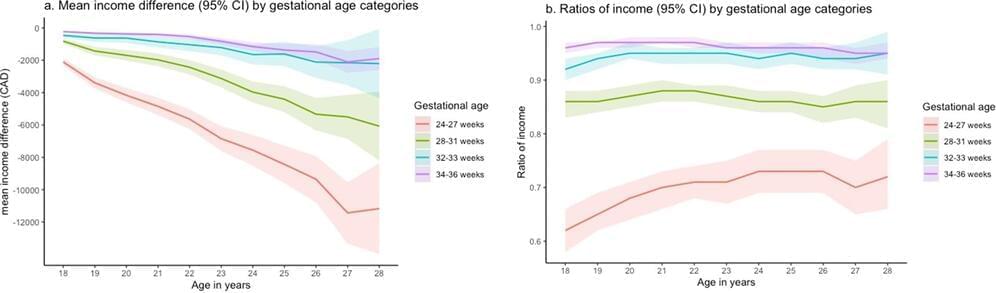
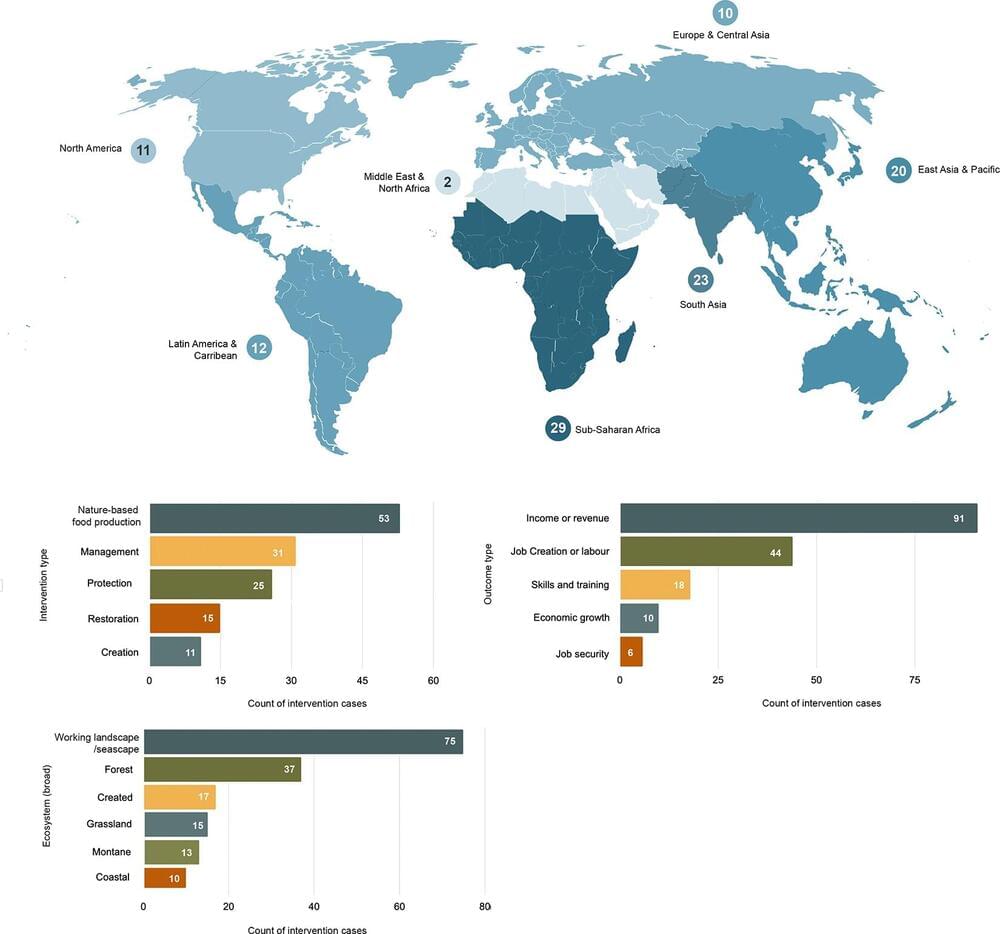
Since the public release of OpenAI’s ChatGPT, artificial intelligence (AI) has quickly become a driving force in innovation and everyday life, sparking both excitement and concern. AI promises breakthroughs in fields like medicine, education, and energy, with the potential to solve some of society’s toughest challenges. But at the same time, fears around job displacement, privacy, and the spread of misinformation have led many to call for tighter government control.
Many are now seeking swift government intervention to regulate AI’s development in the waning “lame duck” session before the inauguration of the next Congress. These efforts have been led by tech giants, including OpenAI, Amazon, Google, and Microsoft, under the guise of securing “responsible development of advanced AI systems” from risks like misinformation and bias. Building on the Biden administration’s executive order to create the U.S. Artificial Intelligence Safety Institute (AISI) and mandate that AI “safety tests,” among other things, be reported to the government, the bipartisan negotiations would permanently authorize the AISI to act as the nation’s primary AI regulatory agency.
The problem is, the measures pushed by these lobbying campaigns favor large, entrenched corporations, sidelining smaller competitors and stifling innovation. If Congress moves forward with establishing a federal AI safety agency, even with the best of intentions, it risks cementing Big Tech’s dominance at the expense of startups. Rather than fostering competition, such regulation would likely serve the interests of the industry’s largest corporations, stifling entrepreneurship and limiting AI’s potential to transform America—and the world—for the better. The unintended consequences are serious: slower product improvement, fewer technological breakthroughs, and severe costs to the economy and consumers.