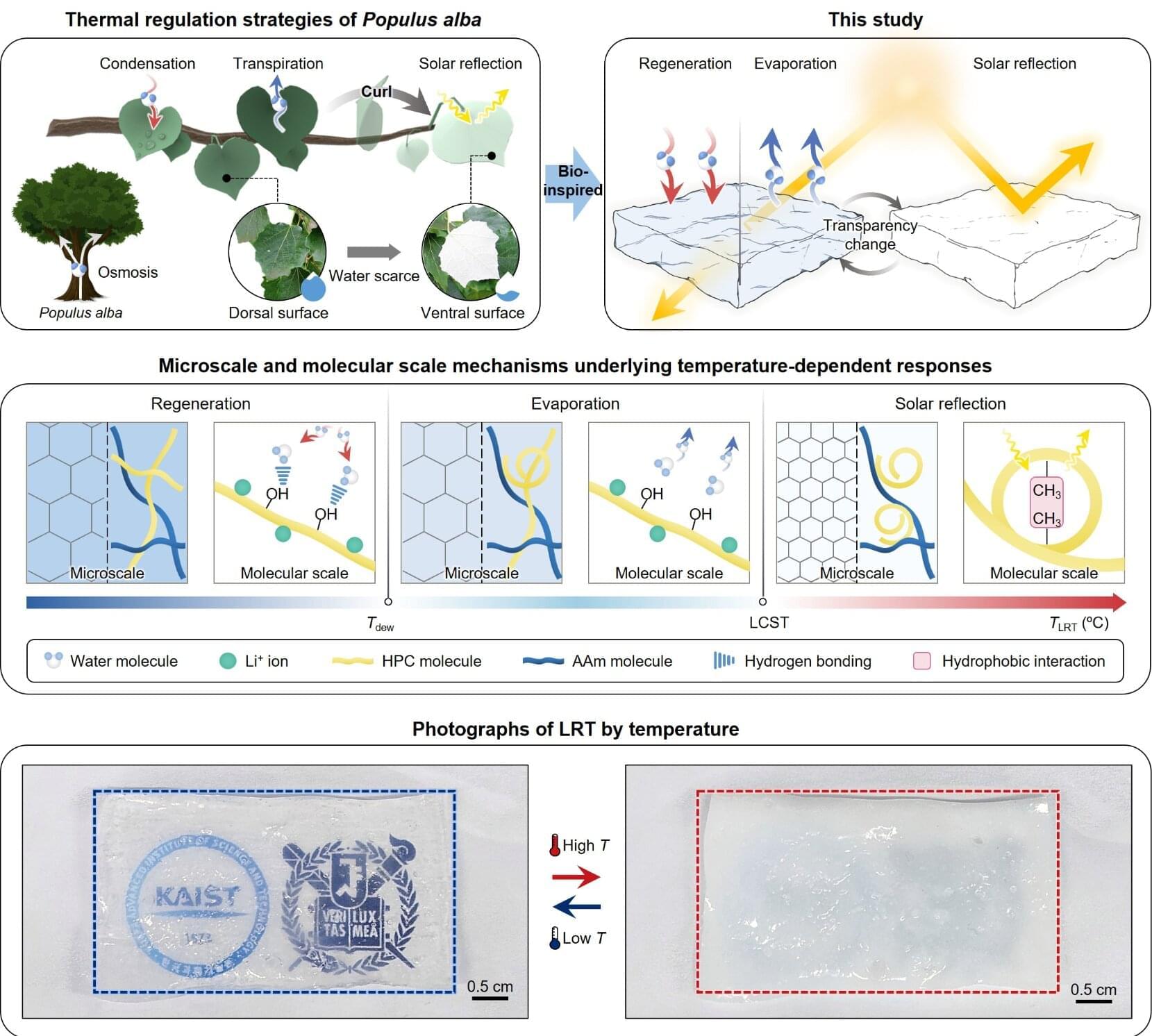
The poplar (Populus alba) has a unique survival strategy: when exposed to hot and dry conditions, it curls its leaves to expose the ventral surface, reflecting sunlight, and at night, the moisture condensed on the leaf surface releases latent heat to prevent frost damage. Plants have evolved such intricate mechanisms in response to dynamic environmental fluctuations in diurnal and seasonal temperature cycles, light intensity, and humidity, but there have been few instances of realizing such a sophisticated thermal management system with artificial materials.
Now, a KAIST research team has developed an artificial material that mimics the thermal management strategy of the poplar leaf, significantly increasing the applicability of power-free, self-regulating thermal management technology in applications such as building facades, roofs, and temporary shelters. The paper is published in the journal Advanced Materials.
The research team led by Professor Young Min Song of the School of Electrical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Dae-Hyeong Kim’s team at Seoul National University, has developed a flexible hydrogel-based “Latent-Radiative Thermostat (LRT)” that mimics the natural heat regulation strategy of the poplar leaf.