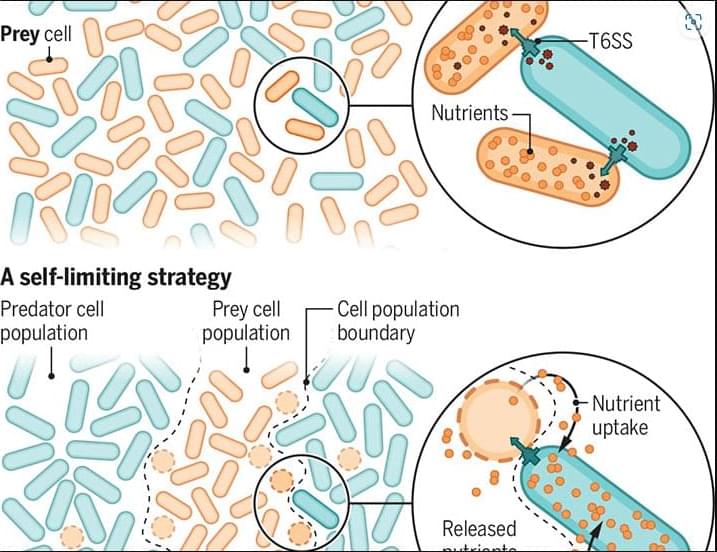
Bacteria leverage a secretion system to kill and scavenge nutrients from nearby competitors

Please consider joining my Substack at https://rupertsheldrake.substack.com.
Does Nature Obey Laws? | Sheldrake-Vernon Dialogue 95.
The conviction that the natural world is obedient, adhering to laws, is a widespread assumption of modern science. But where did this idea originate and what beliefs does it imply? In this episode of the Sheldrake-Vernon Dialogues, Rupert Sheldrake and Mark Vernon discuss the impact on science of the Elizabethan lawyer, Francis Bacon. His New Instrument of Thought, or Novum Organum, put laws at the centre of science and was intended as an upgrade on assumptions developed by Aristotle. But does the existence of mind-like laws of nature, somehow acting on otherwise mindless matter, even make sense? What difference is made by insights subsequent to Baconian philosophy, such as the discovery of evolution or the sense that the natural world is not machine-like but behaves like an organism? Could the laws of nature be more like habits? And what about the existence of miracles, the purposes of organisms, and the extraordinary fecundity of creativity?
—
Dr Rupert Sheldrake, PhD, is a biologist and author best known for his hypothesis of morphic resonance. At Cambridge University, as a Fellow of Clare College, he was Director of Studies in biochemistry and cell biology. As the Rosenheim Research Fellow of the Royal Society, he carried out research on the development of plants and the ageing of cells, and together with Philip Rubery discovered the mechanism of polar auxin transport. In India, he was Principal Plant Physiologist at the International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics, where he helped develop new cropping systems now widely used by farmers. He is the author of more than 100 papers in peer-reviewed journals and his research contributions have been widely recognized by the academic community, earning him a notable h-index for numerous citations. On ResearchGate his Research Interest Score puts him among the top 4% of scientists.
https://www.sheldrake.org/about-rupert-sheldrake?svd=95
—

PFOS, also known as “forever chemicals,” are synthetic compounds popular for several commercial applications, like making products resistant to stains, fire, grease, soil and water. They have been used in non-stick cookware, carpets, rugs, upholstered furniture, food packaging and firefighting foams deployed at airports and military airfields.
PFOS (perfluorooctane sulfonate or perfluorooctane sulfonic acid) are part of the larger class of forever chemicals called PFAS (per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances.) Both types have been linked to a variety of health issues, including liver disease, immune system malfunction, developmental issues and cancer.
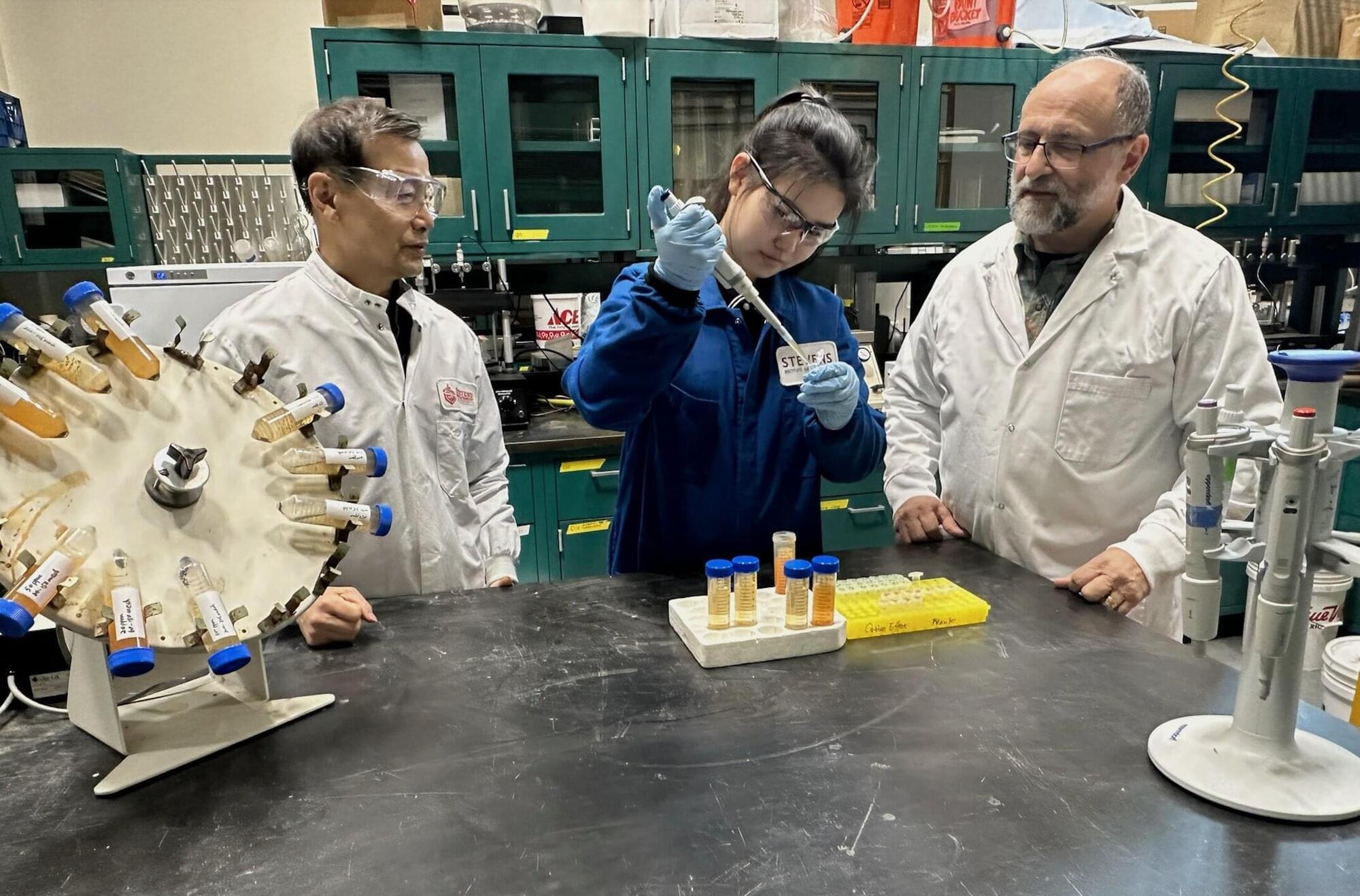
Because of their widespread use, PFOS are found in soil, agricultural products and drinking water sources, presenting a health risk. Xiaoguang Meng and Christos Christodoulatos, professors at the Department of Civil, Environmental and Ocean Engineering at Stevens Institute of Technology, and Ph.D. student Meng Ji working in their lab, wanted to identify the most efficient way to remove these toxins from the water.
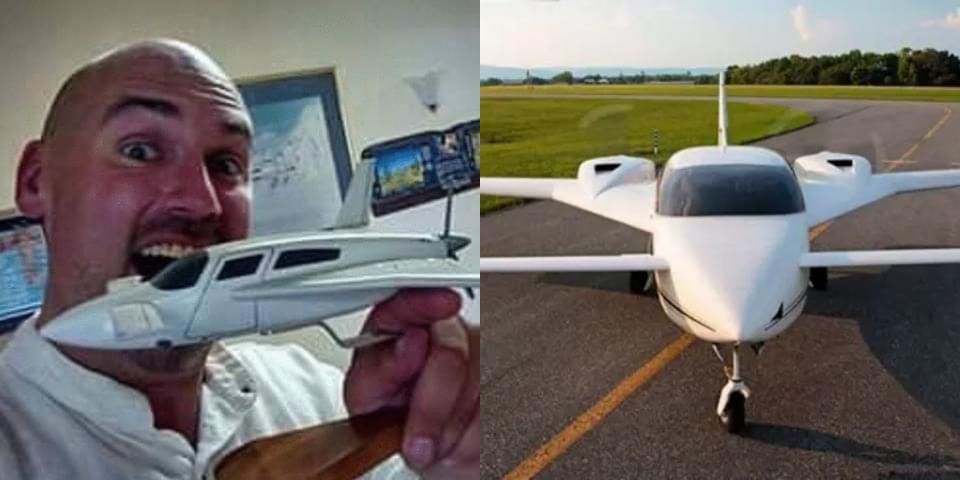


A company based in Canada has created the world’s very first plane that’s made mostly from hemp and powered by cannabis oil, giving completely new meaning to the term “sky high”
Designed and built by the weed company Hempearth – who also sell other weed-related items such as food, clothing, and accessories, the plane is claimed to be much stronger, lighter, and much more environmentally friendly than normal planes. Then it physically gets you higher than marijuana, but your plane is made of marijuana, and on marijuana fuel.
But how does it do it, exactly? Almost the entire plane is made from composite hemp fibers that are said to be 10 times stronger than steel, and this includes not only the chassis, but also everything inside of the plane including the seats, walls, and cushions.
When you want to get sky high.

Wastewater generated by animal farms poses a significant environmental risk, as it can pollute soil and groundwater and can be hazardous to human health. However, animal farm wastewater also contains carbon and many other nutrients. What if we could extract the carbon and nutrients and then release treated water back into the environment?
That’s the future envisioned by Prathap Parameswaran, an associate professor at Kansas State University who researches how to use environmental biotechnology platforms for biological wastewater treatment and sustainable resource recovery.
ABPDU and Kansas State University researchers make progress on extracting useful products from animal farm wastewater.
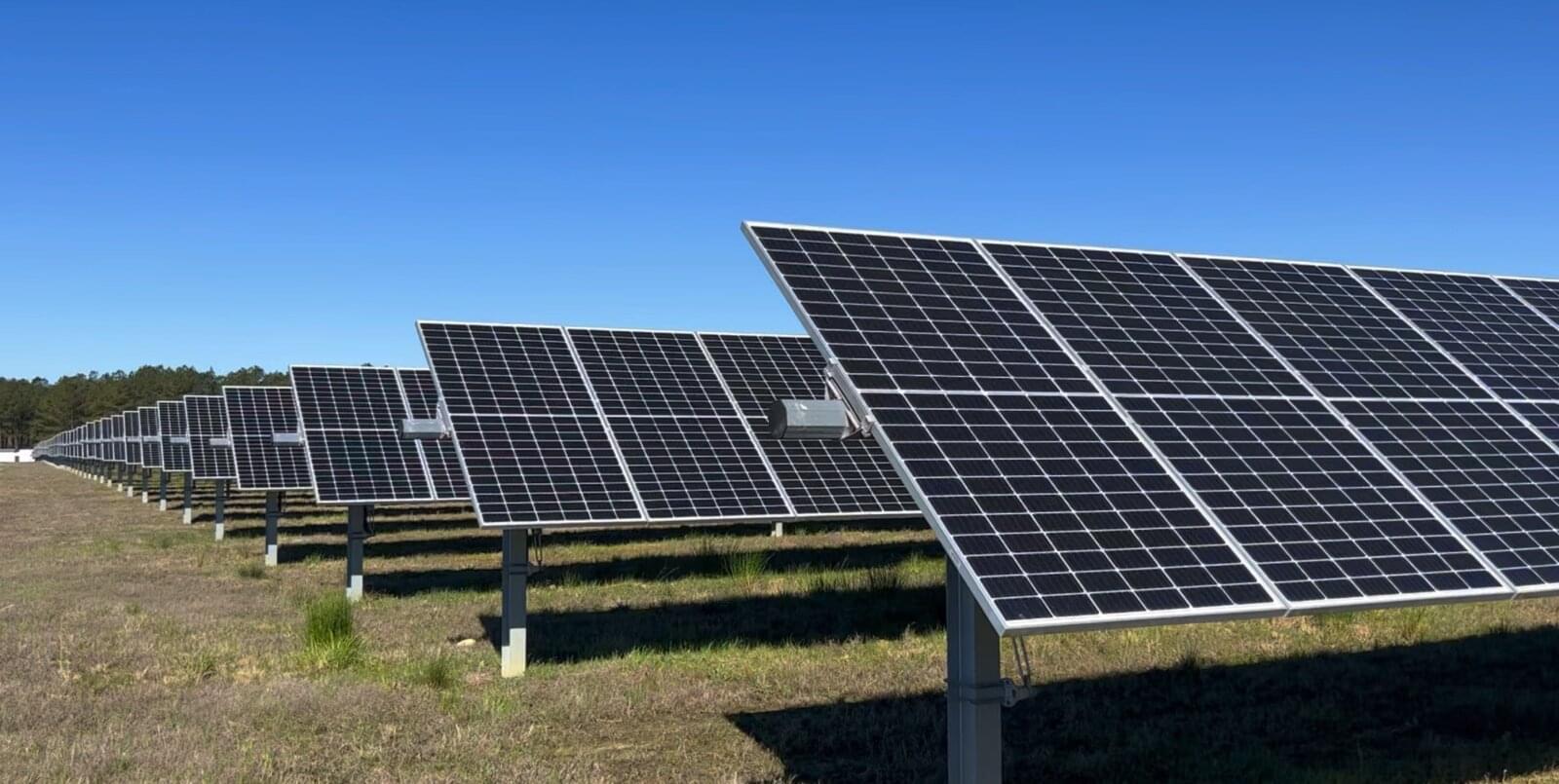

As solar energy becomes more affordable and widespread, farmland has emerged as a prime location for large-scale solar development. But with this expansion comes a persistent question: Do nearby property values suffer when solar farms move in?
In a paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers in Virginia Tech’s Department of Agricultural and Applied Economics in the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences looked at millions of property sales and thousands of commercial solar sites to shed some light on one of the most commonly cited downsides of large-scale solar adoption.
“As the U.S. scales up renewable energy, solar installations are increasingly being sited near homes and on farmland, and this often leads to pushback from residents worried about aesthetics or property value loss,” said Chenyang Hu, a graduate research assistant in the Department of Agricultural and Applied Economics and the paper’s lead author.
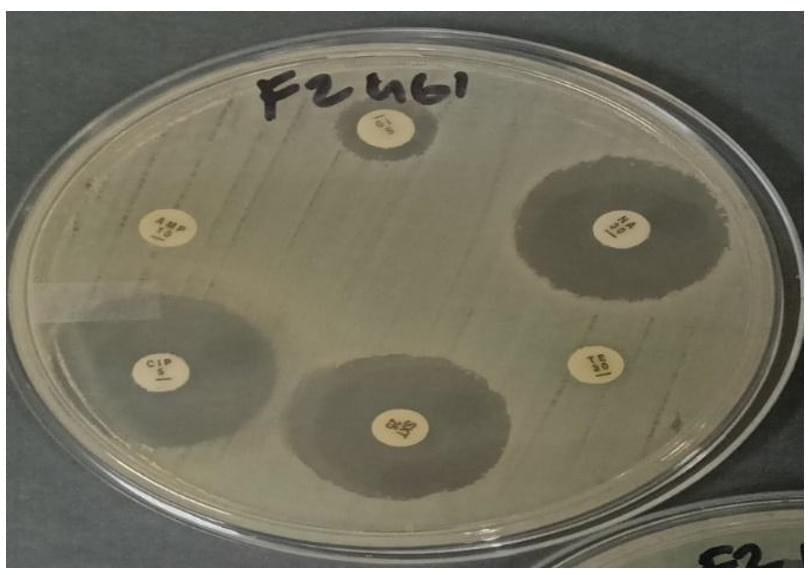
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a common bacterium that lives in the intestines of animals and humans, and it is often used to identify fecal contamination within the environment. E. coli can also easily develop resistance to antibiotics, making it an ideal organism for testing antimicrobial resistance—especially in certain agricultural environments where fecal material is used as manure or wastewater is reused.
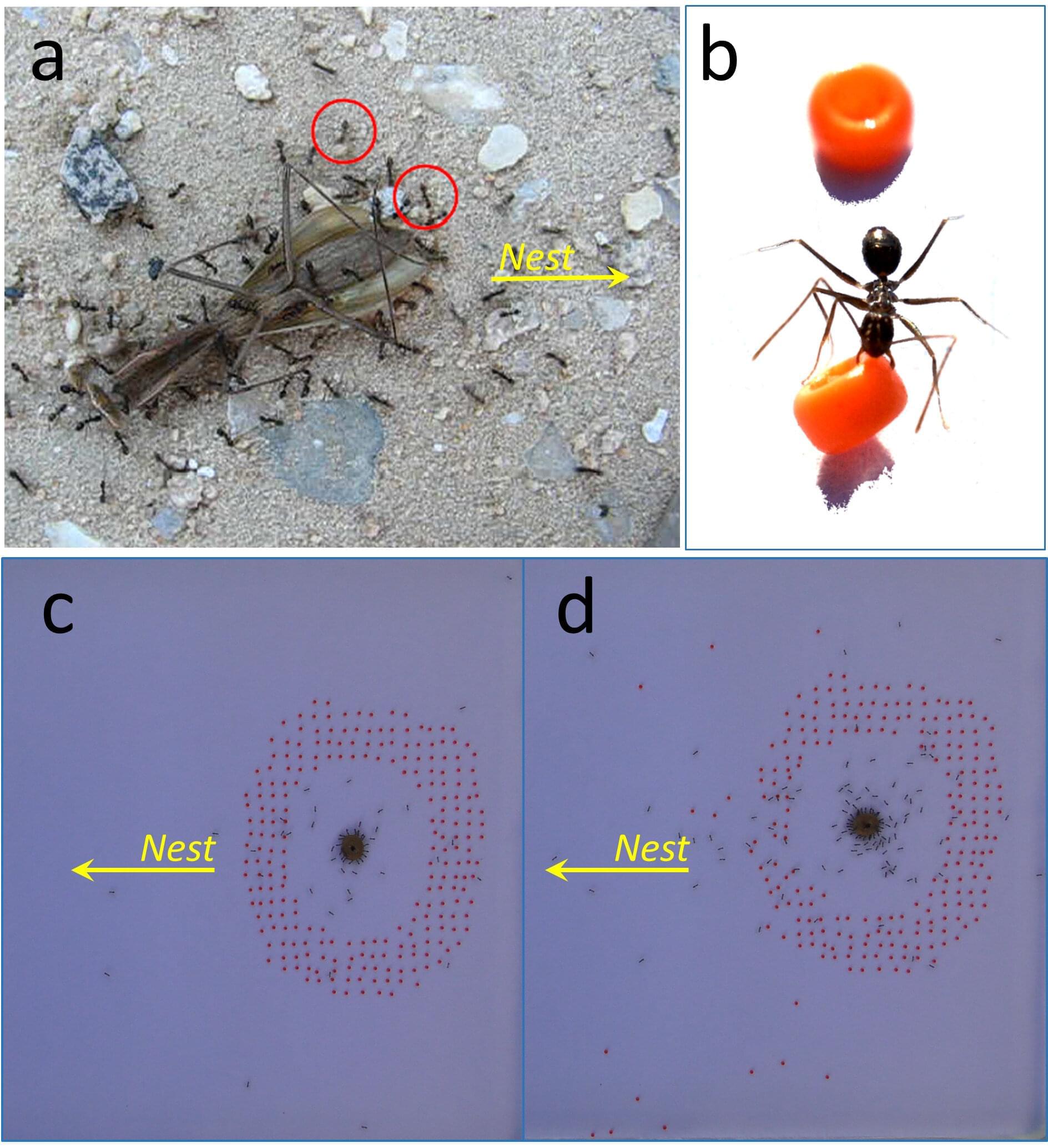
Among the tens of thousands of ant species, incredible “intelligent” behaviors like crop culture, animal husbandry, surgery, “piracy,” social distancing, and complex architecture have evolved.
Yet at first sight, the brain of an ant seems hardly capable of such feats: it is about the size of a poppy seed, with only 0.25m to 1m neurons, compared to 86bn for humans.
Now, researchers from Israel and Switzerland have shown how “swarm intelligence” resembling advance planning can nevertheless emerge from the concerted operation of many of these tiny brains. The results are published in Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience.
