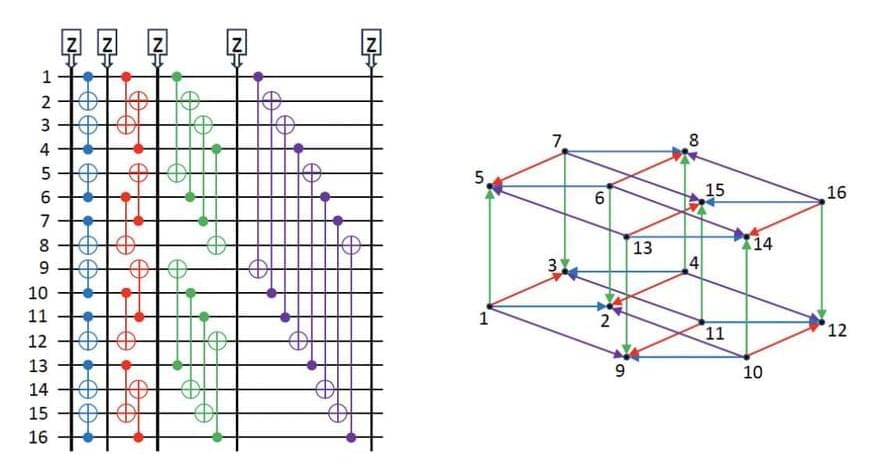
Despite the Harvard 48 logical #qubits paper is perhaps the biggest leap in #quantum technologies, still the final circuit is classically simulable.
Politics makes strange bedfellows, apparently so does quantum benchmarking.
In a surprising development, IBM Quantum and IonQ researchers teamed up to reveal an alternative classical simulation algorithm for an impressive error correction study conducted by a Harvard and QuEra team and published recently in Nature. IBM is a leader in superconducting quantum computers, while IonQ is noted as a pioneer in trapped ion devices.
The IBM-IonQ team reports in ArXiv that their classical algorithm accomplished the same computational task that was performed by the 48-qubit quantum setup in that Nature study, in a mere 0.00257947 seconds.