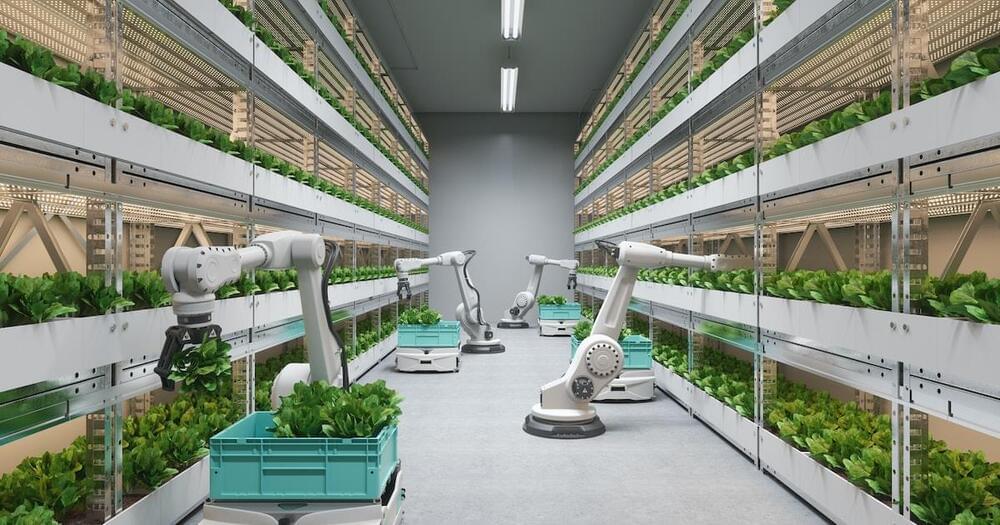
After decades of research, robots are finally starting to take over farms — it isn’t clear how human workers will be affected.



Year 2018 o.o! This could be the first step toward avatars and as well as medical sciences finding a way to treat a human being better essentially with more precision. Also this means we really are wetware computers that can be coded and controlled much like robots are which can lead to our own level of superintelligence in the future by having more abilities with downloaded information.
Cannot be used to help you avoid snack food.
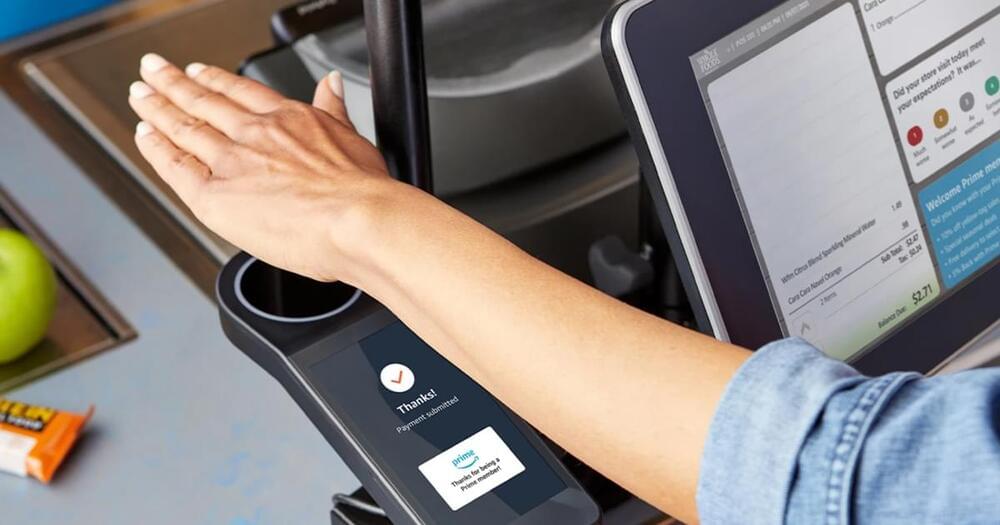


Amazon is bringing its palm print-scanning biometric payment technology to several Whole Foods locations.
Biometrics: Every person has measurable physical characteristics that are unique to them — and because these attributes are unique and measurable, they can be used to verify our identity.
Biometric technologies — like the one that probably unlocks your phone — automate this verification, analyzing a face, fingerprint, or palm for distinct identifiers linked to a specific person.



With the help of AI, researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, have succeeded in designing synthetic DNA that controls the cells’ protein production. The technology can contribute to the development and production of vaccines, drugs for severe diseases, as well as alternative food proteins much faster and at significantly lower costs than today. How our genes are expressed is a process that is fundamental to the functionality of cells in all living organisms. Simply put, the genetic code in DNA is transcribed to the molecule messenger RNA (mRNA), which tells the cell’s factory which protein to produce and in which quantities.
Researchers have put a lot of effort into trying to control gene expression because it can, among other things, contribute to the development of protein-based drugs. A recent example is the mRNA vaccine against Covid-19, which instructed the body’s cells to produce the same protein found on the surface of the coronavirus. The body’s immune system could then learn to form antibodies against the virus. Likewise, it is possible to teach the body’s immune system to defeat cancer cells or other complex diseases if one understands the genetic code behind the production of specific proteins. Most of today’s new drugs are protein-based, but the techniques for producing them are both expensive and slow, because it is difficult to control how the DNA is expressed. Last year, a research group at Chalmers, led by Aleksej Zelezniak, Associate Professor of Systems Biology, took an important step in understanding and controlling how much of a protein is made from a certain DNA sequence.
“First it was about being able to fully ‘read’ the DNA molecule’s instructions. Now we have succeeded in designing our own DNA that contains the exact instructions to control the quantity of a specific protein,” says Aleksej Zelezniak about the research group’s latest important breakthrough. The principle behind the new method is similar to when an AI generates faces that look like real people. By learning what a large selection of faces looks like, the AI can then create completely new but natural-looking faces. It is then easy to modify a face by, for example, saying that it should look older, or have a different hairstyle. On the other hand, programming a believable face from scratch, without the use of AI, would have been much more difficult and time-consuming. Similarly, the researchers’ AI has been taught the structure and regulatory code of DNA. The AI then designs synthetic DNA, where it is easy to modify its regulatory information in the desired direction of gene expression.
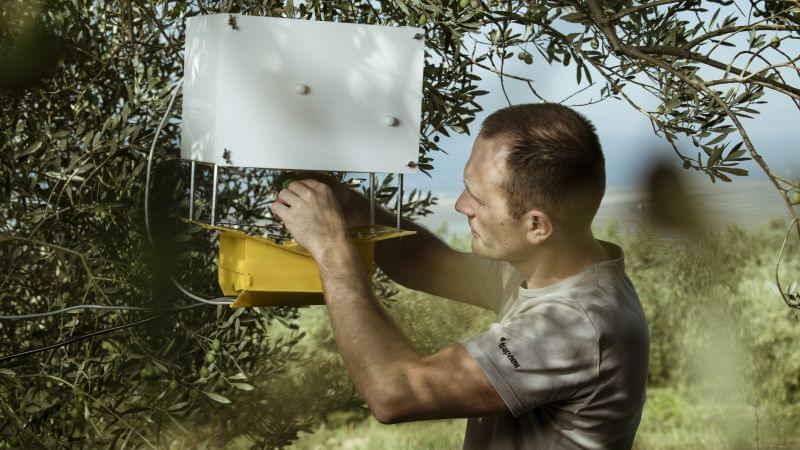

Pests destroy up to 40% of the world’s crops each year, causing $220 billion in economic losses, according to the UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Trapview is harnessing the power of AI to help tackle the problem.
The Slovenian company has developed a device that traps and identifies pests, and acts as an advance warning system by predicting how they will spread.
“We’ve built the biggest database of pictures of insects in the world, which allows us to really use modern AI-based computing vision in the most optimal way,” says Matej Štefančič, CEO of Trapview and parent company EFOS.

Amazon will shut down its food delivery business in India by the end of the year, the retailer said Friday, retreating from a $20 billion vertical it entered less than three years ago.
The retailer will shut down the food delivery business, called Amazon Food, on December 29 in India. It launched Food in India in May 2020 in parts of Bengaluru. The company later expanded the service across the city, tying up with additional restaurants, but it never heavily promoted or marketed the platform.
“Customers have been telling us for some time that they would like to order prepared meals on Amazon in addition to shopping for all other essentials. This is particularly relevant in present times as they stay home safe,” the company said at the time of Food launch.