The synthesis of plastic precursors, such as polymers, involves specialized catalysts. However, the traditional batch-based method of finding and screening the right ones for a given result consumes liters of solvent, generates large quantities of chemical waste, and is an expensive, time-consuming process involving multiple trials.
Ryan Hartman, professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at the NYU Tandon School of Engineering, and his laboratory developed a lab-based “intelligent microsystem” employing machine learning, for modeling chemical reactions that shows promise for eliminating this costly process and minimizing environmental harm.
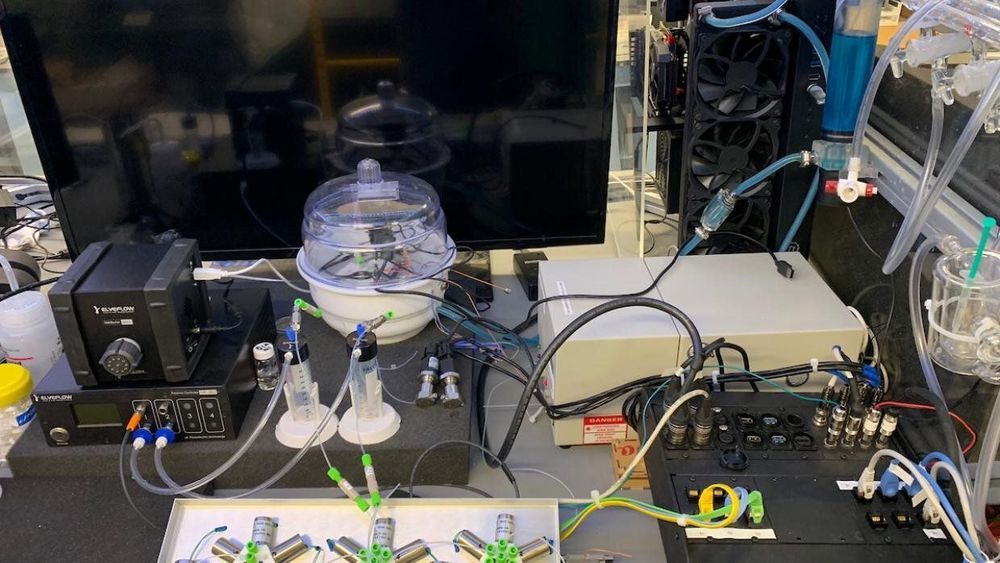
In their research, “Combining automated microfluidic experimentation with machine learning for efficient polymerization design,” published in Nature Machine Intelligence, the collaborators, including doctoral student Benjamin Rizkin, employed a custom-designed, rapidly prototyped microreactor in conjunction with automation and in situ infrared thermography to study exothermic (heat generating) polymerization—reactions that are notoriously difficult to control when limited experimental kinetic data are available. By pairing efficient microfluidic technology with machine learning algorithms to obtain high-fidelity datasets based on minimal iterations, they were able to reduce chemical waste by two orders of magnitude and catalytic discovery from weeks to hours.