Imagine that instead of viewing an image through a lens, you look through a kaleidoscope that focuses invisible light to obtain a new range of colors. The photon, the ephemeral messenger of light, usually appears alone, but here it appears in a duet, which is the basis of two-photon vision. This is an extraordinary phenomenon in which the human eye, instead of perceiving traditional light, receives pulses of infrared lasers, the gateway to the invisible world.
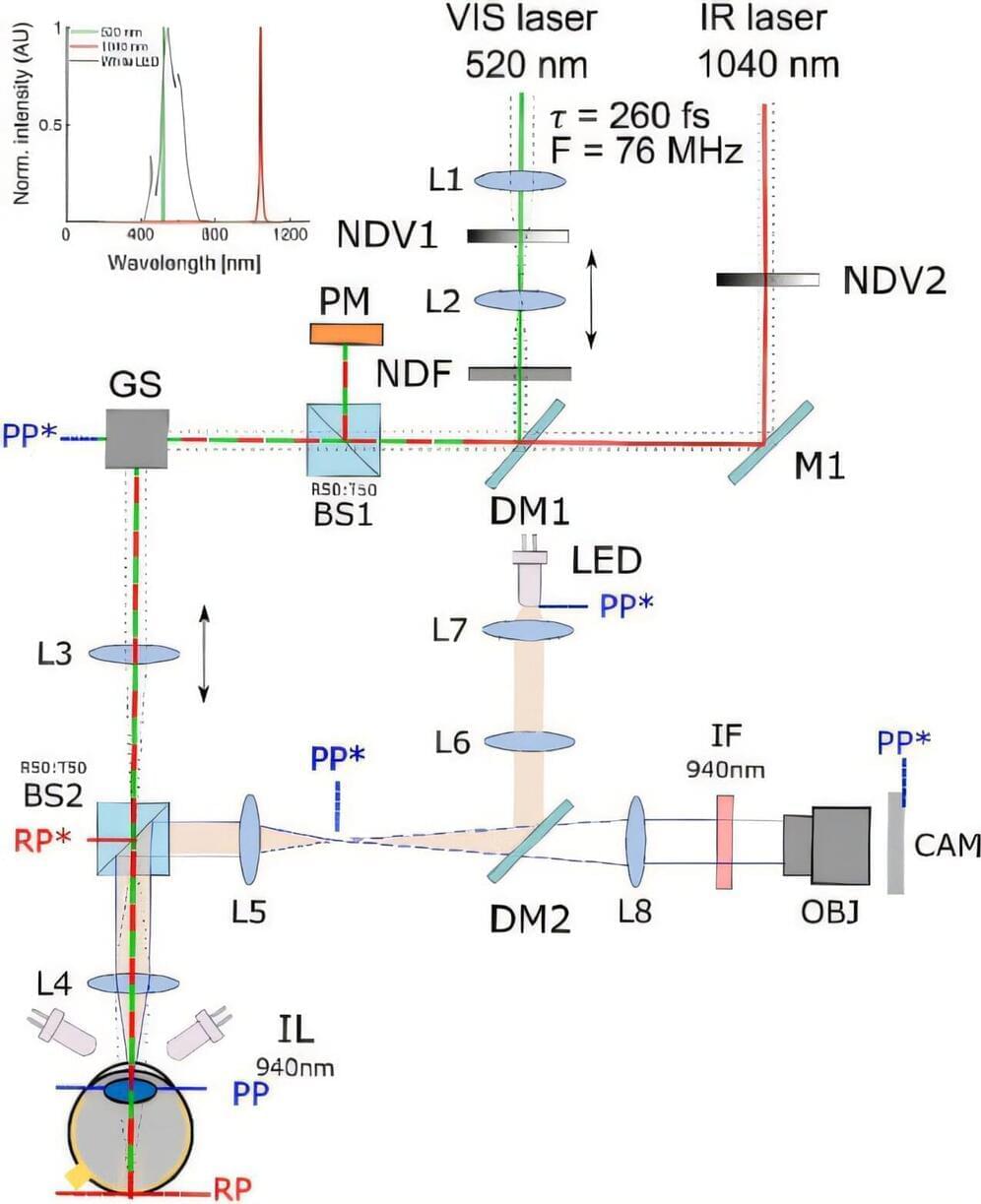
However, the key to this is measuring the brightness of two-photon stimuli, which until now was only possible for visible light. ICTER scientists have made a breakthrough and determined the luminance value for infrared using photometric units (cd/m2). Thanks to this approach, it is possible to link the luminance of two-photon stimuli to a new physical quantity related to perceived brightness: the two-photon retinal illumination.
Research—conducted by scientists from the International Centre for Eye Research (ICTER) with the participation of Ph.D. student Oliwia Kaczkoś, Ph.D. Eng. Katarzyna Komar and Prof. Maciej Wojtkowski—has shown that the luminance of a two-photon stimulus can reach almost 670 cd/m2 in the safe range of laser power for the eye.