Large-capacity wireless data transmission systems are demanded along with the development of multimedia services, video-based interactions, and cloud computing in the era of big data. Compared with radio-frequency communication systems, free-space optical (FSO) signal transmission technology has the merits of high data rate, great flexibility, less power consumption, high security, and large license-free bandwidths [1– 3], which has been widely applied in terrestrial transmission [4], last mile solutions [5], ground-to-satellite optical communication [6], disaster recovery [7], and so on. To date, up to 10 Gbit/s FSO communication system has been realized for transmission distance over 1,000 km of star-ground or inter-star communications [8], and 208 Gbit/s terrestrial communication is also reported at 55 m transmission distance [9]. Wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) technology is commonly employed to improve data transmission capacity in fiber communication systems, which would be more effective in FSO communication systems benefitting from very weak non-linear cross talk between different frequency channels in free space. Based on a simulation platform, a WDM FSO communication system could boost the signal transmission capacity to 1.28 Tbit/s by modulating 32 optical channels with dual-polarization 16 quadrature amplitude modulation signals [10]. To date, beyond 10 Tbit/s FSO communication systems have been experimentally demonstrated recently using WDM technology [11,12]. However, a WDM communication system becomes power-hungry and bulky with the increase of transmission channels while traditional distributed feedback lasers are used as optical carriers. In addition, more rigorous requirement is imposed on the frequency tolerance of carrier lasers to avoid channel overlap with the decrease of channel frequency interval.
The invention of microresonator-based optical frequency combs provides novel integrated optical laser sources with the natural characteristic of equi-spaced frequency intervals which can overcome the challenge of massive parallel carrier generation [13 – 19]. In particular, the spontaneously organized solitons in continuous-wave (CW)-driven microresonators provide a route to low-noise ultra-short pulses with a repetition rate from 10 GHz to beyond terahertz. Soliton microcombs (SMCs) are typical stable laser sources where the double balances of non-linearity and dispersion as well as dissipation and gain are reached in microcavities. Meanwhile, the linewidth of the comb lines is similar with the pump laser, which enables low power consumption and costs multiwavelength narrow-linewidth carriers for a wide range of applications. Through designing the scale of microresonators, the repetition rate of SMCs could be compatible with dense wavelength-division multiplexing (DWDM) communication standard. To date, several experiments have demonstrated the potential capacity for ultra-high-speed fiber communication systems using SMCs as multiwavelength laser sources [20 – 30]. For instance, a coherent fiber communication system has improved the transmission capacity up to 55 Tbit/s using single bright SMCs as optical carriers and a local oscillator [20]. And dark solitons and soliton crystals are also employed as multiwavelength laser sources for WDM communication systems [27 – 30]. However, few studies have carried out massive parallel FSO communication systems using the integrated SMCs as laser sources.
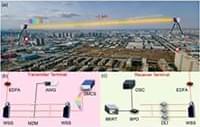
In this paper, we experimentally demonstrate a massive parallel FSO communication system using an SMC as a multiple optical carrier generator. 102 comb lines are modulated by 10 Gbit/s differential phase shift keying (DPSK) signals to boost the FSO transmission rate up to beyond 1 Tbit/s. The transmitter and receiver terminals are installed in two buildings at a distance of ∼1 km, respectively. Using a CW laser as reference, the influence of optical signal-to-noise ratios (OSNRs) on the bit error rate (BER) performance is experimentally analyzed. Our results show an effective solution for large-capacity spatial signal transmission using an integrated SMC source which has potential applications in future satellite-to-ground communication systems.