The debate is focused on a subset of gain-of-function studies that manipulate deadly viruses to increase their transmissibility or virulence. “This is what happens to viruses in the wild”, explains Carrie Wolinetz, head of the NIH Office of Science Policy. “Gain-of-function experiments allow us to understand how pandemic viruses evolve, so that we can make predictions, develop countermeasures, and do disease surveillance”. Although none of the widely publicised mishaps of 2014 involved such work, the NIH decided to suspend funding for gain-of-function studies involving influenza, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV.
The US moratorium on gain-of-function experiments has been rescinded, but scientists are split over the benefits—and risks—of such studies. Talha Burki reports.
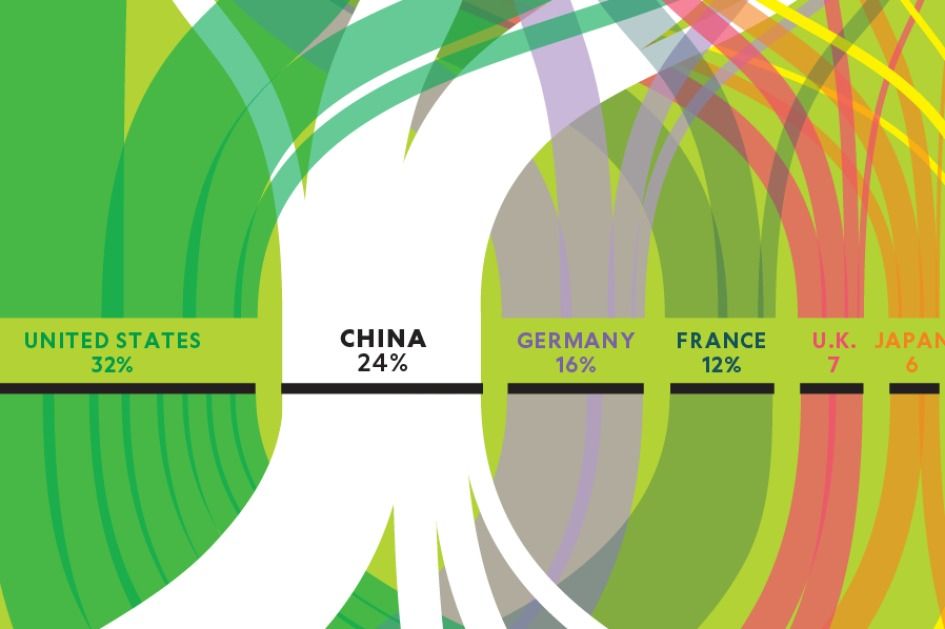
On Dec 19, 2017, the US National Institutes of Health (NIH) announced that they would resume funding gain-of-function experiments involving influenza, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus, and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. A moratorium had been in place since October, 2014. At the time, the NIH had stated that the moratorium “will be effective until a robust and broad deliberative process is completed that results in the adoption of a new US Government gain-of-function research policy”. This process has now concluded. It was spearheaded by the National Science Advisory Board for Biosecurity (NSABB) and led to the development of a new framework for assessing funding decisions for research involving pathogens with enhanced pandemic potential. The release of the framework by the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), of which NIH is part, signalled the end of the funding pause.
The situation has its roots in 2011, when the NSABB suppressed two studies involving H5N1 viruses that had been modified to allow airborne transmission from ferret to ferret. They worried that malign actors could replicate the work to deliberately cause an outbreak in human beings. After much debate, the studies were published in full in 2012. HHS subsequently issued guidelines for funding decisions on experiments likely to result in highly pathogenic H5N1 viruses transmissible from mammal to mammal via respiratory droplets. The guidelines were later expanded to include H7N9 viruses.