In this very special episode of Jay Leno’s Garage, Jay is once again joined by Tesla’s Head of Design, Franz von Holzhausen who along with Tesla’s Vice President of Vehicle Engineering, Lars Moravy, bring with them this very special 2024 Tesla Cybertruck Foundation Series, aka, the CYBERBEAST!
Category: engineering – Page 72

Mathematics and Engineering
Advances in Civil Engineering Using Recycled Concrete Powder, Waste Glass Powder, and Plastic Powder to Improve the Mechanical Properties of Compacted Concrete: Cement Elimination Approach Erfan Najaf and Hassan Abbasi.
International Journal of Rotating Machinery Experimental and Numerical Studies of the Film Cooling Effectiveness Downstream of a Curved Diffusion Film Cooling Hole Fan Yang and Mohammad E. Taslim.
World’s first Generation IV nuclear reactor gets operational in China
The reactor uses tiny balls of fuel and heats gas to generate electricity.
In what can be termed a significant achievement in the development of next-generation nuclear reactor technology, China claims to have successfully commissioned the world’s first Generation IV commercial nuclear reactor.
The Shidao Bay Nuclear Power Plant’s HTR-PM high-temperature gas-cooled (HTGR) pebble-bed reactor, situated in Shidao Bay, Shandong Province, reportedly commenced operations earlier this month. According to China’s National Energy Administration (NEA), the feat was achieved following a 168-hour demonstration run on December 6.
The HTR-PM Demo project is a joint initiative led by Tsinghua University for R&D and primary components/systems design, China Huaneng Group Co. as the plant owner and operator, and China National Nuclear Co. (CNNC) serving as the Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) contractor and fuel manufacturer.
New way to charge batteries harnesses the power of ‘indefinite causal order’
Batteries that exploit quantum phenomena to gain, distribute and store power promise to surpass the abilities and usefulness of conventional chemical batteries in certain low-power applications. For the first time, researchers, including those from the University of Tokyo, take advantage of an unintuitive quantum process that disregards the conventional notion of causality to improve the performance of so-called quantum batteries, bringing this future technology a little closer to reality.
When you hear the word “quantum,” the physics governing the subatomic world, developments in quantum computers tend to steal the headlines, but there are other upcoming quantum technologies worth paying attention to. One such item is the quantum battery which, though initially puzzling in name, holds unexplored potential for sustainable energy solutions and possible integration into future electric vehicles. Nevertheless, these new devices are poised to find use in various portable and low-power applications, especially when opportunities to recharge are scarce.
At present, quantum batteries only exist as laboratory experiments, and researchers around the world are working on the different aspects that are hoped to one day combine into a fully functioning and practical application. Graduate student Yuanbo Chen and Associate Professor Yoshihiko Hasegawa from the Department of Information and Communication Engineering at the University of Tokyo are investigating the best way to charge a quantum battery, and this is where time comes into play. One of the advantages of quantum batteries is that they should be incredibly efficient, but that hinges on the way they are charged.
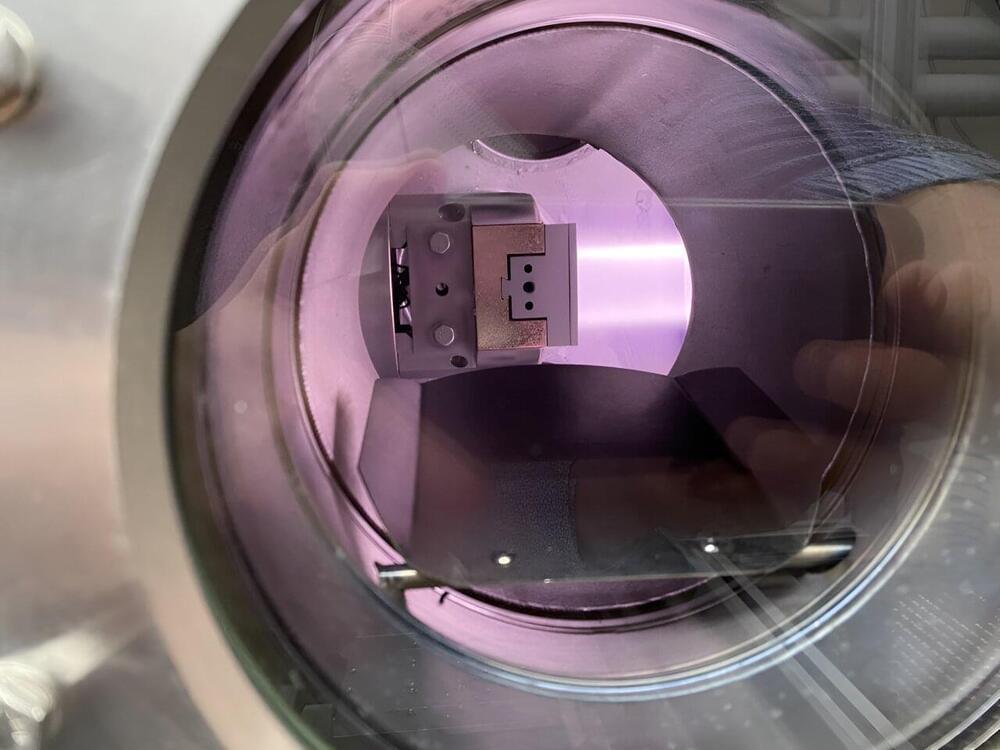

Newly developed material gulps down hydrogen, spits it out, protects fusion reactor walls
University of Wisconsin–Madison engineers have used a spray coating technology to produce a new workhorse material that can withstand the harsh conditions inside a fusion reactor.
The advance, detailed in a paper published recently in the journal Physica Scripta, could enable more efficient compact fusion reactors that are easier to repair and maintain.
“The fusion community is urgently looking for new manufacturing approaches to economically produce large plasma-facing components in fusion reactors,” says Mykola Ialovega, a postdoctoral researcher in nuclear engineering and engineering physics at UW–Madison and lead author on the paper. “Our technology shows considerable improvements over current approaches. With this research, we are the first to demonstrate the benefits of using cold spray coating technology for fusion applications.”
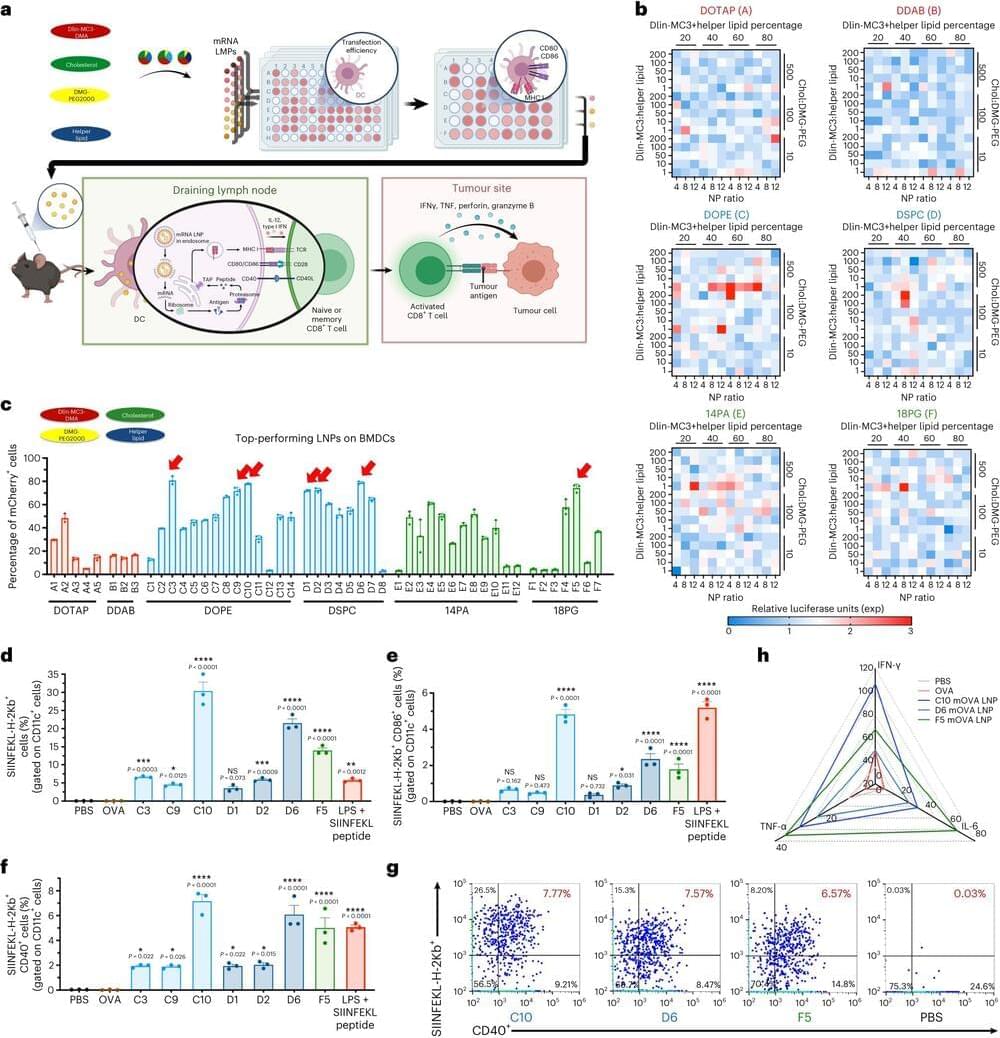
Nanoparticles amplify potential cancer vaccine power
Johns Hopkins researchers have identified minuscule particles that supercharge therapeutic cancer vaccines, which train the immune system to attack tumors. These new lipid nanoparticles—tiny structures made of fat—not only stimulate a two-pronged immune system response that enhances the body’s ability to fight cancer but also make vaccines more effective in targeting tumors.
“This research marks a pivotal turning point in our understanding of how lipid nanoparticles can be harnessed to optimize anticancer immunity,” said Hai-Quan Mao, director of Johns Hopkins’ Institute for NanoBioTechnology and professor in the Whiting School of Engineering’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering. “Our findings unlock new avenues for enhancing the efficacy of RNA-based treatments for cancer and infectious diseases.”
The team’s results appear in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
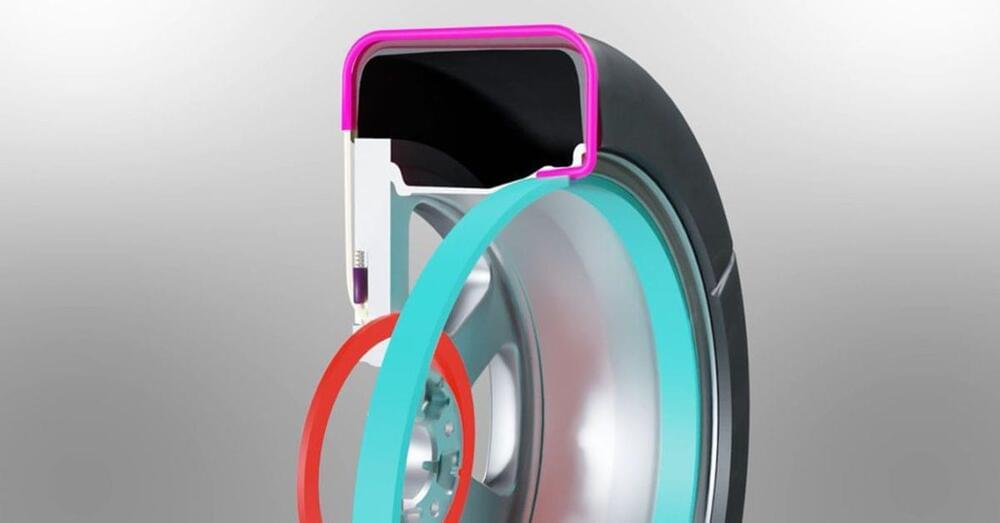

Hyundai and Kia boast another breakthrough, unveiling new tire with retractable ‘snow chains’
Weeks after introducing a potentially game-changing “Uni-wheel” drive system for EVs, Hyundai and Kia are showing off another next-generation technology to keep EV drivers safer during inclement weather. Today, Kia and Hyundai introduced a new snow chain-integrated tire that utilizes shape memory alloy modules inside the wheel. See how this incredible new tech works in the video below.
As EVs continue to saturate the global automotive market, their respective technologies are evolving to benefit consumers. Now more than ever, these electric vehicles drive farther, charge faster, and come equipped with exciting new technologies like vehicle-to-load (V2L) capabilities and Plug & Charge.
Hyundai Motor Group has been one of the early proponents of such technologies, featuring them in EVs atop its E-GMP platform. In fact, Hyundai and Kia especially have rolled out some exciting technologies throughout the electric mobility segment and allocated considerable funds to R&D to explore new engineering breakthroughs.
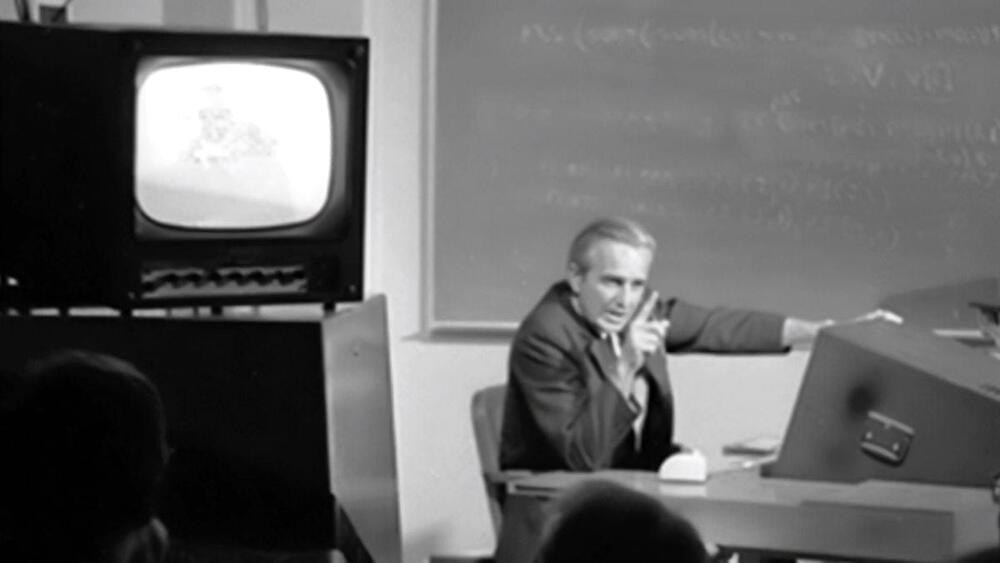

55 years ago, the ‘Mother of All Demos’ foresaw modern computing
Engelbart grew up on a small farm in Southeast Portland where his father operated a radio store.
He graduated from Franklin High School in 1942 and enrolled at Oregon State College, now called Oregon State University, to study electrical engineering.
When World War II interrupted his studies, he spent two years working as a Navy radio and radar technician in the Philippines.