O,.o.
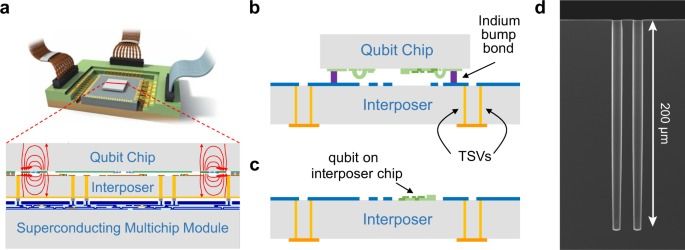
As superconducting qubit circuits become more complex, addressing a large array of qubits becomes a challenging engineering problem. Dense arrays of qubits benefit from, and may require, access via the third dimension to alleviate interconnect crowding. Through-silicon vias (TSVs) represent a promising approach to three-dimensional (3D) integration in superconducting qubit arrays—provided they are compact enough to support densely-packed qubit systems without compromising qubit performance or low-loss signal and control routing. In this work, we demonstrate the integration of superconducting, high-aspect ratio TSVs—10 μm wide by 20 μm long by 200 μm deep—with superconducting qubits. We utilize TSVs for baseband control and high-fidelity microwave readout of qubits using a two-chip, bump-bonded architecture. We also validate the fabrication of qubits directly upon the surface of a TSV-integrated chip. These key 3D-integration milestones pave the way for the control and readout of high-density superconducting qubit arrays using superconducting TSVs.