Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.
Category: life extension – Page 119
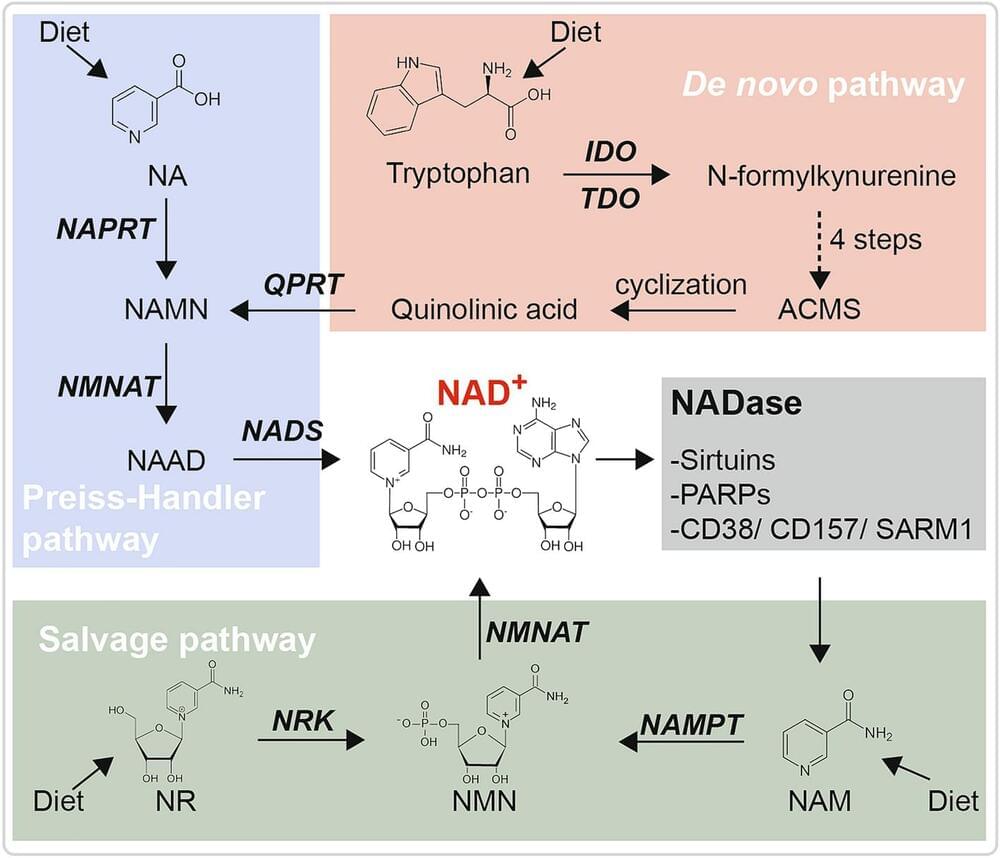
Targeting NAD Metabolism for the Therapy of Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases
Shan C, Gong YL, Zhuang QQ, Hou YF, Wang SM, Zhu Q, et al. Protective effects of β- nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide against motor deficits and dopaminergic neuronal damage in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neuro Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2019, 94: 109670.
Humanity’s newest brain gains are most at risk from ageing
In the more than six million years since people and chimpanzees split from their common ancestor, human brains have rapidly amassed tissue that helps decision-making and self-control.
The large prefrontal cortex provides evolutionary and cognitive advantages over non-human primates — but there’s a cost.

15 Best Longevity Foods
Did you know letting crushed garlic sit for 10+ minutes before cooking it helps preserve more of its healthy polyphenols from heat? I learned a bunch of similar tidbits while researching this article on the best longevity foods!
Want to know the best longevity foods that increase lifespan to add to your diet? We pored through hundreds of studies and made a list!
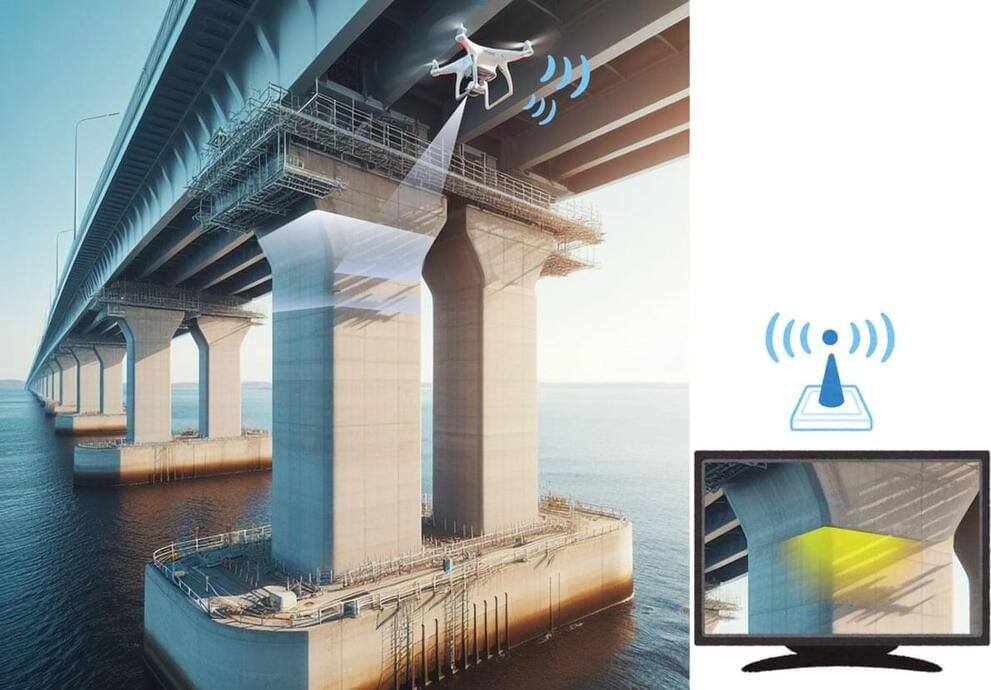

New Luminescent Material Could Be the Answer to Crumbling Infrastructure
A new material developed by Tohoku University records and stores stress history in structures through a luminescent effect, offering an innovative solution to monitor aging infrastructure without needing power or complex equipment.
Identifying deteriorating infrastructure can be as challenging as fixing it. However, researchers at Tohoku University have made this process easier with the development of an innovative new material.
The material responds to mechanical stimuli by recording stress history through a luminescent effect called an afterglow. This information is stored for a long time, and by applying the material to the surfaces of structures, researchers can observe changes in the afterglow to determine the amount of stress the material has experienced.

Have a history of stomach issues?
This new technology will give doctors a closer look. Introducing Pillbot: a tiny disposable robot that you swallow to let doctors see inside your body. In a live demo on the TED Talk stage, creators Alex Luekbe and Vivek Kumbhari show how this pill-sized device navigates the inside of your stomach with a camera, giving a direct view of the entire organ — without the discomfort of invasive procedures — paving the way for further exploration of the human body. “Inside each and every one of us holds mysteries and wonders that if unlocked, lead to better health, performance and longevity,” says Luebke. Visit the link in bio to watch the full talk.’
Telomere Length Test #16: My Best Data Yet
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.
From Today To The Year 3000: Let’s Dive Into The Future!
What does the future hold? What will become of this planet and its inhabitants in the centuries to come?
We are living in a historical period that sometimes feels like the prelude to something truly remarkable or terribly dire about to unfold.
This captivating video seeks to decipher the signs and attempt to construct plausible scenarios from the nearly nothing we hold in our hands today.
As always, it will be scientific discoveries leading the dance of change, while philosophers, writers, politicians, and all the others will have the seemingly trivial task of containing, describing, and guiding.
Before embarking on our journey through time, let me state the obvious: No one knows the future!
Numerous micro and macro factors could alter this trajectory—world wars, pandemics, unimaginable social shifts, or climate disasters.
Nevertheless, we’re setting off. And we’re doing so by discussing the remaining decades of the century we’re experiencing right now.
-
DISCUSSIONS \& SOCIAL MEDIA
Commercial Purposes: [email protected].
Tik Tok: / insanecuriosity.
Reddit: / insanecuriosity.
Instagram: / insanecuriositythereal.
Twitter: / insanecurio.
Facebook: / insanecuriosity.
Linkedin: / insane-curiosity-46b928277
Our Website: https://insanecuriosity.com/
–
Credits: Ron Miller, Mark A. Garlick / MarkGarlick.com, Elon Musk/SpaceX/ Flickr.
–
00:00 Intro.
01:20 Artificial Intelligence.
02:40 2030 The ELT telescope.
03:20 2031 The International Space Station is deorbited.
04:05 2035 The cons.
04:45 2036 Humans landed on mars.
05:05 2037. The global population reaches 9 billion.
05:57 2038 2038. Airplane accident casualties = 0
06:20 Fusion power is nearing commercial availability.
07:01 2042 Supercomputers.
07:30 2045 turning point for human-artificial intelligence interactions.
08:58 2051 Establishment of the first permanent lunar base.
09:25 2067 The first generation of antimatter-powered spacecraft emerging.
10:07 2080 Autonomous vehicles dominate the streets.
10:35 2090 Religion is fading from European culture.
10:55 2099 Consideration of Mars terraforming.
11:28 22nd century Moon and Mars Settlements.
12:10 2,130 transhumanism.
12:41 2,132 world records are shattered.
12:57 2,137 a space elevator.
14:32 2,170 By this year, there are dozens of human settlements on the Moon.
15:18 2180
16:18 23rd century Immortality.
16:49 2,230 Hi-Tech and Automated Cities.
17:23 2,310 23rd Century: Virtual Reality and Immortality.
18:01 2,320 antimatter-powered propulsion.
18:40 2,500 Terraforming Mars Abandoned.
19:05 2,600 Plastic Cleanup.
19:25 2,800 Silent Probes.
19:37 3,100 Humanity as a Type 2 Civilization.
–
#insanecuriosity #timelapseofthefuture #futuretime
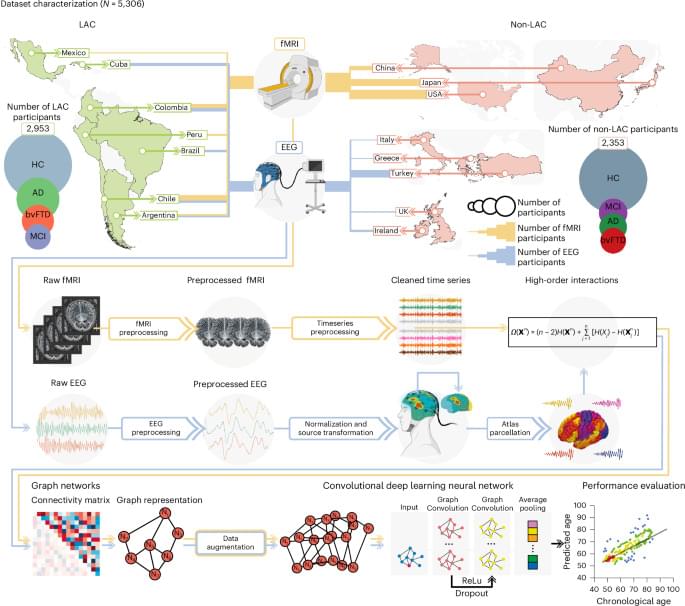
Brain clocks capture diversity and disparities in aging and dementia across geographically diverse populations
The brain undergoes dynamic functional changes with age1,2,3.
Analyses of neuroimaging datasets from 5,306 participants across 15 countries found generally larger brain-age gaps in Latin American compared with non-Latin American populations, which were influenced by disparities in socioeconomic and health-related factors.
A primer on the current state of longevity research
Note: This post is co-authored with Stacy Li, a PhD student at Berkeley studying aging biology! Highly appreciate all her help in writing, editing, and fact-checking my understanding!