Scientists can now snap ultra-powerful laser pulses in one shot. RAVEN reveals distortions instantly, unlocking breakthroughs in energy, acceleration, and physics.


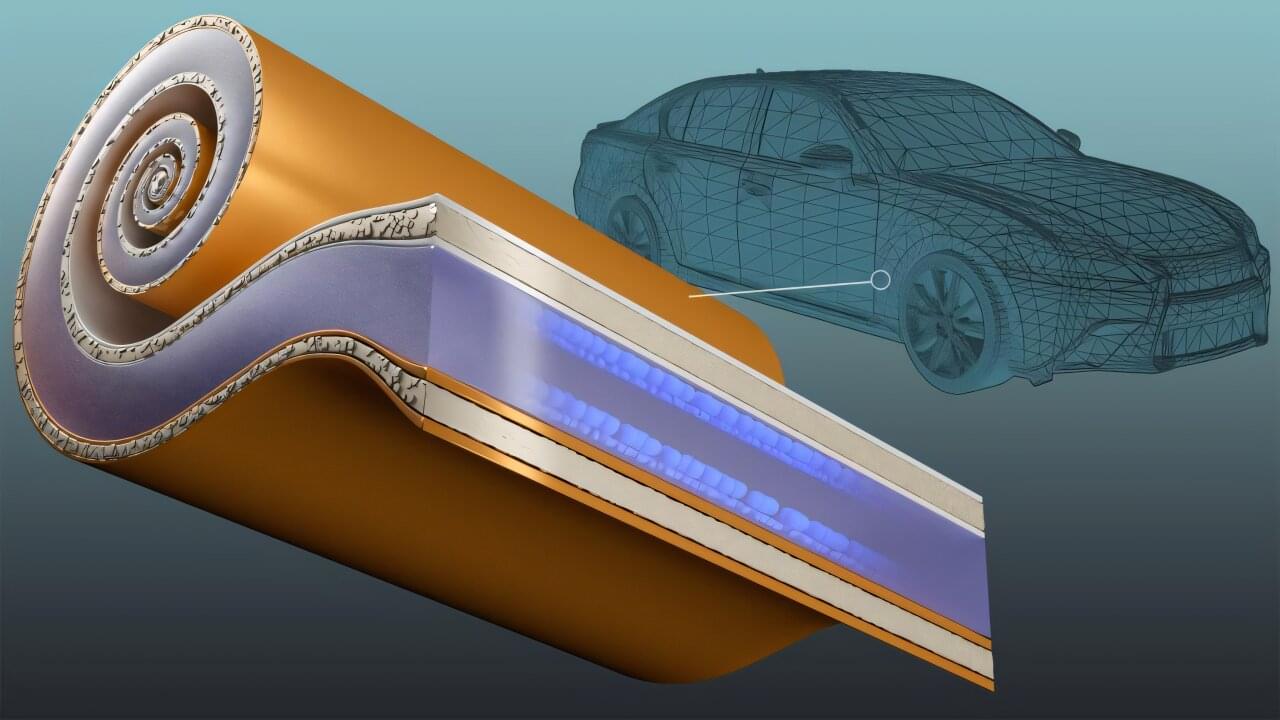
Strengthening the competitiveness of the American transportation industry relies on developing domestically produced electric vehicle batteries that enable rapid charging and long-range performance. The energy density needed to extend driving distance can, however, come at the expense of charging rates and battery life.
By integrating a new type of current collector, which is a key battery component, researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have demonstrated how to manufacture a battery with both superior energy density and a lasting ability to handle extreme fast charging. This enables restoring at least 80% of battery energy in 10 minutes. By using less metal, particularly high-demand copper, the technology also relieves strain on U.S. supply chains.
“This provides a significant savings on near-critical materials, because much less copper and aluminum are needed,” said lead researcher Georgios Polyzos. “At the same time, this will greatly enhance the energy density achievable with a 10-minute charge.”

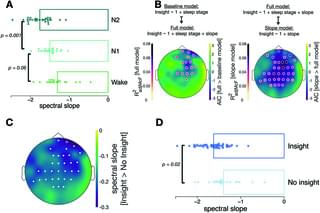
Sleep supports memory consolidation, but can it also facilitate memory reorganization? This study reveals that N2 sleep, but not N1 sleep during a nap, increases the likelihood of having an ‘aha’ moment about a previous decision-making task, and that spectral slopes of EEG power spectra predict future insights.
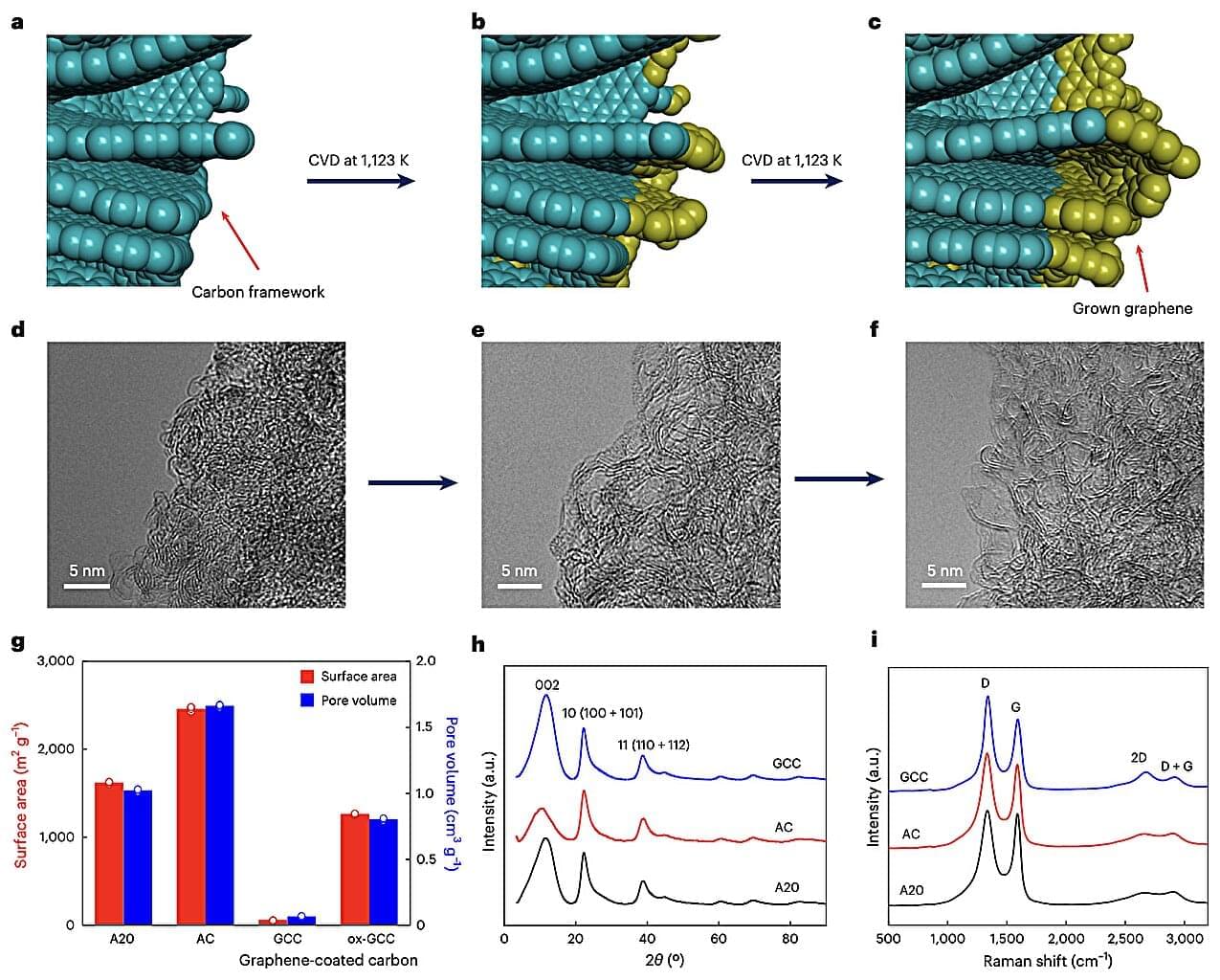
Methane (CH4), one of the most abundant natural gases on Earth, is still widely used to power several buildings and to fuel some types of vehicles. Despite its widespread use, storing and transporting this gas safely remains challenging, as it is highly flammable and requires compression at high pressures of around 25 megapascals (MPa).
Most existing solutions to store CH4 at high pressures rely on expensive equipment and infrastructure, such as reinforced tanks, specialized valves and advanced safety systems. In addition, damage to this equipment or its malfunction that prompts leakage of gas can lead to explosions, fires and other serious accidents.
Some researchers have thus been trying to devise alternative strategies to store and transport CH4 that are both safer and more cost-effective. One of these recently proposed methods, known as absorbed natural gas (ANG), entails the use of nanoporous materials, solid materials containing tiny pores in which gas molecules could be trapped at moderate pressures.
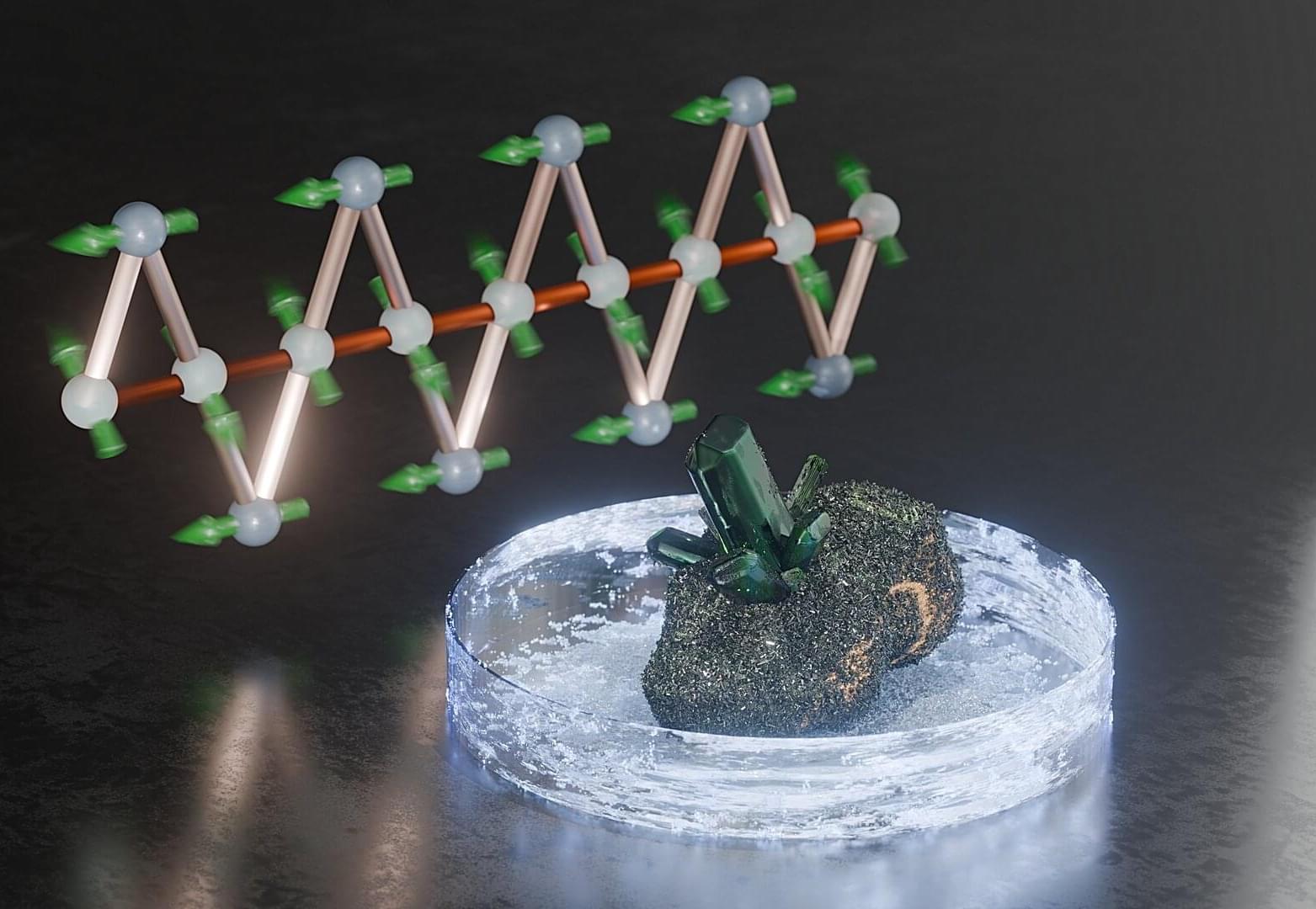
Natural crystals fascinate with their vibrant colors, their nearly flawless appearance and their manifold symmetrical forms. But researchers are interested in them for quite different reasons: Among the countless minerals already known, they always discover some materials with unusual magnetic properties.
One of these is atacamite, which exhibits magnetocaloric behavior at low temperatures—that is, the material’s temperature changes significantly when it is subjected to a magnetic field. A team headed by TU Braunschweig and the HZDR has now investigated this rare property. In the long term, the results, now published in Physical Review Letters, could help to develop new materials for energy-efficient magnetic cooling.
The emerald-green mineral atacamite, named for the place it was first found, the Atacama Desert in Chile, gets its characteristic coloring from the copper ions it contains. These ions also determine the material’s magnetic properties: they each have an unpaired electron whose spin gives the ion a magnetic moment —comparable to a tiny needle on a compass.
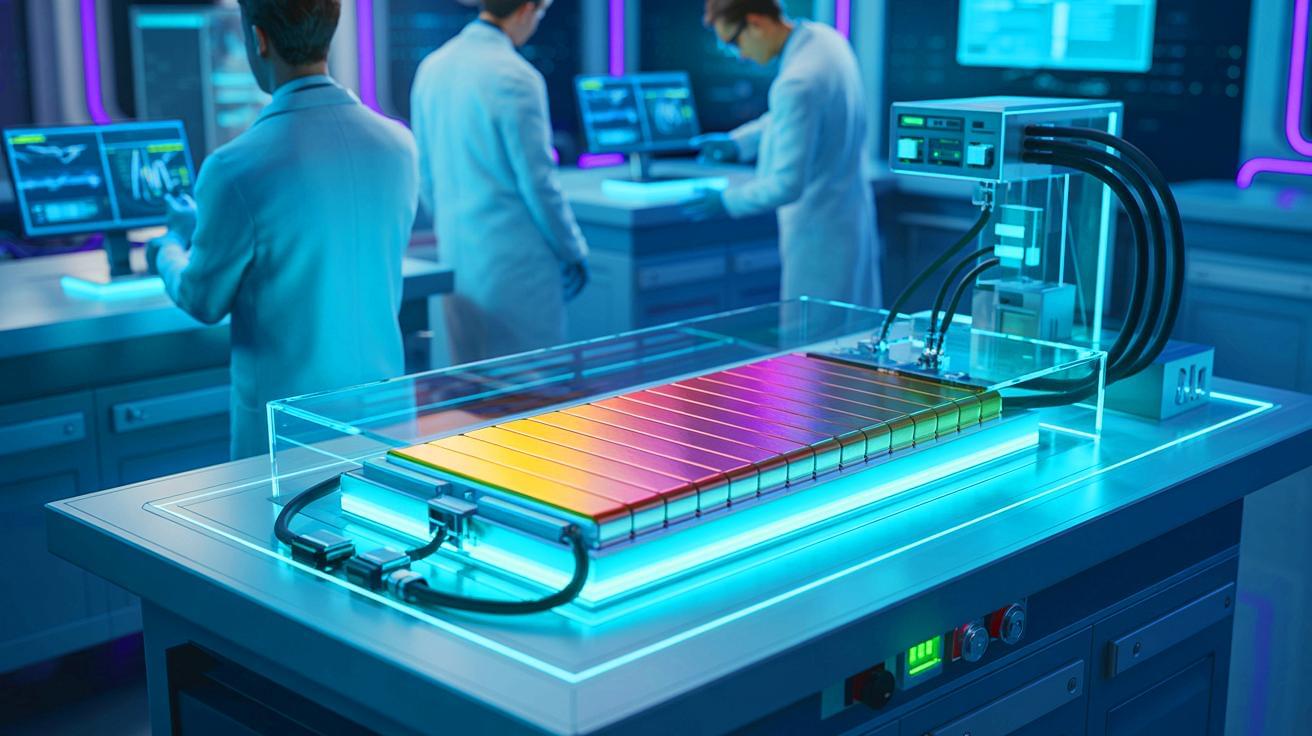



IN A NUTSHELL 🔋 Researchers in South Korea developed a cost-effective MoS2 thin film that boosts battery lifespan sevenfold. 💡 The innovation uses molybdenum disulfide to prevent dendrite formation, enhancing the safety and performance of anode-free solid-state batteries. 🌟 This breakthrough offers a scalable, affordable alternative to noble metals, promising to accelerate the commercialization of