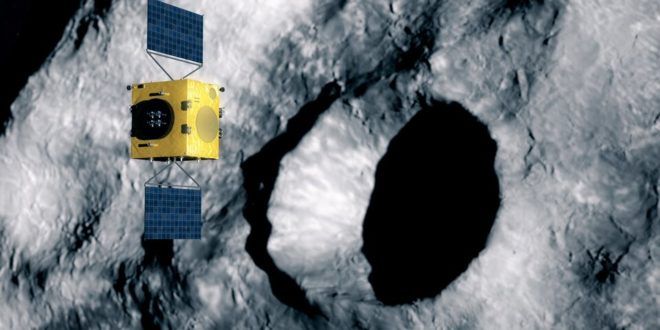
Darmstadt, 15 September 2020. – The European Space Agency (ESA) awarded a €129.4 million contract covering the design, manufacturing and testing of Hera, the space agency’s first mission for planetary defence, ESA announced today.
The contract was signed by Franco Ongaro, ESA Director of Technology, Engineering and Quality, and Marco Fuchs, CEO of Germany space company OHB, prime contractor of the Hera consortium, ESA said today. The signing took place at ESA’s European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) in Darmstadt, Germany, which will serve as mission control for the 2024-launched Hera.
The mission will be Europe’s contribution to an international asteroid deflection effort, set to perform sustained exploration of a double asteroid system, ESA said.
Hera will be, along with NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirect Test (DART) spacecraft, humankind’s first probe to rendezvous with a binary asteroid system, a little understood class making up around 15% of all known asteroids, the agency said.
Hera is the European contribution to an international planetary defence collaboration among European and US scientists called the Asteroid Impact & Deflection Assessment (AIDA).