This Star Trek-like ‘tricorder’ can help you understand what things are made of.
Category: electronics – Page 96
Quantum sensors for high-precision magnetometry of superconductors
Quantum Sensors enables precise imaging of magnetic fields of superconductors.
Scientists at the Swiss Nanoscience Institute and the Department of Physics at the University of Basel have developed a new method that has enabled them to image magnetic fields on the nanometer scale at temperatures close to absolute zero for the first time. They used spins in special diamonds as quantum sensors in a new kind of microscope to generate images of magnetic fields in superconductors with unrivaled precision. In this way the researchers were able to perform measurements that permit new insights in solid state physics, as they report in Nature Nanotechnology.
Researchers in the group led by the Georg-H. Endress Professor Patrick Maletinsky have been conducting research into so-called nitrogen-vacancy centers (NV centers) in diamonds for several years in order to use them as high-precision sensors. The NV centers are natural defects in the diamond crystal lattice. The electrons contained in the NVs can be excited and manipulated with light, and react sensitively to electrical and magnetic fields they are exposed to. It is the spin of these electrons that changes depending on the environment and that can be recorded using various measurement methods.
Maletinsky and his team have managed to place single NV spins at the tips of atomic force microscopes to perform nanoscale magnetic field imaging. So far, such analyses have always been conducted at room temperature. However, numerous fields of application require operation at temperatures close to absolute zero. Superconducting materials, for example, only develop their special properties at very low temperatures around −200°C. They then conduct electric currents without loss and can develop exotic magnetic properties with the formation of so-called vortices.

Sony Patents Own Contact Lens Camera
I forgot Sony in the list of contact lens patents. Sony’s new camera contact patent. So, we have Google, Huawei, and Samsung with AR and CPU patents and Sony’s patents on the camera. Waiting for Apple and my favorite Microsoft’s announcements.
Sony has joined Google and Samsung in the world of contact lens camera patents, Sony’s version also has zoom and aperture control built in.
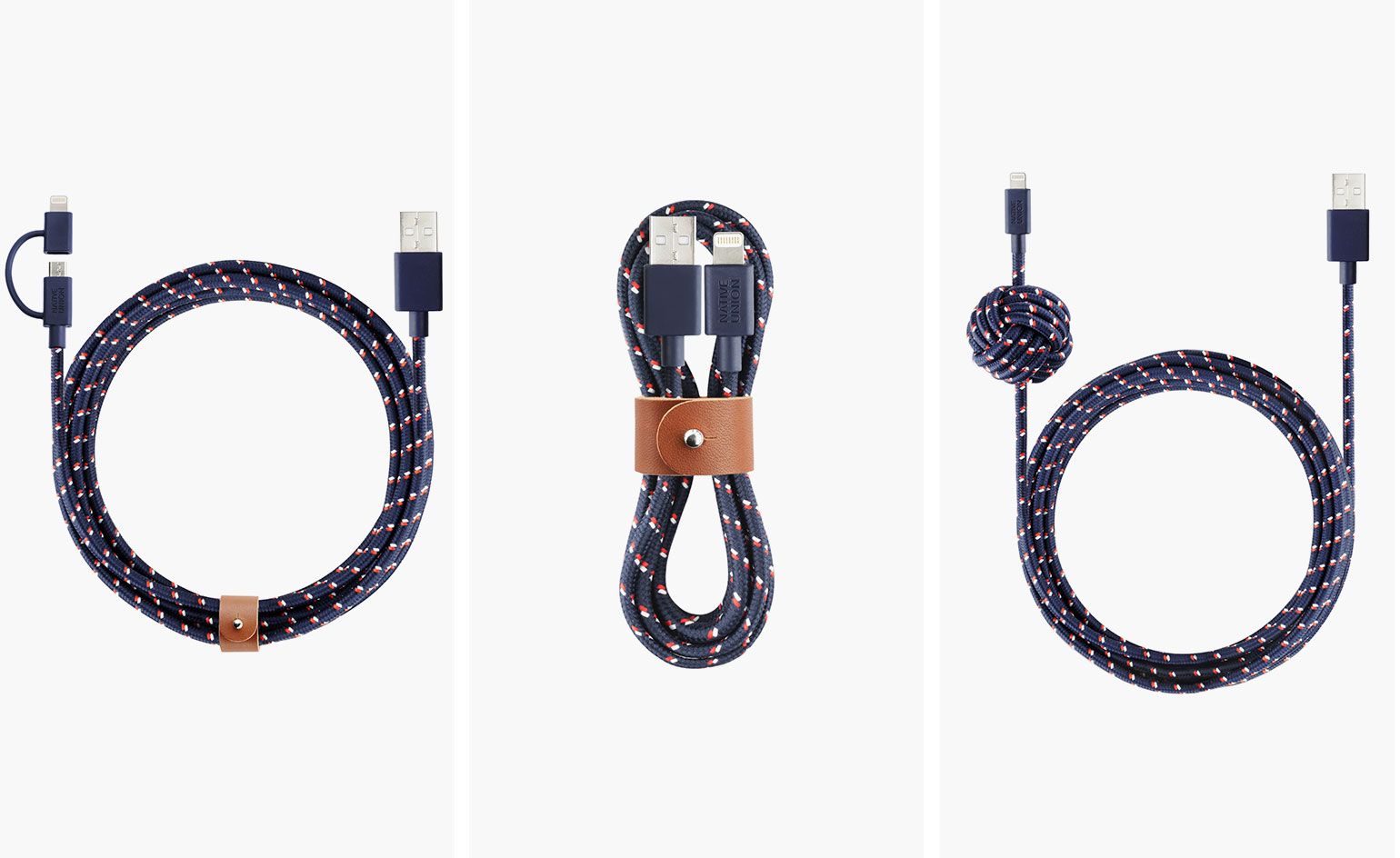

Knot your typical tech accessories: Native Union’s new cable range — By Sam Clark | Wallpaper
“These cables, whilst stylish, still put a large emphasis on practicality – having been crafted from durable, braided nylon designed to withstand wear and tear. The range also goes further, the company professes, by solving everyday problems such as ‘forgetting your cable, running out of battery on-the-go, or straining to use your device while charging’.”
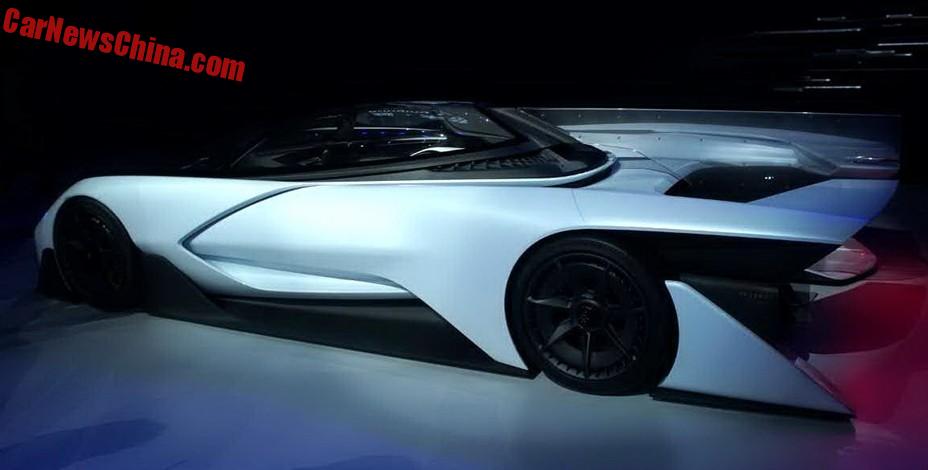

China’s Jia Yueting intends to outmuscle Musk — Taking on Tesla
LeEco is known as the “Netflix of China” due to its very popular video streaming service, but the conglomerate also has interests in a much wider range of sectors including smartphones, TVs and electric vehicles.
Ding Lei, LeEco’s auto chief and a former top official at General Motors’ China venture with SAIC Motor, says part of LeEco’s advantage in tomorrow’s auto industry is that it carries no baggage from today’s.
This, the man said, is the future of cars, and the Chinese consumer electronics company LeEco is going to make that future a reality.

Blockchain Smart Contracts: A Hyper-Deflationary Force for Health Care Delivery
Blockchaining coming to healthcare digital services.
Blockchain and digital health services could be a perfect match for each other across a variety of applications. From distributed interoperable health records to proof of adherence for medication, the healthcare industry is ripe for digital innovation. More generally, technology is a hyper-deflationary force, and this could be particularly effective in delivering quality health care through more effective channels such as mobile apps.
Investments in the digital health space have increased significantly in the past two years. This is largely possible because of improved low-power sensors and user-friendly cloud platforms that interface with those hardware devices. The Rock Health Funding Database shows a $4.5 billion increase in venture funding in digital health from 2014 to 2015.
Smart contract technology is built on top of virtual currencies such as Bitcoin and is a hallmark of “Bitcoin 2.0” platforms. Blockchain is the fundamental infrastructure needed for Bitcoin transactions to work, and an enabling technology for the next generation of asset-based platforms.
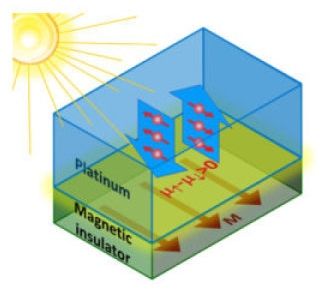
The light stuff: A brand-new way to produce electron spin currents
With apologies to Isaac Asimov, the most exciting phase to hear in science isn’t “Eureka,” but “That’s funny…”
A “that’s funny” moment in a Colorado State University physics lab has led to a fundamental discovery that could play a key role in next-generation microelectronics.
Publishing in Nature Physics April 25, the scientists, led by Professor of Physics Mingzhong Wu in CSU’s College of Natural Sciences, are the first to demonstrate using non-polarized light to produce in a metal what’s called a spin voltage — a unit of power produced from the quantum spinning of an individual electron. Controlling electron spins for use in memory and logic applications is a relatively new field called spin electronics, or spintronics, and the subject of the 2007 Nobel Prize in Physics.
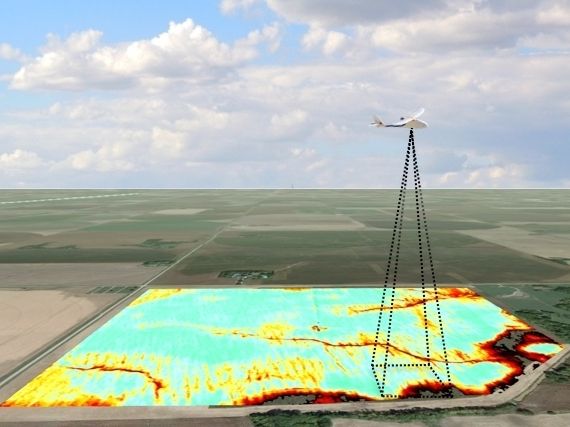

SLANTRANGE Secures $5M to Scale Sensor and Analytics Technology for Agricultural Drones
Nice
SAN DIEGO, Calif.—(BUSINESS WIRE)— SLANTRANGE, pioneers of a smarter approach to aerial remote sensing and analytics for agriculture, today announced its $5 million Series A equity financing from a consortium of investors led by The Investor Group, a leading San Diego based investment firm. The funding will accelerate the development and scaling of SLANTRANGE’s proprietary drone sensor and analytics technology to help farmers improve operations amid a rapidly transforming business landscape.
“Farmers are continually seeking ways to improve crop yields with minimal risk. Drones offer an exciting solution, but historically haven’t been built for the precise needs of the agriculture industry,” said Mike Ritter, CEO of SLANTRANGE. “SLANTRANGE delivers on the promise of drones with an intelligence system that combines hardware and software to bring farmers crop information they need to make better operational decisions. This investment enables us to scale our technology and team to meet the soaring demand we’re seeing from the agricultural community in the United States and beyond.”
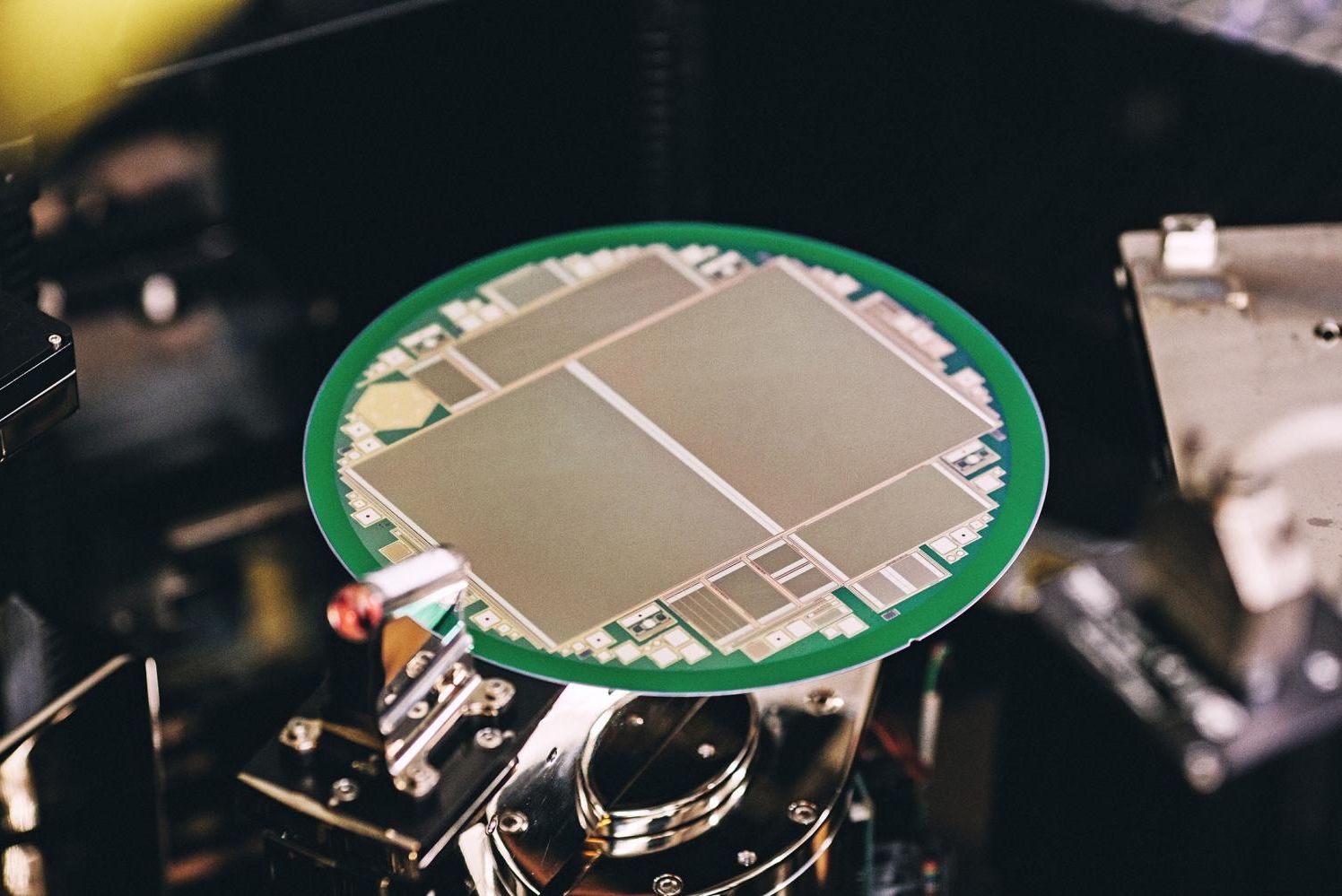
At CERN, eight-inch sensor chips from Infineon could reveal the mysteries of the universe
Ninety-five percent of the universe is still considered unexplored. Scientists at CERN, the world’s largest particle physics research center, located in Geneva, are working on solving these mysteries. In May 2012, researchers there discovered the so-called Higgs Boson, whose prediction won Peter Higgs and François Englert the Nobel prize in physics. One of the things CERN scientists are researching at the moment is dark matter: Although it may well have five times the mass of visible matter in the universe, this extent can only be indirectly proved. With a bit of luck, CERN will also succeed in generating dark matter.
A unique sensor chip can contribute to proving the existence of dark matter: It is eight inches or 15 cm x 10 cm and was developed jointly by Infineon Technologies Austria and the Austrian Academy of Sciences’ Institute of High Energy Physics (HEPHY). Tens of thousands of these silicon components could be used at CERN in the near future. They are not only more economical to produce than previous sensors, which measured up to six inches. The components also stand up better to constant radiation and thus age slower than the previous generation. Planned experiments will scarcely be possible without resistant sensors.
The experiments at CERN are analyzing the structure of matter and the interplay among elementary particles: Protons are accelerated almost to the speed of light and then made to collide, giving rise to new particles whose properties can be reconstructed with various detectors. “In particle physics and cosmology, there are many questions that are still open and to which mankind still has no answer,” says Dr. Manfred Krammer, head of the Experimental Physics Department at CERN. “To make new advances in these areas, we need a new generation of particle sensors. Cooperation with high-tech companies like Infineon allows us to develop the technologies we need for that.”

Why precision medicine is important for our future
We definitely need precision medicine. If you don’t believe it is worth that; then I have a few widows & widowers who you should speak to; I have parents that you should speak with; I have a list of sisters & brothers that you should speak with; and I have many many friends (including me) that you should speak with about how we miss those we love because things like precision medicine wasn’t available and could have saved their lives.
Precision medicine is the theme for the 10th annual symposium of the Johns Hopkins Institute for Nano Biotechnology, Friday, April 29, 2016 at 9 a.m. in the Owens Auditorium at the School of Medicine. This year’s event is cohosted by Johns Hopkins Individualized Health Initiative (also known as Hopkins in Health) and features several in Health affiliated speakers.
By developing treatments that overcome the limitations of the one-size-fits-all mindset, precision medicine will more effectively prevent and thwart disease. Driven by data provided from sources such as electronic medical records, public health investigations, clinical studies, and from patients themselves through new point-of-care assays, wearable sensors and smartphone apps, precision medicine will become the gold standard of care in the not-so-distant future. Before long, we will be able to treat and also prevent diseases such as diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, heart disease, and cancer with regimes that are tailor-made for the individual.
Hopkins in Health is a signature initiative of Johns Hopkins University’s $4.5 billion Rising to the Challenge campaign is a collaboration among three institutions: the University, the Johns Hopkins Health System, and the Applied Physics Laboratory. These in Health researchers combine clinical, genetic, lifestyle, and other data sources to create innovative tools intended to improve decision-making in the prevention and treatment of a range of conditions, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, autoimmune disorders, and infectious disease. The goal is to “provide the right care to the right person at the right time.”