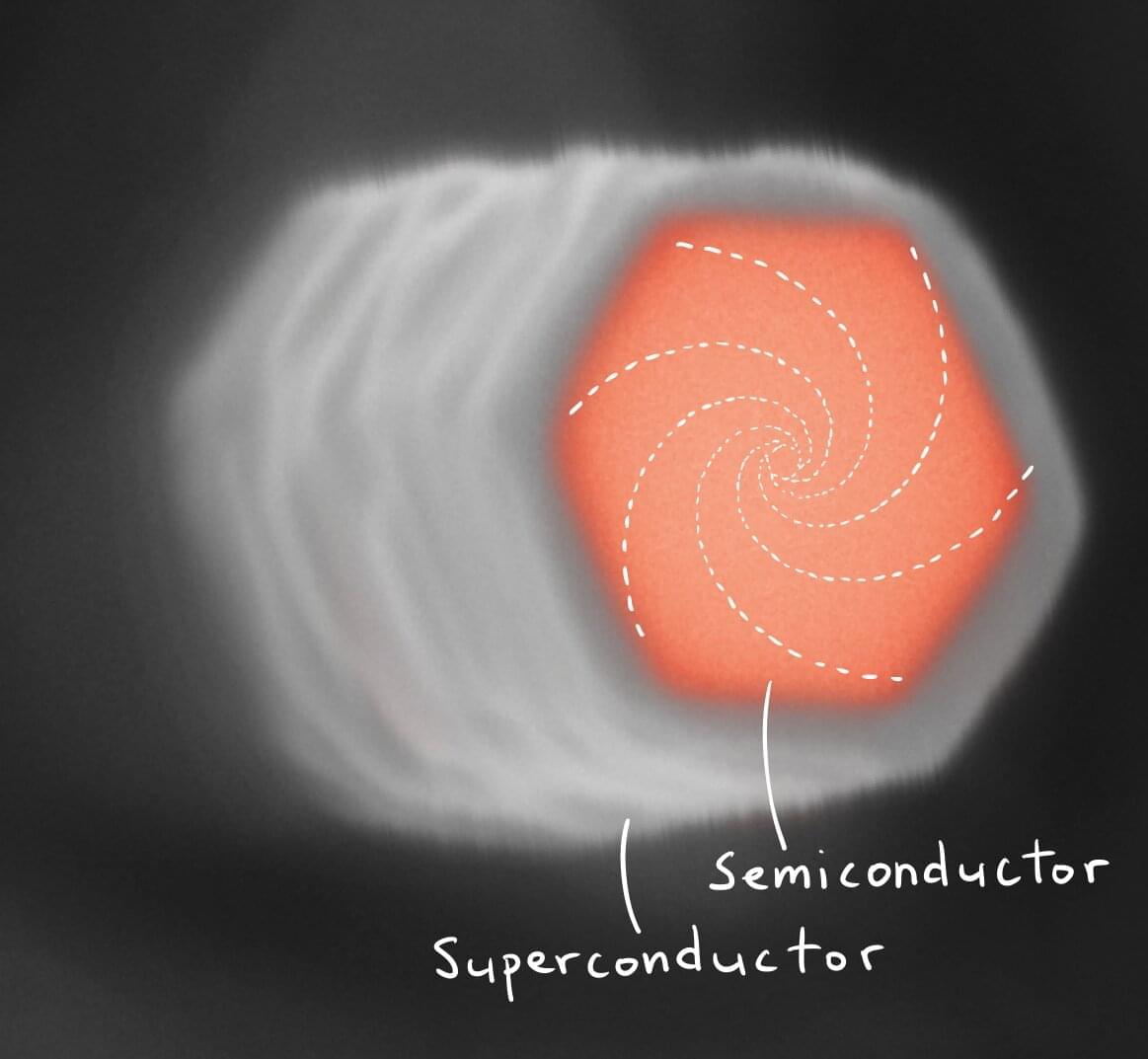
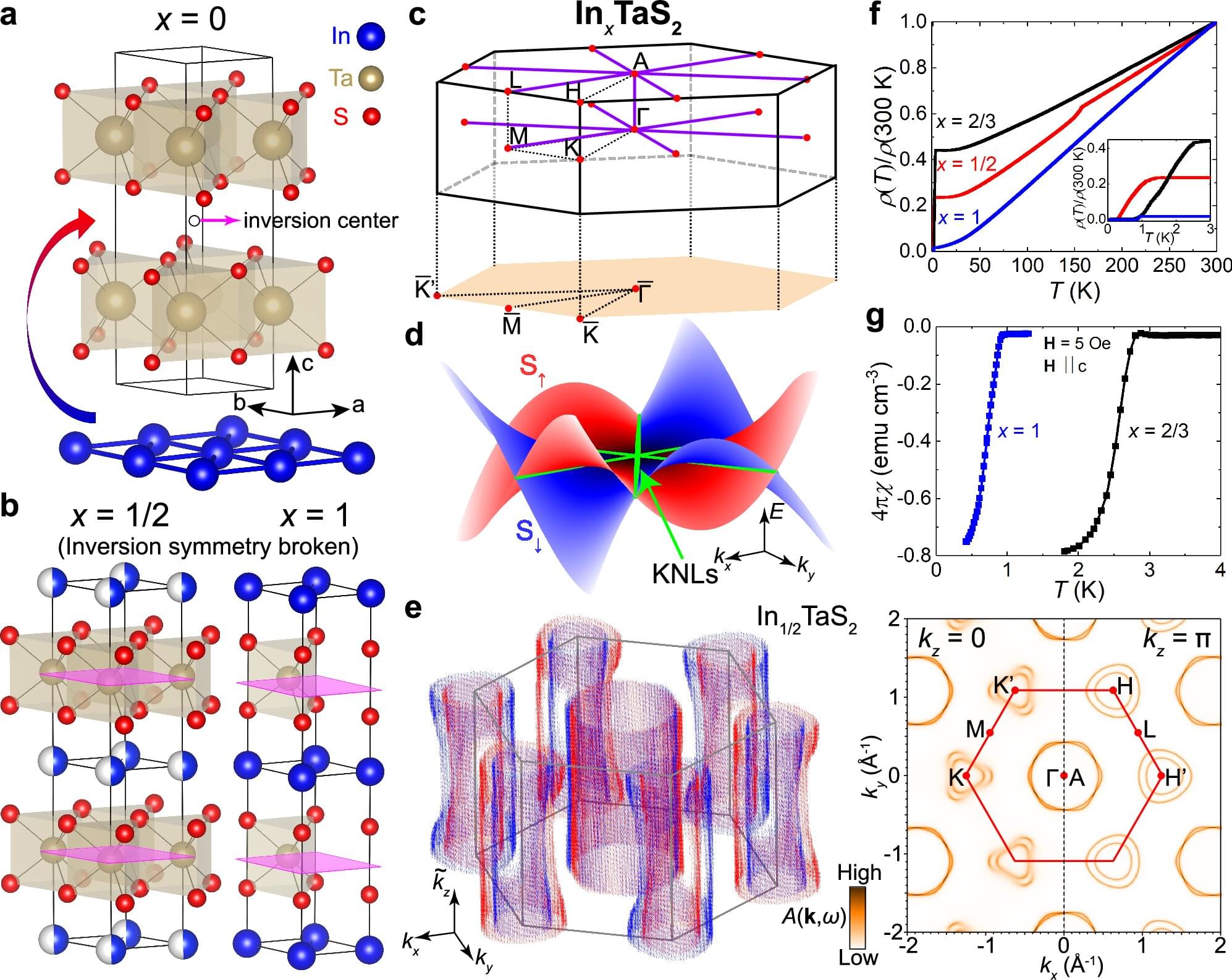
Researchers from the Niels Bohr Institute, University of Copenhagen, have created a novel pathway into the study of the elusive quantum states in superconducting vortices. The existence of these was flaunted in the 1960s, but has remained very difficult to verify directly because those states are squeezed into energy scales smaller than one can typically resolve in experiments.
The result was made possible by a combination of ingenuity and the expanding research in designer materials created in the labs at the Niels Bohr Institute. It is now published in Physical Review Letters.