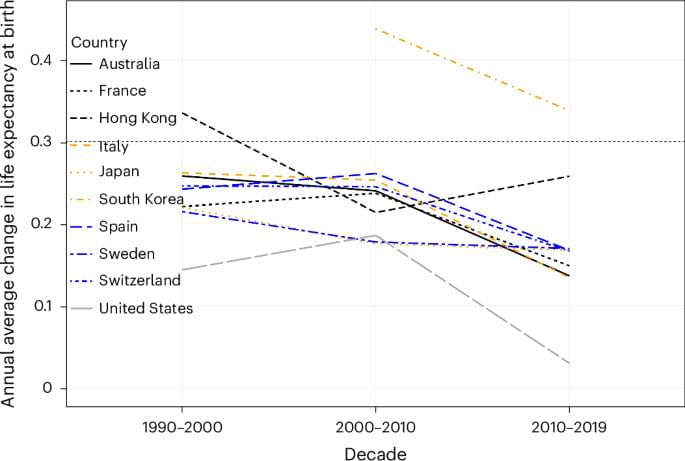
Abstract Over the course of the twentieth century, human life expectancy at birth rose in high-income nations by approximately 30 years, largely driven by advances in public health and medicine.
In the twentieth century, human life expectancy rose dramatically. Based on the past three decades of observed mortality in the eight countries with the longest-lived populations and in Hong Kong and the United States, Olshansky et al. propose that, without medical breakthroughs that slow aging, radical lifespan extension is implausible in this century.


Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.
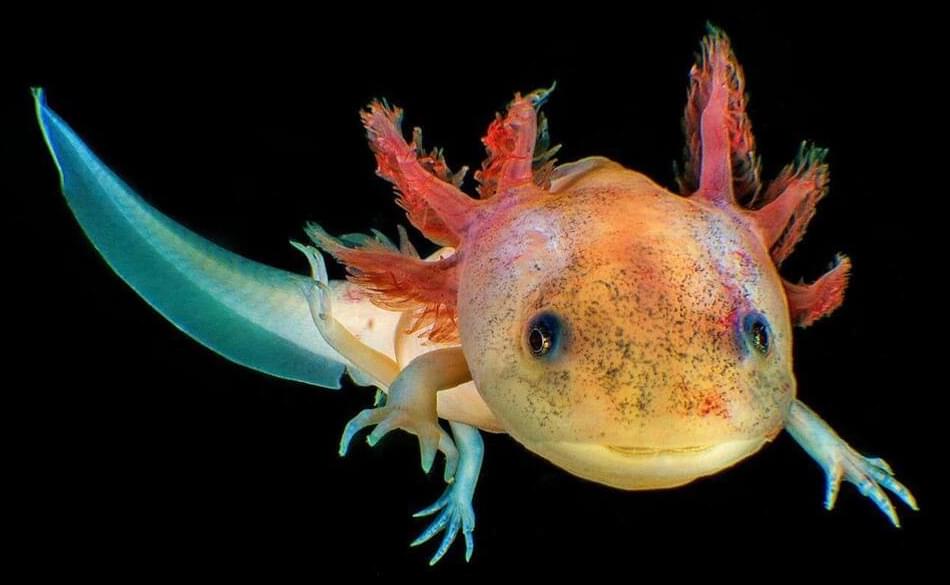

In most vertebrates, a pattern of chemical marks on the genome is a reliable indicator of age, but in axolotls this clock seems to stop after the first four years of life.