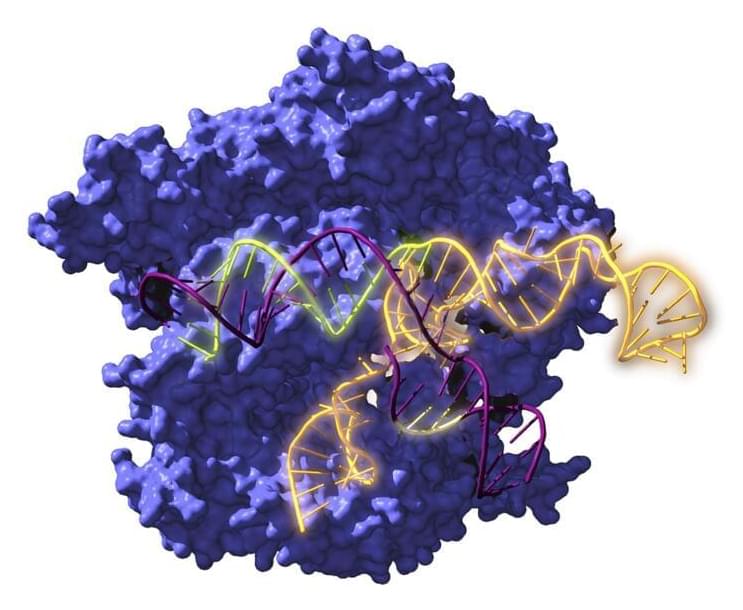
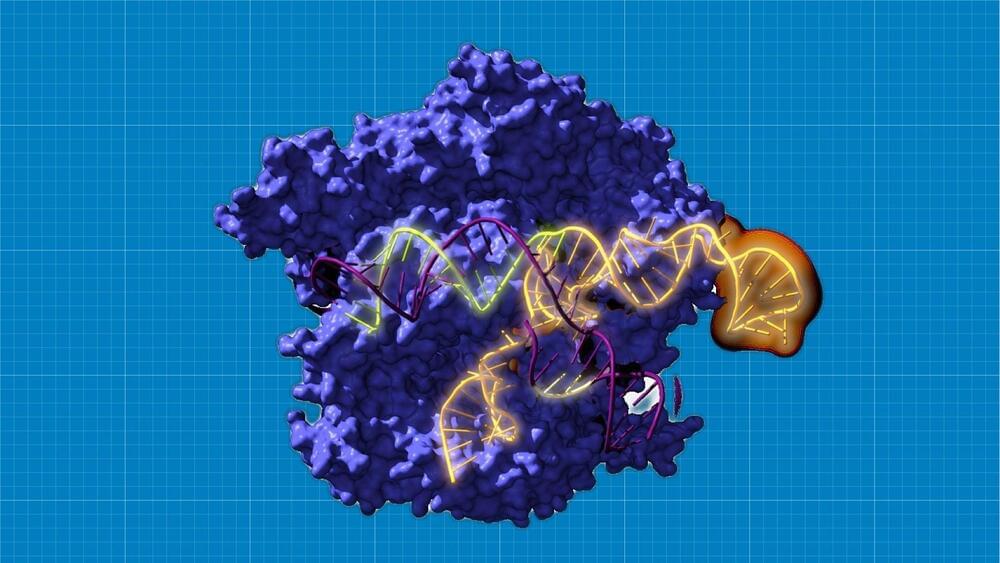
An international research group has for the first time reconstructed ancestors dating back 2.6 billion years of the well-known CRISPR-Cas system, and studied their evolution over time. The results suggest that the revitalized systems not only work, but are more versatile than current versions and could have revolutionary applications. Nature Microbiology has published the results of this research, which, in the opinion of the research team, “opens up new avenues for gene editing.”
The project, led by Ikerbasque research professor Rául Pérez-Jiménez of CIC nanoGUNE, involves teams from the Spanish National Research Council, the University of Alicante, the Rare Diseases Networking Biomedical Research Center (CIBERER), the Ramón y Cajal Hospital-IRYCIS and other national and international institutions.
The acronym CRISPR refers to the repeated sequences present in the DNA of bacteria and archaea (prokaryotic organisms). Among the repeats, these microorganisms harbor fragments of genetic material from viruses that infected their ancestors; that enables them to recognize a repeat infection and defend themselves by cutting the invaders’ DNA using Cas proteins associated with these repeats. It is a mechanism (CRISPR-Cas system) of antiviral defense. This ability to recognize DNA sequences is the basis of their usefulness, and they act as if they were molecular scissors. Nowadays CRISPR-Cas technology enables pieces of genetic material to be cut and pasted into any cell, so that it can be used to edit DNA.