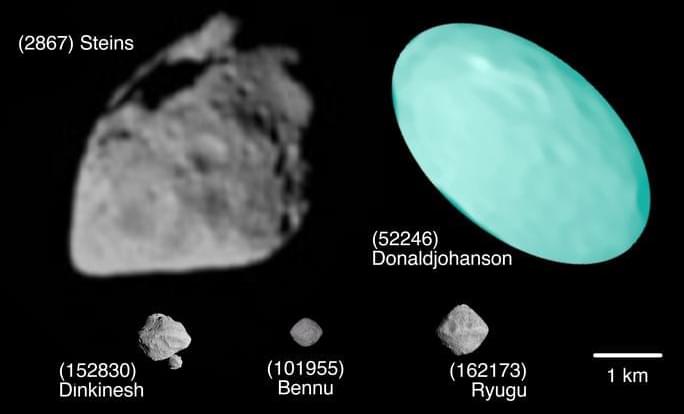
“We can hardly wait for the flyby because, as of now, Donaldjohanson’s characteristics appear very distinct from Bennu and Ryugu. Yet, we may uncover unexpected connections,” said Dr. Simone Marchi.
How old is asteroid (52246) Donaldjohanson (DJ), which is about to be studied by NASA’s Lucy spacecraft in an upcoming flyby on April 20, 2025? This is what a recent study published in The Planetary Science Journal hopes to address as an international team of researchers conducted a pre-flyby analysis of DJ with the goal of ascertaining the asteroid’s potential age. This study has the potential to help scientists better understand the formation and evolution of asteroids throughout the solar system, and specifically the main asteroid belt, which is where DJ orbits.
For the study, the researchers used ground-based telescopes and instruments to analyze the size, shape, and composition of DJ with the goal of ascertaining its relative age. For context, relative age indicates an object’s approximate age based on observational and data analysis, which contrasts an object’s absolute age that is determined from laboratory analysis with samples. Lucy will only be conducting a flyby and will not be returning samples to Earth.
In the end, the researchers not only discovered that DJ has elongated shape with estimates putting its approximate age at 150 million years old and formed when a larger asteroid broke apart. This upcoming flyby comes after the Hayabusa2 and OSIRIS-REX missions visited asteroids Ryugu and Bennu, respectively, with DJ hypothesized to orbit in the approximate regions where both Ryugu and Bennu formed.