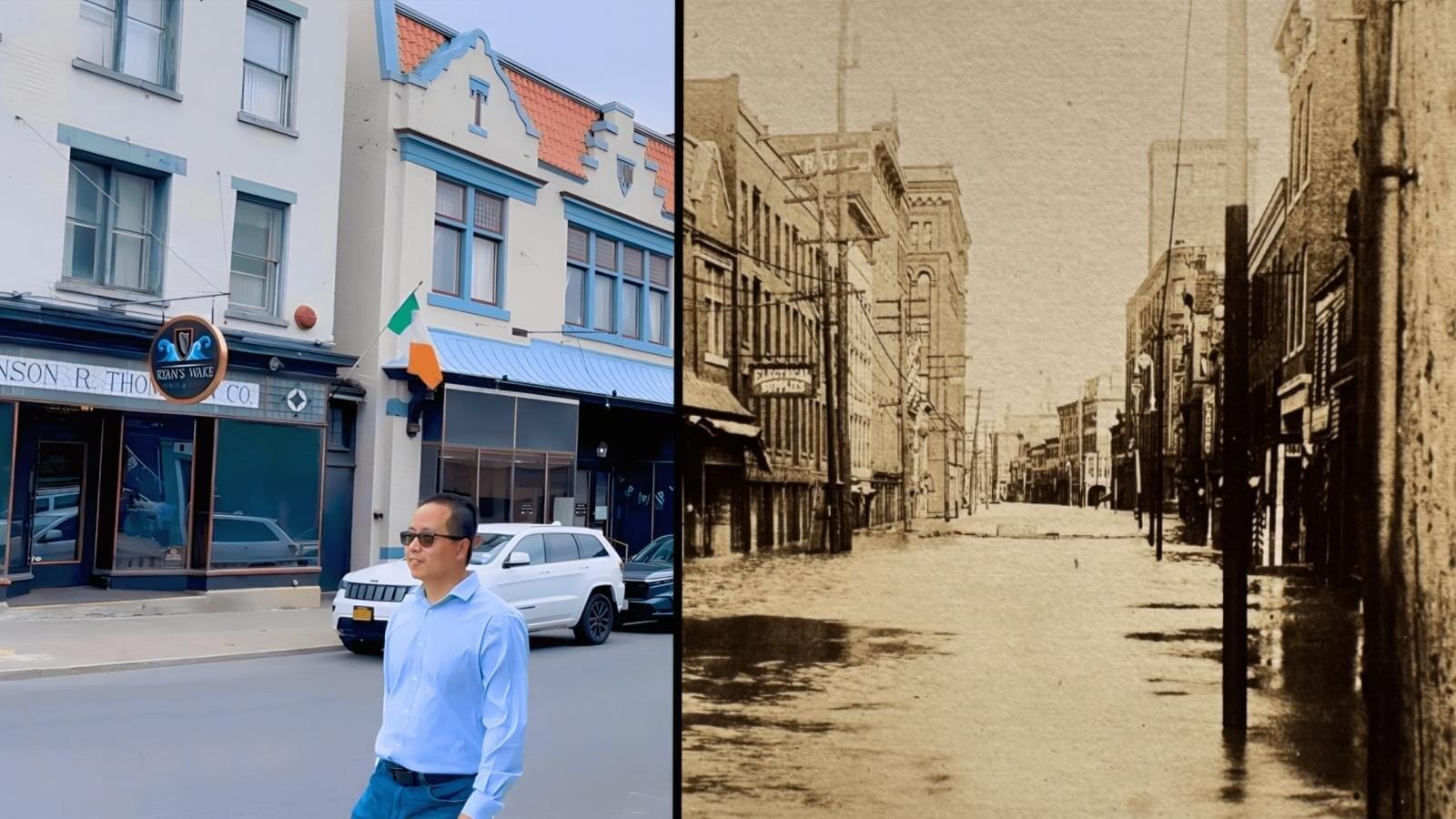
When a 100-year flood hits a city, traffic doesn’t suddenly stop or disappear—it adapts.
“In spite of increasing flood risks, more and more people are moving into flood-prone areas,” said Jianxi Gao, associate professor of computer science at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute. “This makes it even more urgent to understand how resilient our infrastructure is—and how people adapt when disaster strikes.”
Gao is part of an international team studying how urban transportation systems adapt to extreme weather events like floods. Their work, “Adaptive capacity for multimodal transport network resilience to extreme weather,” published in Nature Sustainability, uses an innovative modeling approach to uncover a universal law governing how travelers shift between private vehicles and public transit during such disruptions. This law reveals that shifts between transport modes, such as from cars to buses, follow predictable patterns driven by changes in travel demand, the density of transport networks, and how modes either compete or support each other.