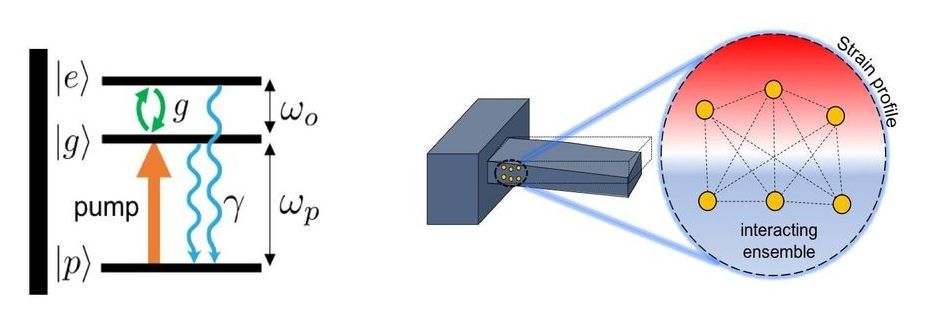
Center for Nanoscale Materials researchers present a quantum model for achieving ground-state cooling in low frequency mechanical resonators and show how cooperativity and entanglement are key factors to enhance the cooling figure of merit.
A resonator with near-zero thermal noise has better performance characteristics in nanoscale sensing, quantum memories, and quantum information processing applications. Passive cryogenic cooling techniques, such as dilution refrigerators, have successfully cooled high-frequency resonators but are not sufficient for lower frequency systems. The optomechanical effect has been applied successfully to cool low-frequency systems after an initial cooling stage. This method parametrically couples a mechanical resonator to a driven optical cavity, and, through careful tuning of the drive frequency, achieves the desired cooling effect. The optomechanical effect is expanded to an alternative approach for ground-state cooling based on embedded solid-state defects. Engineering the atom-resonator coupling parameters is proposed, using the strain profile of the mechanical resonator allowing cooling to proceed through the dark entangled states of the two-level system ensemble.