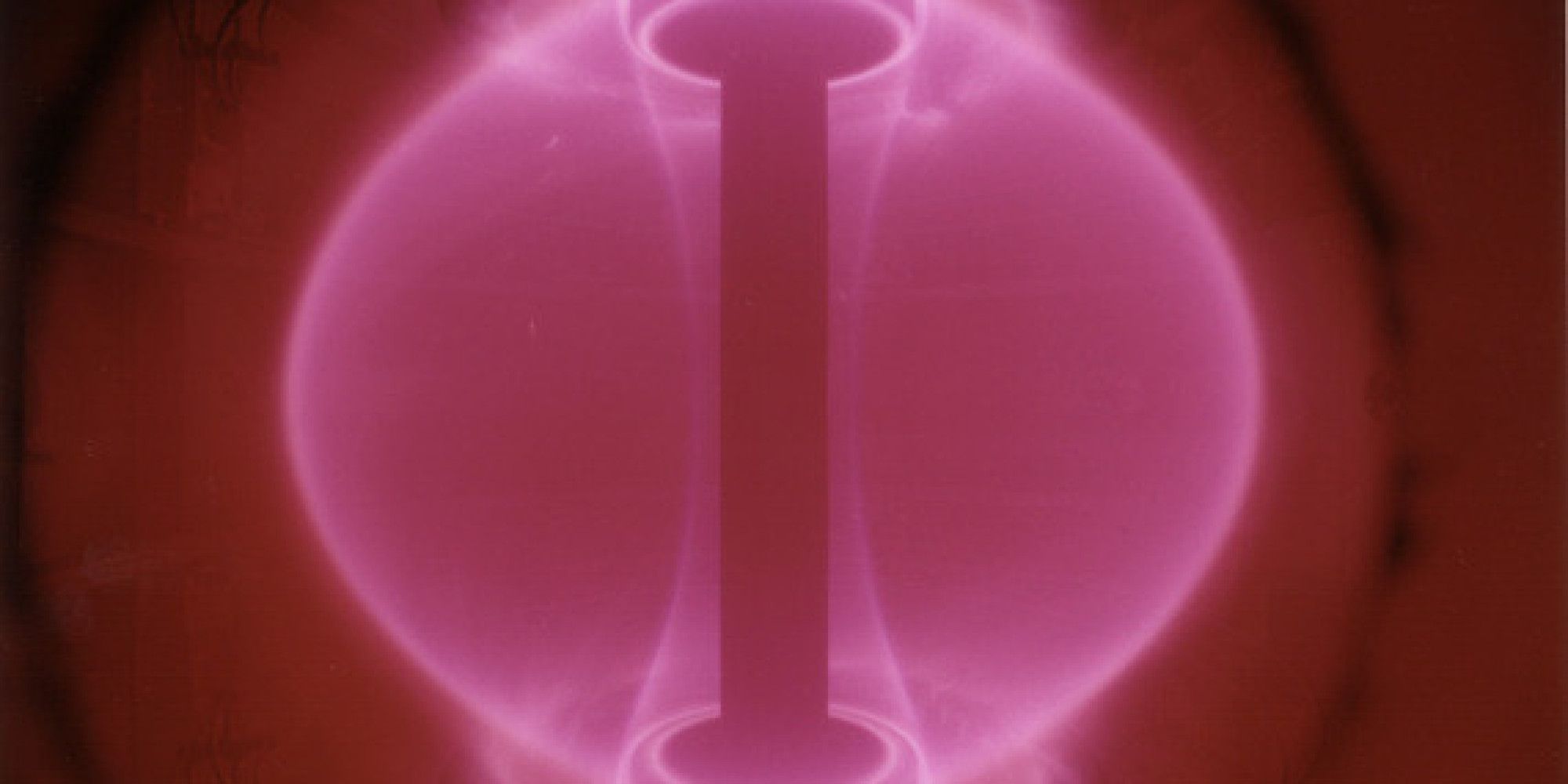
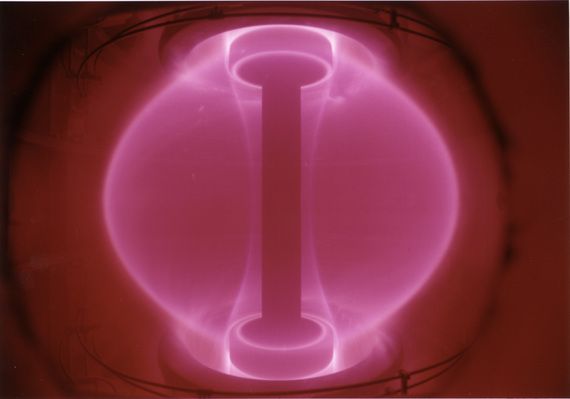
The world needs abundant, clean energy. Nuclear fusion — with no CO2 emissions, no risk of meltdown and no long-lived radioactive waste — is the obvious solution, but it is very hard to achieve.
The challenge is that fusion only happens in stars, where the huge gravitational force creates pressures and temperatures so intense that usually repulsive particles will collide and fuse; hence “fusion”. On Earth we need to create similar conditions, holding a hot, electrically-charged plasma at high enough pressure for long enough for fusion reactions to occur. The scientific and engineering challenges behind putting a star in a box are large, to say the least. Without proper confinement of the plasma, the reaction would stop. The plasma must be isolated from the walls of the reactor — a feat that can be performed most effectively by magnets. The most advanced machine for this purpose is the ‘tokamak’.