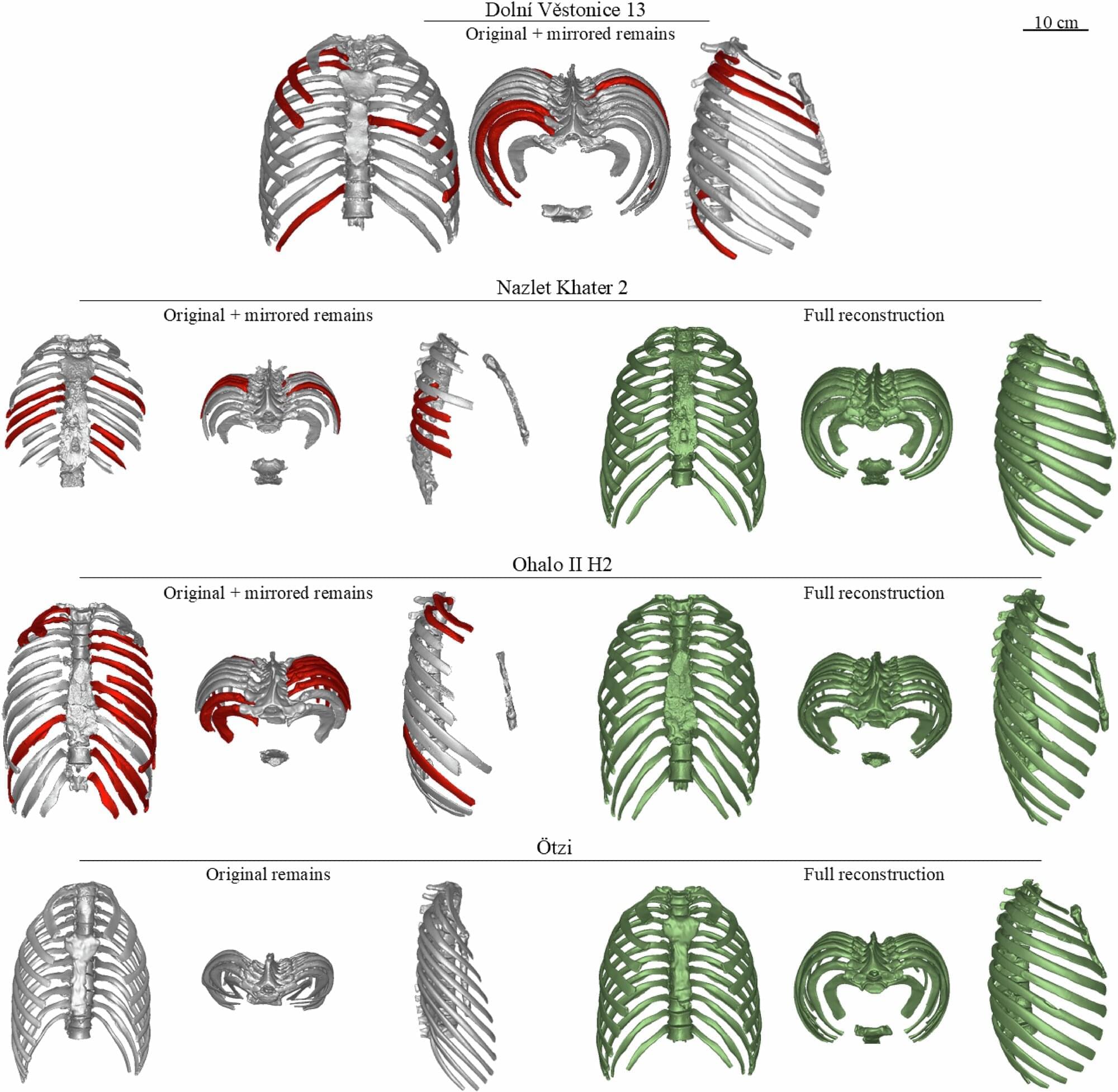
Using data from the T2T reference, scientists linked two new genes to changes in brain size and synapse signaling.


What makes the human brain distinctive? A new study published in Cell identifies two genes linked to human brain features and provides a road map to discover many more. The research could lead to insights into the functioning and evolution of the human brain, as well as the roots of language disorders and autism.
Not all genes respond in the same way to regulation by the same molecule—a property that might enable cells to produce complex genetic responses.
Genes in living cells may become active or may be suppressed in response to environmental stimuli such as heat or the availability of nutrients. For bacteria, this gene regulation often appears to be a simple “on-off switch” controlled by regulatory proteins called transcription factors (TFs). But researchers have now found that different genes might respond differently to the same stimulus even if they are regulated by the same TF [1]. The team activated genes involved in DNA repair and observed gene-to-gene variations in their protein production patterns. Such differences might have been exploited by evolution to achieve complex responses with relatively few molecular components, the researchers suggest.
In the typical scenario, a TF binds to a region of a so-called promoter, a DNA sequence next to a gene. If the TF is the type that blocks gene expression, it prevents the enzyme RNA polymerase from binding and thus from beginning the process of producing the protein that the gene encodes. Because of thermal fluctuations (noise), the TF may spontaneously unbind, allowing gene expression to proceed until it rebinds. The rate of TF binding depends on its concentration, so fluctuations in concentration will cause changes in gene expression.
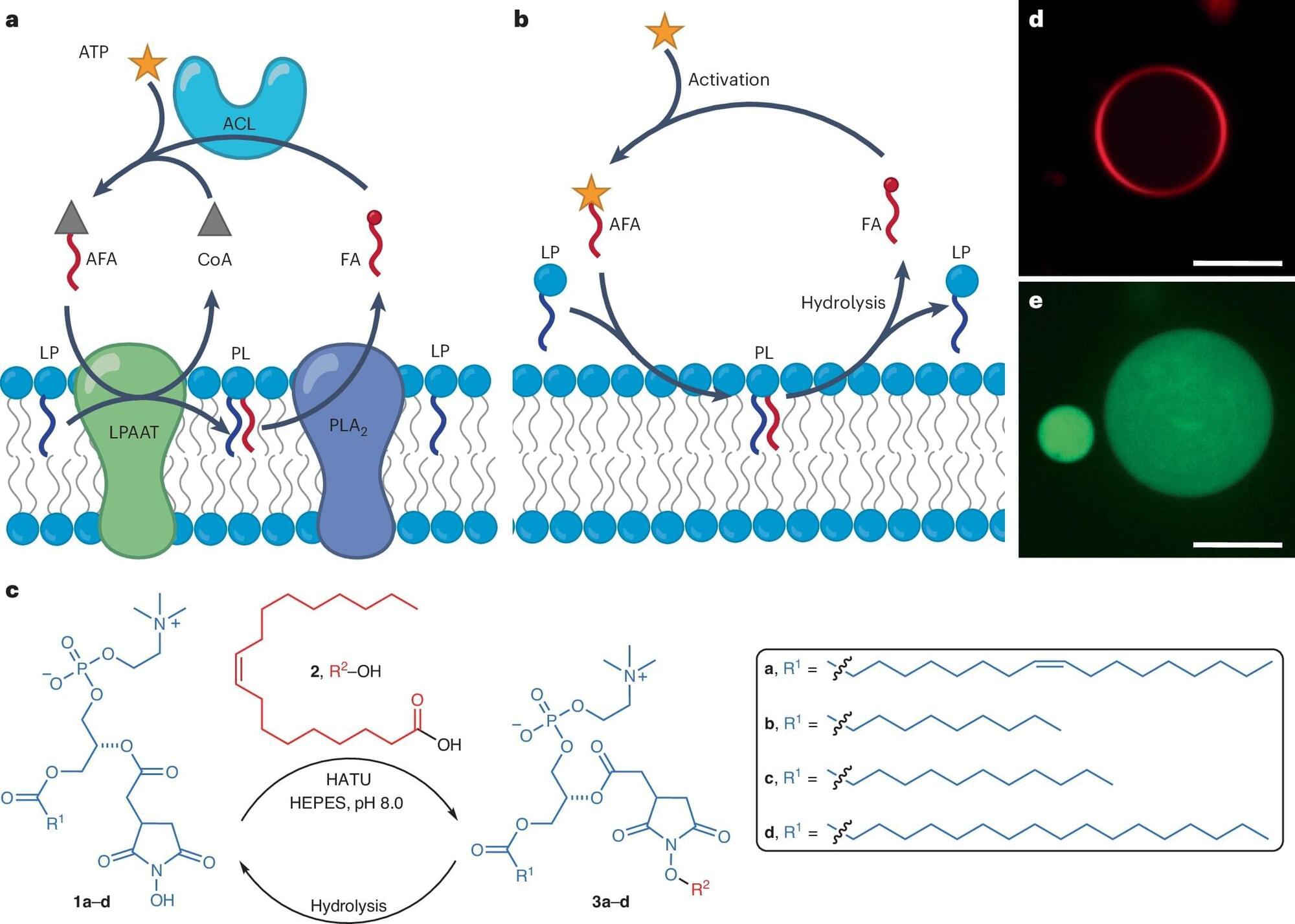
At some point during the evolution of life on Earth, inorganic matter became organic, nonliving matter became living. How this happened is one of humankind’s greatest mysteries. Today, scientists work to develop synthetic cells that mimic living cells, hoping to uncover clues that will help answer the question: how did life on Earth begin?
Physicist and fusion researcher Eric Lerner presents a sweeping critique of the Big Bang theory and the standard model of cosmology at Demysticon 25. He builds on the foundations of plasma physics and the work of Nobel laureate Hannes Alfvén to outline an alternative cosmological framework rooted in known physical laws—gravity, nuclear fusion, and electromagnetic plasma behavior—rather than hypothetical concepts like dark matter, dark energy, or cosmic inflation. He explores how filamentary plasma structures may account for galaxy formation, how fusion research using dense plasma focus devices parallels cosmic processes, and how the cosmic microwave background may not be relic radiation from a singular origin. Merging astrophysics, plasma cosmology, and energy research, this talk reframes the origin and structure of the universe—and calls into question the prevailing narratives at the heart of modern theoretical physics.
PATREON
/ demystifysci.
PARADIGM DRIFT
https://demystifysci.com/paradigm-dri… Go! Introduction the Big Bang Debate 00:03:57 Eric Lerner’s Perspective on Cosmic Evolution 00:04:21 The Pinch Effect and Electrical Currents in Plasmas 00:10:27 Evolutionary Hierarchies and Cosmic Filaments 00:14:50 Interplay of Forces in Structure Formation 00:18:14 Evidence of Filaments Across Scales 00:25:04 Dynamics of Galaxy Formation and Star Development 00:29:08 Cosmic Microwave Background and Element Formation 00:30:29 The Formation and Properties of Early Galaxies 00:35:22 Energy Flows and the Cosmic Evolution Crisis 00:39:58 Plasma Focus Devices and Fusion Energy Research 00:41:16 Q&A Understanding Galaxy Components and Rotation 00:51:33 Q&A The Implications of Missing Gravity and Galaxy Dynamics 00:58:07 Q&A Gravitational Lensing and Mass Distribution 01:00:32 Q&A Lensing and Galactic Observations 01:02:04 Q&A Fractal Patterns in Cosmology #cosmology, #space, #galaxyformation, #gravitationalwaves, #cosmicstructures, #astrophysics, #fusionenergy, #magneticfields, #spacephysics, #electricuniverse, #criticalthinking #philosophypodcast, #sciencepodcast, #longformpodcast ABOUS US: Anastasia completed her PhD studying bioelectricity at Columbia University. When not talking to brilliant people or making movies, she spends her time painting, reading, and guiding backcountry excursions. Shilo also did his PhD at Columbia studying the elastic properties of molecular water. When he’s not in the film studio, he’s exploring sound in music. They are both freelance professors at various universities. PATREON: get episodes early + join our weekly Patron Chat https://bit.ly/3lcAasB MERCH: Rock some DemystifySci gear : https://demystifysci.myspreadshop.com… AMAZON: Do your shopping through this link: https://amzn.to/3YyoT98 DONATE: https://bit.ly/3wkPqaD SUBSTACK: https://substack.com/@UCqV4_7i9h1_V7h… BLOG: http://DemystifySci.com/blog RSS: https://anchor.fm/s/2be66934/podcast/rss MAILING LIST: https://bit.ly/3v3kz2S SOCIAL:
MUSIC:-Shilo Delay: https://g.co/kgs/oty671
00:00 Go! Introduction the Big Bang Debate.
00:03:57 Eric Lerner’s Perspective on Cosmic Evolution.
00:04:21 The Pinch Effect and Electrical Currents in Plasmas.
00:10:27 Evolutionary Hierarchies and Cosmic Filaments.
00:14:50 Interplay of Forces in Structure Formation.
00:18:14 Evidence of Filaments Across Scales.
00:25:04 Dynamics of Galaxy Formation and Star Development.
00:29:08 Cosmic Microwave Background and Element Formation.
00:30:29 The Formation and Properties of Early Galaxies.
00:35:22 Energy Flows and the Cosmic Evolution Crisis.
00:39:58 Plasma Focus Devices and Fusion Energy Research.
00:41:16 Q&A Understanding Galaxy Components and Rotation.
00:51:33 Q&A The Implications of Missing Gravity and Galaxy Dynamics.
00:58:07 Q&A Gravitational Lensing and Mass Distribution.
01:00:32 Q&A Lensing and Galactic Observations.
01:02:04 Q&A Fractal Patterns in Cosmology.
#cosmology, #space, #galaxyformation, #gravitationalwaves, #cosmicstructures, #astrophysics, #fusionenergy, #magneticfields, #spacephysics, #electricuniverse, #criticalthinking #philosophypodcast, #sciencepodcast, #longformpodcast.
ABOUS US: Anastasia completed her PhD studying bioelectricity at Columbia University. When not talking to brilliant people or making movies, she spends her time painting, reading, and guiding backcountry excursions. Shilo also did his PhD at Columbia studying the elastic properties of molecular water. When he’s not in the film studio, he’s exploring sound in music. They are both freelance professors at various universities.
In this video we look at the thought of French Paleontologist, Cosmologist, WWI veteran and Jesuit Priest, Teilhard De Chardin, and his conceptions of the Omega Point and the Noosphere as articulated in his most significant work, The Phenomenon of Man.
Join us on Discord! / discord.
#integral #philosophy #evolution #consciousness #history #noosphere
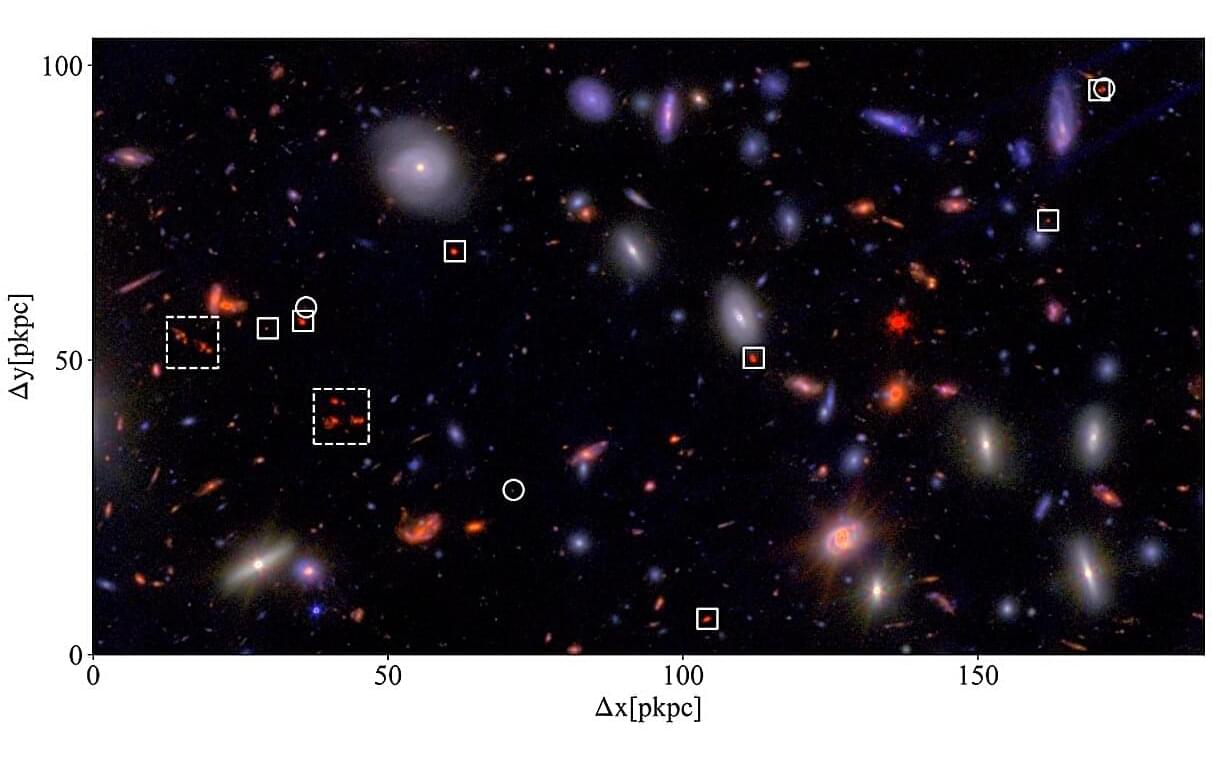
Using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), an international team of astronomers has performed deep and high spectral resolution imaging of a distant protocluster of galaxies, designated A2744-z7p9OD. Results of the new observations, published July 8 on the arXiv preprint server, shed more light on the properties of this protocluster, revealing that it hosts a remarkably evolved core.
Galaxy clusters are collections of hundreds to thousands of galaxies bound together by gravity. Such clusters are the most immense gravitationally bound structures in the universe, and therefore they could serve as excellent laboratories for studying galaxy evolution and cosmology.
Of special interest for astronomers are studies of protoclusters of galaxies—the progenitors of clusters. These objects, found at high redshifts (over 2.0), could provide essential information about the early phases of the universe.

A team of researchers have made progress in understanding how some of the Universe’s heaviest particles behave under extreme conditions similar to those that existed just after the Big Bang.
A study published in Physics Reports provides new insights into the fundamental forces that shaped our Universe and continues to guide its evolution today.
The research, conducted by an international team from the University of Barcelona, the Indian Institute of Technology, and Texas A&M University, focuses on particles containing heavy quarks, the building blocks of some of the most massive particles in existence.