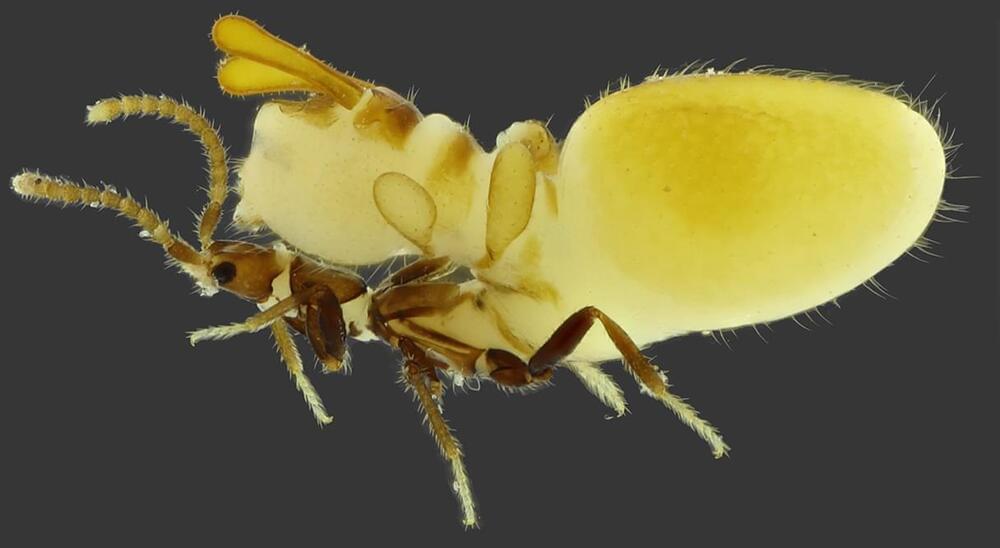
In what may be one of Earth’s craziest forms of mimicry, researchers have discovered a new species of rove beetle that grows a termite puppet on its back to fool real termites into feeding it. The replica is so precise, it even mirrors the termites’ distinct body segments and has three pairs of pseudoappendages that resemble antennae and legs.
Rove beetles (family Staphylinidae) are already infamous in the animal kingdom as masters of disguise. Some, for example, have evolved to look like army ants, allowing the beetles to march alongside them and feed on their eggs and young.
The new beetle species (Austrospirachtha carrijoi)—found beneath the soil in Australia’s Northern Territory—emulates a termite by enlarging its abdomen, a phenomenon known as physogastry. Evolution has reshaped this body part into a highly realistic replica of a termite (as seen above), head and all, which rides on top of the rest of the beetle’s body. The beetle’s real, much smaller head peeks out from beneath its termite disguise, the authors report this month in the journal.