Micron pops the parachute.
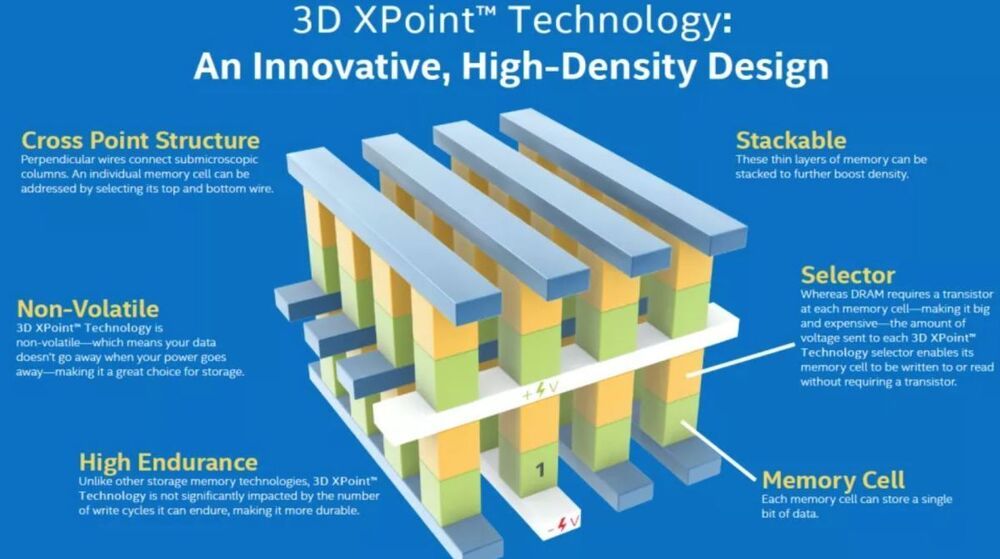
Micron announced today that it has entered into a definitive agreement to sell its Lehi, Utah fab to Texas Instruments for $900 million in cash. In March, Micron announced that it planned to sell off the fab, bringing an end to its production of the radical new 3D XPoint (Optane) memory technology that it developed with Intel. Texas Instruments plans to deploy its own technologies at the site, meaning that it will not be used for 3D XPoint production. Intel currently doesn’t have any known high-volume production of the strategically important storage/memory media. However, it is known to produce a small amount of the media for research and validation at its New Mexico facility. As a result, Intel will likely have to establish its own production lines to ensure the supply of its Optane based SSDs and persistent memory DIMMs for its data center clients, though demand has seemed tepid.
Micron chose to exit 3D XPoint manufacturing due to lackluster demand that the company said had “insufficient market validation to justify the ongoing high levels of investments required to successfully commercialize 3D XPoint at scale.” The company recently divulged that it lost $400 million this year alone due to the lack of demand for 3D XPoint.
Micron has an agreement to produce 3D XPoint (which Intel brands as ‘Optane’) for Intel until the end of 2021. However, Intel’s own efforts to productize Optane, which uses the 3D XPoint media, have met with slow but steady uptake in the data center but fizzled in the consumer market. As such, Intel ceased production of all Optane devices for desktop PCs in January 2021.