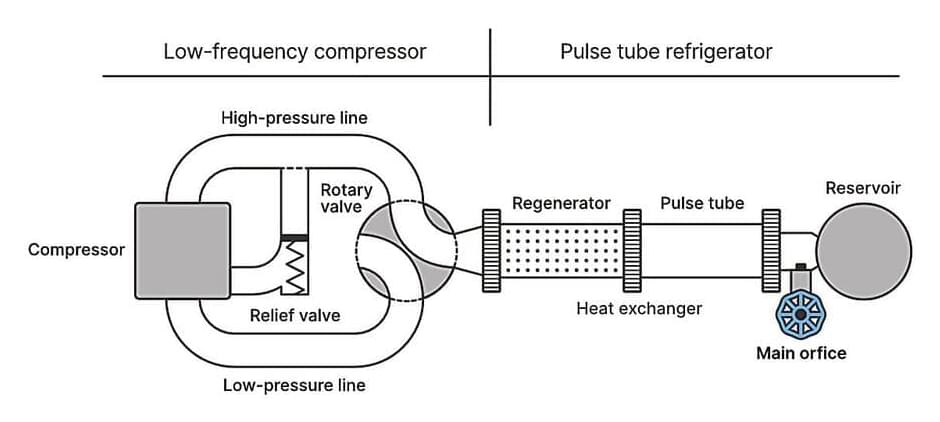
Imagine you’re in a car, pedal to the metal, racing down the highway, but no matter how hard you push, you can’t surpass the speed of the car next to you, which is effortlessly cruising at the same pace. Now, replace the car with light, and you have a real cosmic conundrum: why can’t anything go faster than light?
Back in 1905, Albert Einstein turned the world of physics upside down with his theory of relativity. This wasn’t just about E=mc² or the bending of space-time; it was about something that touches everything we do: the speed of light, which is roughly 299,792 kilometers per second. According to relativity, no matter how fast you’re moving towards or away from a light source, you will always measure the speed of light at the same constant velocity.
This leads us to a mind-boggling realization. As objects speed up, their mass increases. At the speed of light, their mass would become infinite. So, to move an object at the speed of light would require infinite energy, which, quite frankly, is impossible with our current understanding of physics.