Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences‘Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP) have recently found two fossil repositories in the early Silurian strata of southwest Guizhou and Chongqing that are rewriting the “from fish to human” evolutionary story.
Four different papers describing their findings were recently published in the journal Nature.
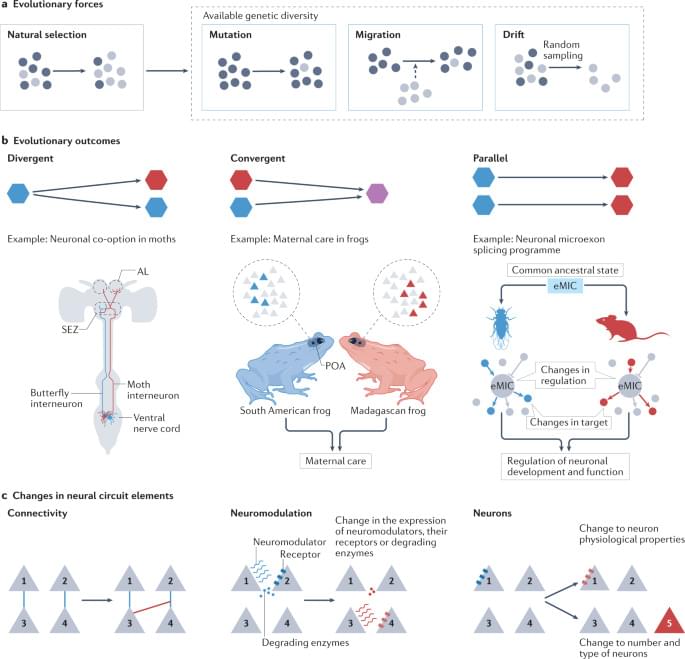
Humans are one of the 99.8% of species of extant vertebrates that are gnathostomes, or jawed vertebrates. The basic body plan and several key organs of humans can be traced back to the origin of gnathostomes. One of the most significant developments in the evolution of vertebrates is the emergence of jaws.