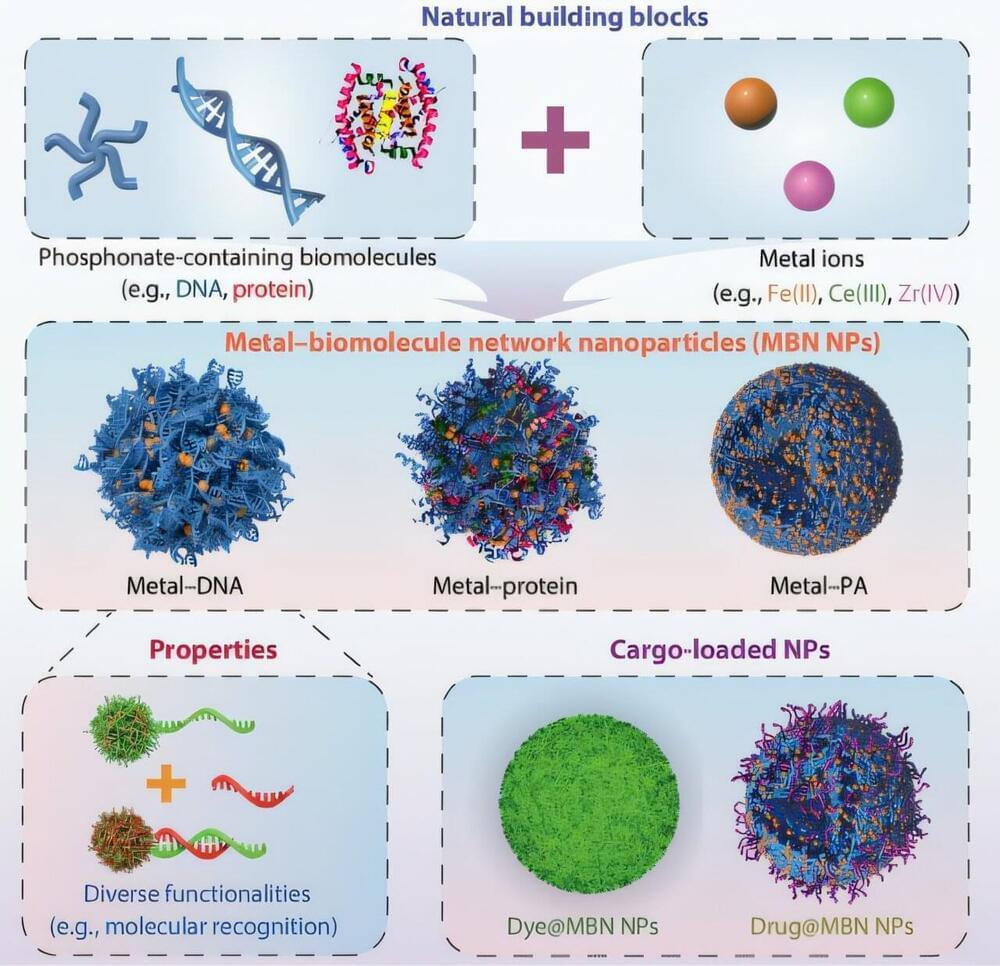
As fringe as the idea of solar radiation modification once was and as generally controversial as it remains, it is gaining some traction. Last spring, the University of Chicago hired David Keith, one of the most visible proponents of solar geoengineering, to lead a new Climate Systems Engineering initiative, committing to at least 10 new faculty hires for the program. The group will study solar geoengineering, as well as other kinds of Earth system modifications aimed at addressing the climate crisis.
With this initiative, the University of Chicago is attempting to position itself as the place for serious scientific consideration of the logistics and implications of Earth system interventions aimed at reversing or counteracting climate change. It is part of a broader university effort to become a global leader in the climate and energy space.
Previously, Keith was at Harvard University, where he helped launch the Solar Geoengineering Research Program. After repeated delays and years of controversy, Harvard recently canceled a small-scale outdoor geoengineering experiment that Keith helped plan. That experiment would have involved launching a high-altitude balloon, releasing fine particles of calcium carbonate into the stratosphere, and then sending the balloon back through the cloud to monitor how those particles disperse and interact within the atmosphere, and with solar radiation.