High-fidelity modelling of nanosecond repetitively pulsed discharges (NRPDs) is burdened by the multiple time and length scales and large chemistry mechanisms involved, which prohibit detailed analyses and parametric studies. In the present work, we propose a ‘frozen electric-field’ modelling approach to expedite the NRPD simulations without adverse effects on the solution accuracy. First, a burst of nanosecond voltage pulses is simulated self-consistently until the discharge reaches a stationary state. The calculated spatial distributions and temporal evolution of the electric field, electron density and electron energy during the last pulse are then stored in a library and the electrical characteristics of subsequent pulses are frozen at these values. This strategy allows the timestep for numerical integration to be increased by four orders of magnitude (from 10−13 to 10−9 s), thereby significantly improving the computational efficiency of the process. Reduced calculations of a burst of 50 discharge pulses show good agreement with the predictions from a complete plasma model (electrical characteristics calculated during each pulse). The error in species densities is less than 20% at the centre of the discharge volume and about 30% near the boundaries. The deviations in temperature, however, are much lower, at 5% in the entire domain. The model predictions are in excellent agreement with measured ignition delay times and temperatures in H2–air mixtures subject to dielectric barrier NRPD over a pressure range of 54–144 Torr with equivalence ratios of 0.7–1.2. The OH density increases with pressure and triggers low-temperature fuel oxidation, which leads to rapid temperature rise and ignition. The ignition delay decreases by a factor of 2, with an increase in pressure from 54 to 144 Torr. In contrast, an increase in the H2–air equivalence ratio from 0.7 to 1.2 marginally decreases the ignition delay by about 20%. This behaviour is attributed to the insensitivity of OH production rates to the variation in the equivalence ratio.
Category: evolution – Page 141
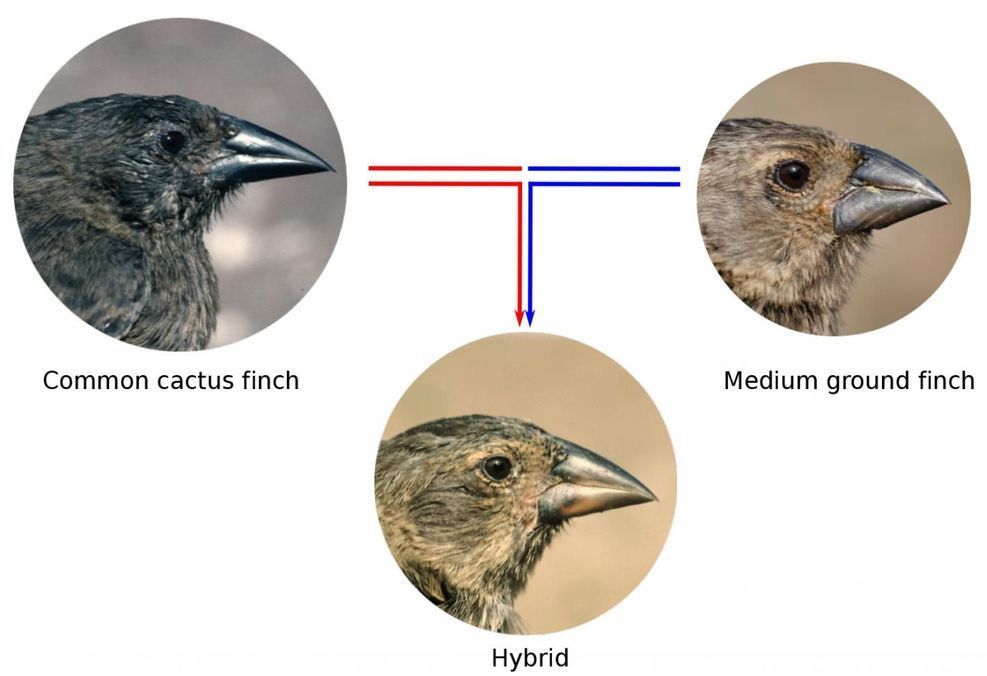
How gene flow between species influences the evolution of Darwin’s finches
Despite the traditional view that species do not exchange genes by hybridisation, recent studies show that gene flow between closely related species is more common than previously thought. A team of scientists from Uppsala University and Princeton University now reports how gene flow between two species of Darwin’s finches has affected their beak morphology. The study is published today in Nature Ecology and Evolution.
Darwin’s finches on the Galápagos Islands are an example of a rapid adaptive radiation in which 18 species have evolved from a common ancestral species within a period of 1–2 million years. Some of these species have only been separated for a few hundred thousand years or less.
Rosemary and Peter Grant of Princeton University, co-authors of the new study, studied populations of Darwin’s finches on the small island of Daphne Major for 40 consecutive years and observed occasional hybridisation between two distinct species, the common cactus finch and the medium ground finch. The cactus finch is slightly larger than the medium ground finch, has a more pointed beak and is specialised to feed on cactus. The medium ground finch has a blunter beak and is specialised to feed on seeds.
Algorithm Developed to Predict the Evolution of Genetic Mutations
Quantitative biologists David McCandlish and Juannan Zhou at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory have developed an algorithm with predictive power, giving scientists the ability to see how specific genetic mutations can combine to make critical proteins change over the course of a species’ evolution.
Described in Nature Communications, the algorithm called “minimum epistasis interpolation” results in a visualization of how a protein could evolve to either become highly effective or not effective at all. They compared the functionality of thousands of versions of the protein, finding patterns in how mutations cause the protein to evolve from one functional form to another.
“Epistasis” describes any interaction between genetic mutations in which the effect of one gene is dependent upon the presence of another. In many cases, scientists assume that when reality does not align with their predictive models, these interactions between genes are at play. With this in mind, McCandlish created this new algorithm with the assumption that every mutation matters. The term “Interpolation” describes the act of predicting the evolutionary path of mutations a species might undergo to achieve optimal protein function.

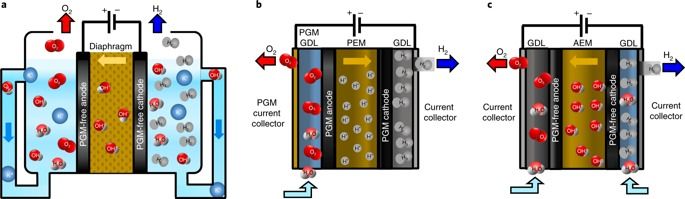
Highly quaternized polystyrene ionomers for high performance anion exchange membrane water electrolysers
Water spliting got cheaper.
Alkaline anion exchange membrane (AEM) electrolysers to produce hydrogen from water are still at an early stage of development, and their performance is far lower than that of systems based on proton exchange membranes. Here, we report an ammonium-enriched anion exchange ionomer that improves the performance of an AEM electrolyser to levels approaching that of state-of-the-art proton exchange membrane electrolysers. Using rotating-disk electrode experiments, we show that a high pH (13) in the electrode binder is the critical factor for improving the activity of the hydrogen- and oxygen-evolution reactions in AEM electrolysers. Based on this observation, we prepared and tested several quaternized polystyrene electrode binders in an AEM electrolyser. Using the binder with the highest ionic concentration and a NiFe oxygen evolution catalyst, we demonstrated performance of 2.7 A cm−2 at 1.8 V without a corrosive circulating alkaline solution. The limited durability of the AEM electrolyser remains a challenge to be addressed in the future.

IMMORTALISTS MAGAZINE’s 4th PUBLICATION!
Dinorah Delphin has unveiled another magnificent issue of the Immortalists Magazine. She has clearly focused her contributing authors on the world pandemic, with impressive results.
One of the outstanding articles is from our pal, the Chairman of the USTP, Gennady Stolyarov. Gennady levels an eviscerating attack on the American health care system.
I can see that Gennady has a visceral reaction to mass death. There is passionate, broiling anger in the lines of his article. He seems to be mounting a crusade, and I’m going to confess that I’m considering arming myself for battle.
“…there has not been the will…to prioritize public health and longevity as the overarching objective of the economy and of society.”
People have amazingly short attention spans. And you might think, after looking back at previous epidemics, that shortly after this subsides that everyone will go back to debating trivia on TV and quibbling over the latest inanities bellowed from the podium by the oompa loompa moron. After all are there vaccines for SARS, MERS, or HIV? No, there are not. It takes will and effort and money and focus and time to create an effective vaccine. I understand that the world record quickest vaccine development was for the mumps and that that effort took 4 years. However, this virus may have a second and a third wave coming, which might function as a nightmare wake-up alarm that can’t be shut off. There is the potential that at some point the mountainous pile of dead bodies will actually focus this nation’s attention on delivering a lasting solution. I credit Gennady for having the foresight to immediately engage the USTP in a series of proposals designed to enable that lasting solution.
What would our world look like if the number one priority was making everyone healthy enough to live forever?
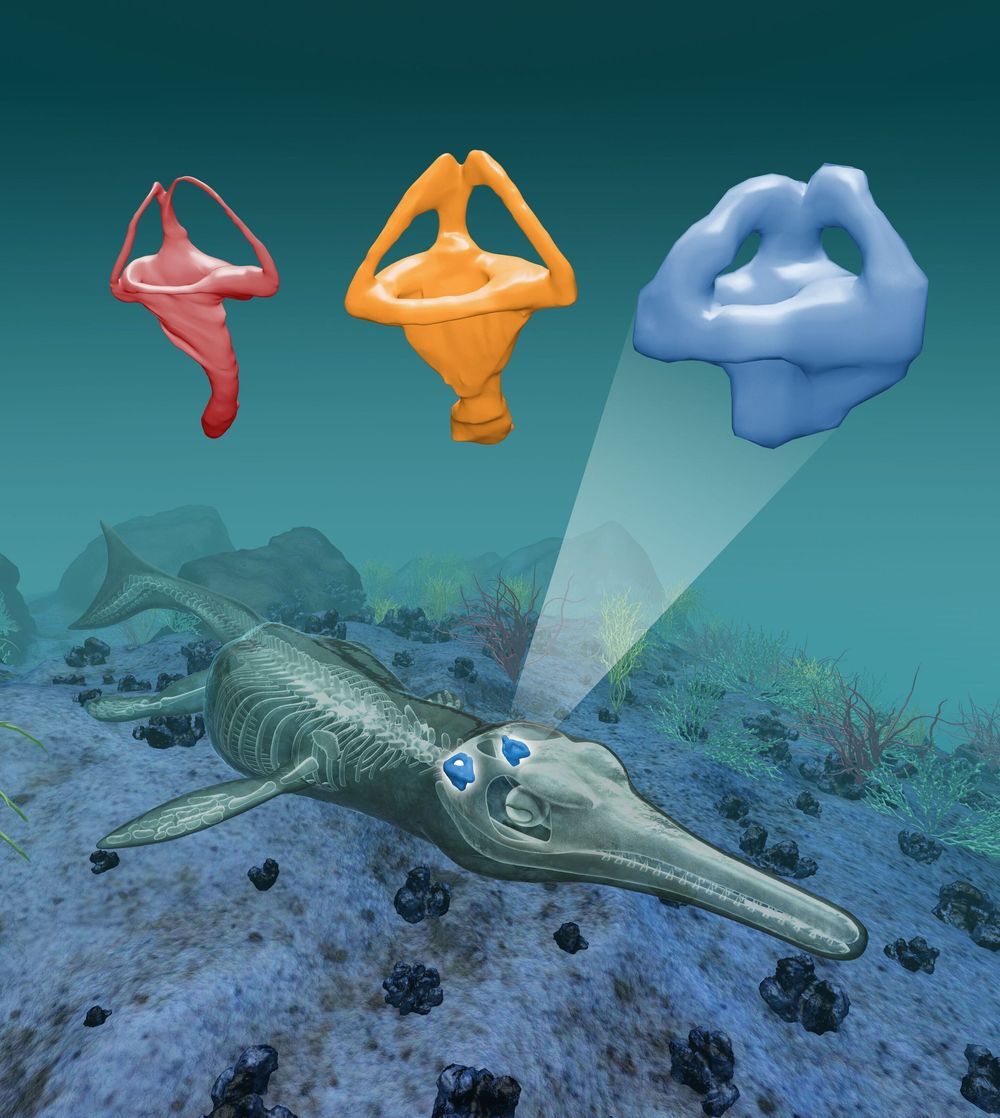

The evolution of the ear canal in an ancient crocodile relative
An international team of researchers has found that an ancient crocodile relative underwent body transitions as it evolved from a land to a sea creature before its ears changed to suit an underwater environment. In their paper published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the group describes their in-depth study of thalattosuchia skulls and what they found.
Thalattosuchia was an ancient crocodile species that lived in the world’s oceans over 150 million years ago. But before that, they were land-dwelling. Prior research has shown that they took to water in a much slower fashion than other creatures like whales, existing as semi-aquatic creatures for many years before becoming full-fledged sea creatures. Study of their fossilized remains has shown their front legs evolving to become fins, and their back legs evolving into a fluked tail. Their bodies grew slimmer and sleeker to so they could glide smoothly through the water. And once they became sea creatures, their internal organs changed to suit the new environment. One such organ was the inner ear. And it was this organ that was the focus of this new work.
To learn more about the evolution of thalattosuchia’s ears, the researchers conducted CAT scans on over a dozen skull fossils. They focused most specifically on the inner ear structures used to maintain balance and equilibrium in land creatures.

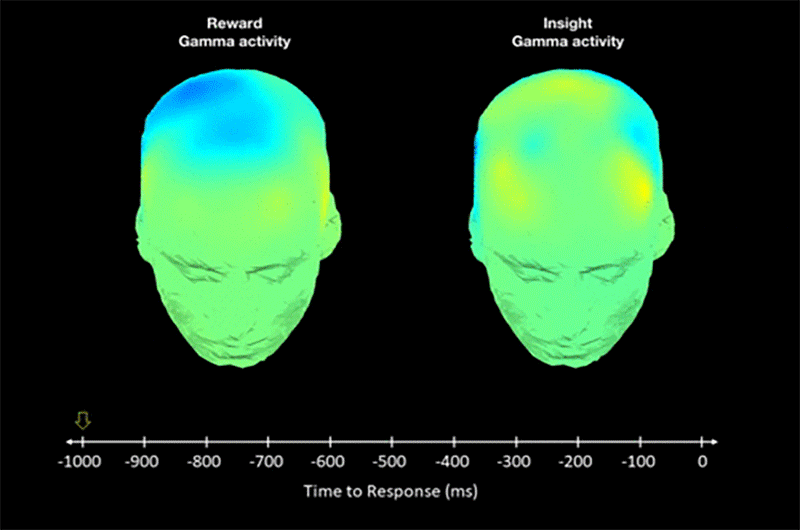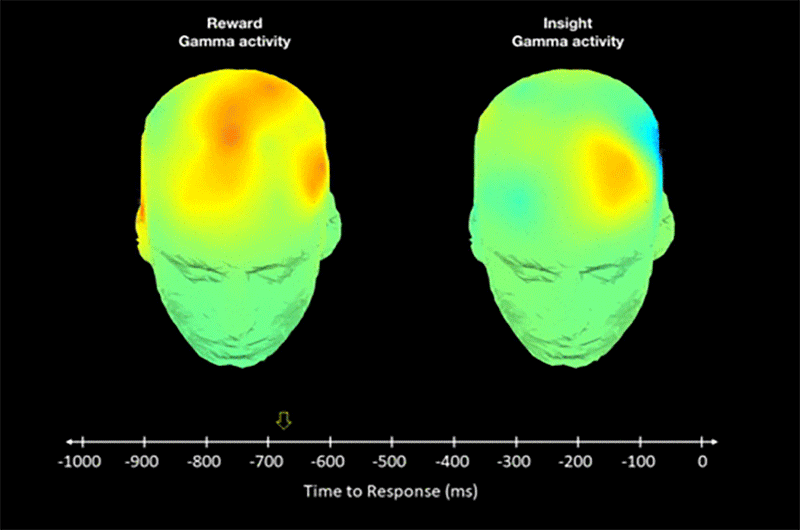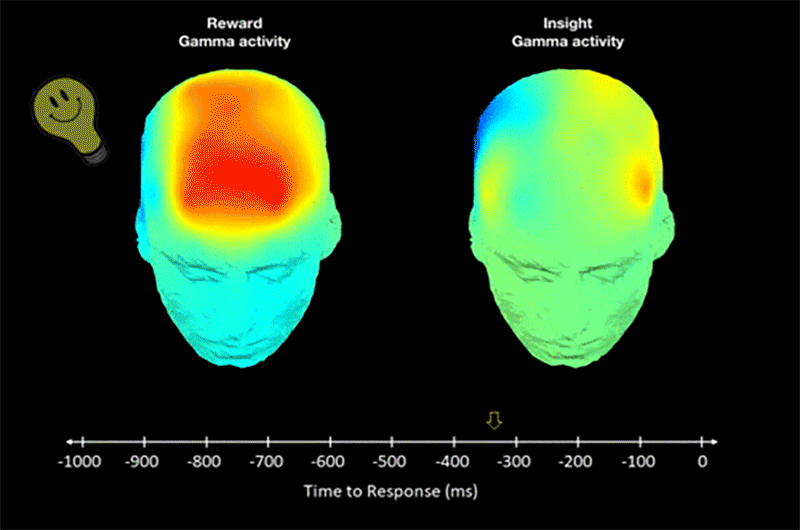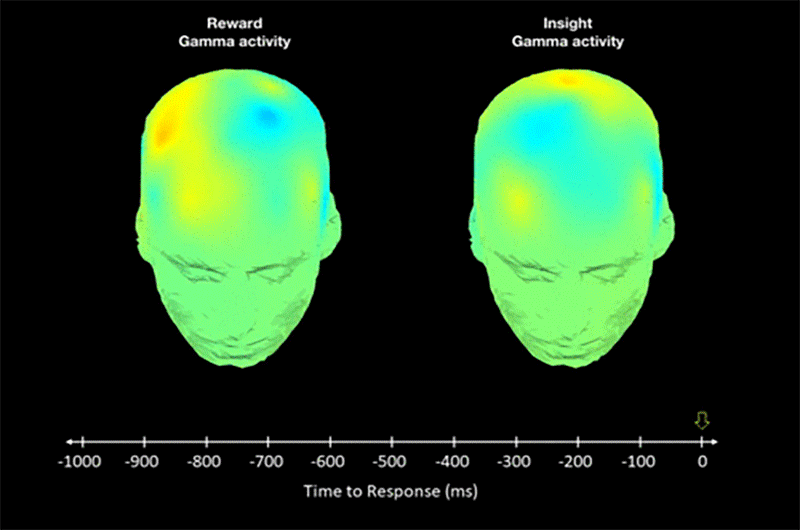
Insightful ideas can trigger orgasmic brain signals, finds study
New psychology study shows that some people have increased brain sensitivity for “aha moments”.
The researchers scanned brains of participants and noticed orgasm-like signals during insights.
The scientists think this evolutionary adaptation drives creation of science and culture.
If you found this article interesting or informative and you’d like to share it you can do so from the following link: https://m.facebook.com/story.php?story_fbid=569991543629194&id=383136302314720
Research shows how “aha moments” affect the brain and cause the evolution of creativity.
Analysis of the mutation dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 reveals the spread history and emergence of RBD mutant with lower ACE2 binding affinity
Via Harvard David A. Sinclair “The coronavirus is part bat & part human virus. A new study says the Frankenstein event happened well before its transmission to humans. Wait, what? Humans first infected bats?
The intermediate Frankenstein coronavirus has part human/part bat versions of the spike protein (the knobs on the outside of the virus & what COVID-19 vaccines target). Coronafrankenstein is formally called RaTG13, the name, rank & serial # of a horseshoe bat sample. If we gave bats coronavirus first, then people, including scientists, should stay away from bats especially if they don’t feel well. That’s why, as much as I like cats, I don’t like how they can catch it from us. It’s a potentially vicious cycle.
The new study says a mutation has changed the spike protein of an Indian strain of coronavirus that likely reduces its ability to transmit, but “raises the alarm that the ongoing vaccine development may become futile in future epidemics” like seasonal flu.”
Monitoring the mutation dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 is critical for the development of effective approaches to contain the pathogen. By analyzing 106 SARS-CoV-2 and 39 SARS genome sequences, we provided direct genetic evidence that SARS-CoV-2 has a much lower mutation rate than SARS. Minimum Evolution phylogeny analysis revealed the putative original status of SARS-CoV-2 and the early-stage spread history. The discrepant phylogenies for the spike protein and its receptor binding domain proved a previously reported structural rearrangement prior to the emergence of SARS-CoV-2. Despite that we found the spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 is particularly more conserved, we identified a mutation that leads to weaker receptor binding capability, which concerns a SARS-CoV-2 sample collected on 27th January 2020 from India. This represents the first report of a significant SARS-CoV-2 mutant, and raises the alarm that the ongoing vaccine development may become futile in future epidemic if more mutations were identified.