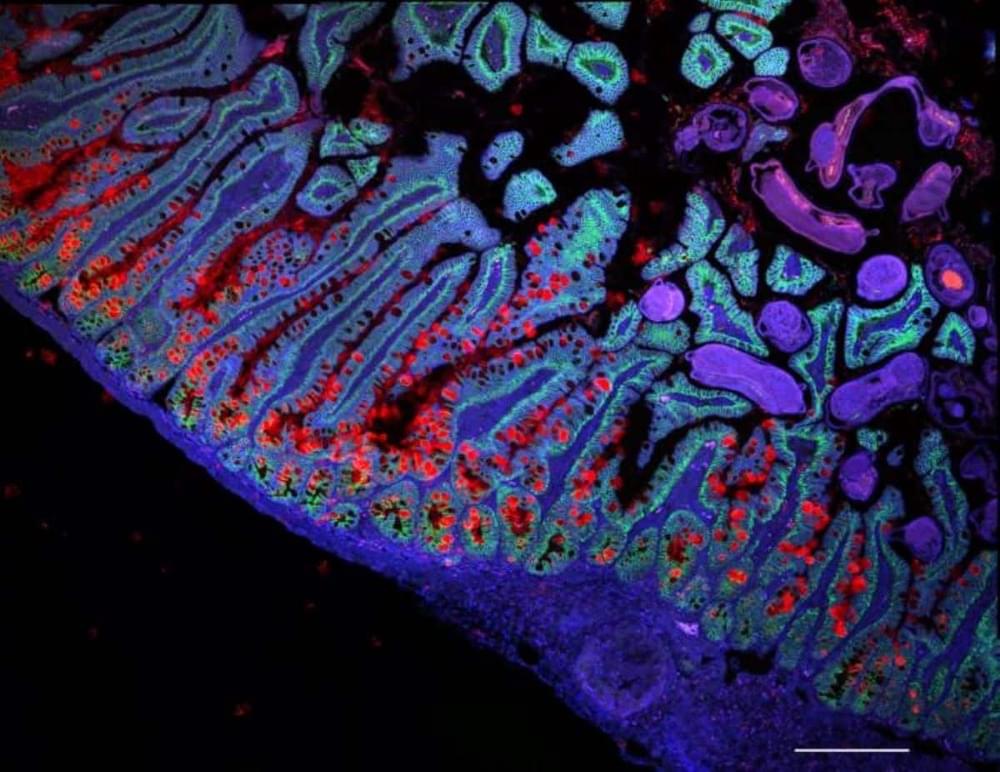
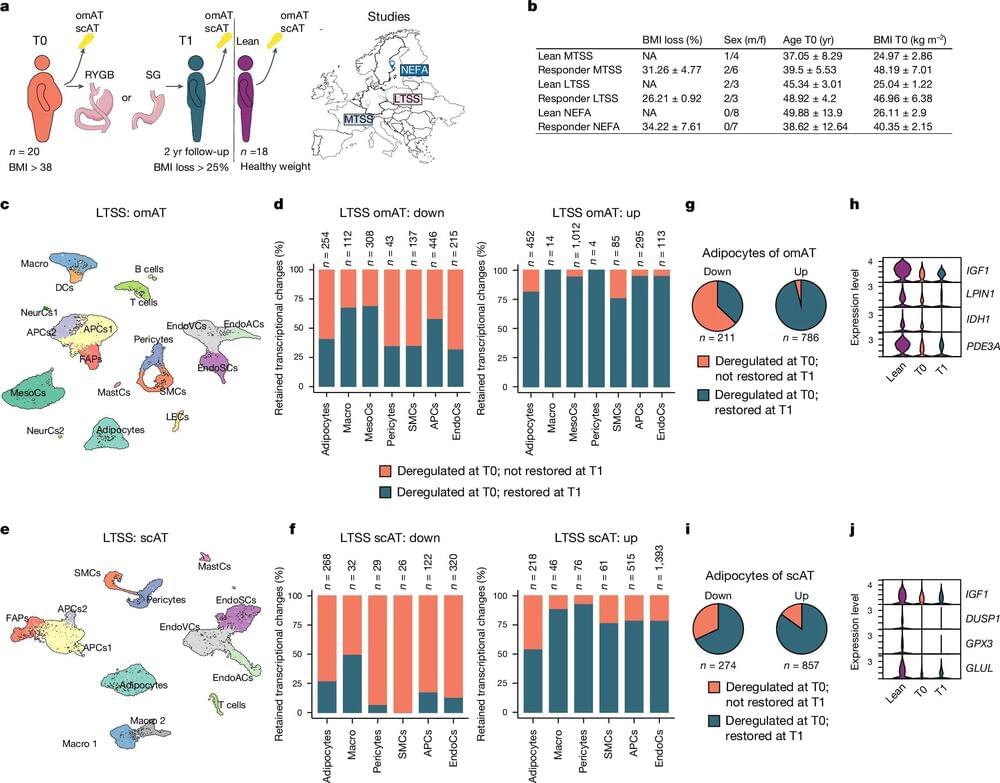
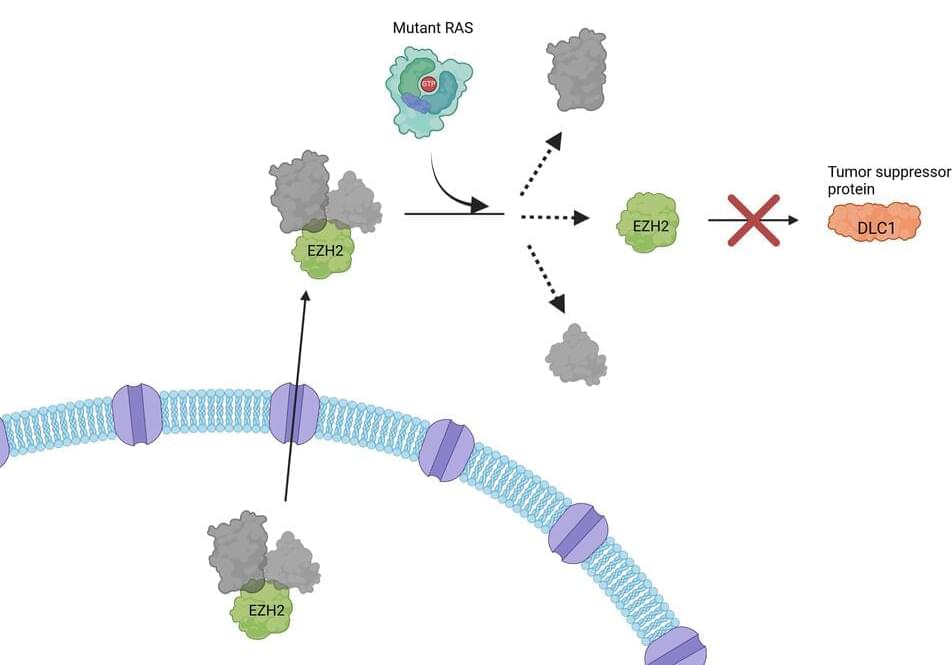
Summary: The Human Cell Atlas (HCA) consortium has published over 40 studies revealing groundbreaking insights into human biology through large-scale mapping of cells. These studies cover diverse areas such as brain development, gut inflammation, and COVID-19 lung responses, while also showcasing the power of AI in understanding cellular mechanisms.
By profiling over 100 million cells from 10,000 individuals, HCA is building a “Google Maps” for cell biology to transform diagnostics, drug discovery, and regenerative medicine. The initiative emphasizes diversity, including underrepresented populations, to ensure a globally inclusive understanding of health and disease.