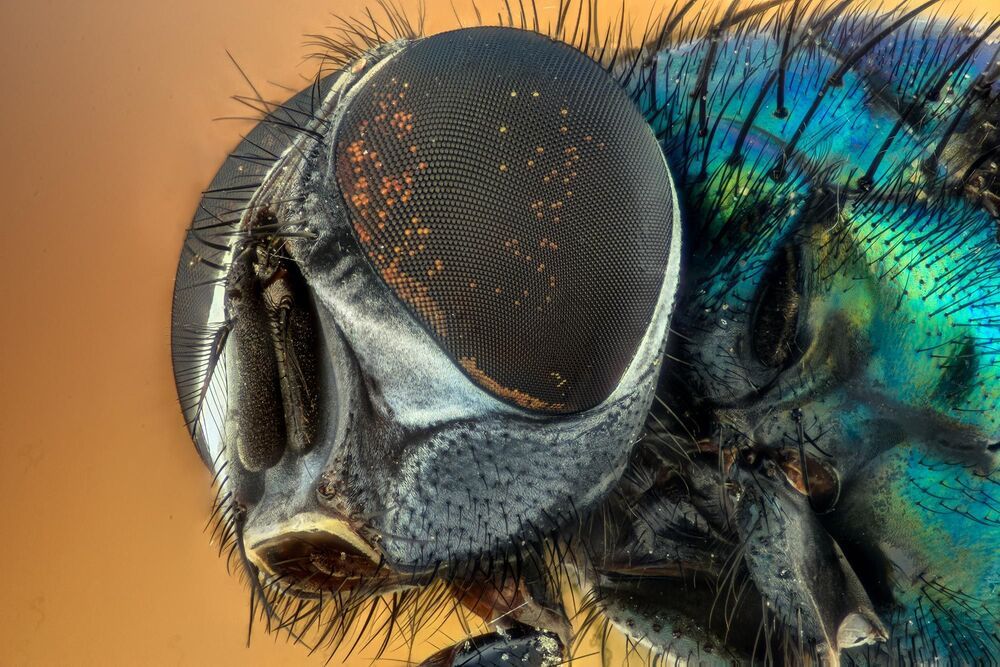
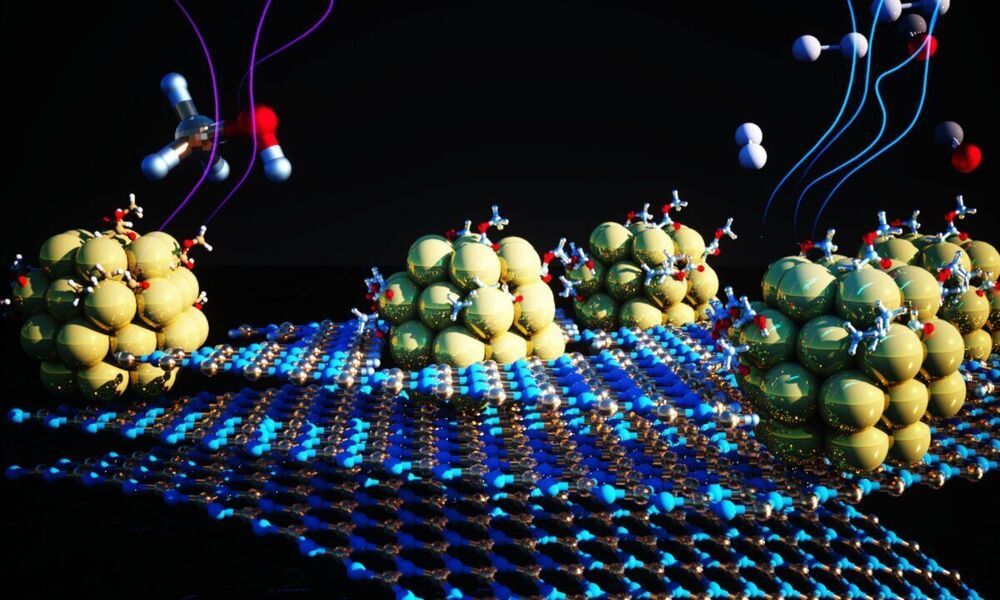
Scientists from Russia and Switzerland have probed into nanostructures covering the corneas of the eyes of small fruit flies. Investigating them the team learned how to produce the safe biodegradable nanocoating with antimicrobial, anti-reflective, and self-cleaning properties in a cost-effective and eco-friendly way. The protection coating might find applications in diverse areas of economics including medicine, nanoelectronics, automotive industry, and textile industry. The article describing these discoveries appears in Nature.
Scientists from Far Eastern Federal University (FEFU, Russia) teamed up with colleagues from University of Geneva, The University of Lausanne, and Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich for an interdisciplinary research project during which they were able to artificially reproduce the nanocoating of the corneas of fruit flies (Drosophila flies) naturally designed to protect the eyes of the insects from the smallest dust particles and shut off the reflection of light.
The craft of nanocoating meets demands in various fields of economics. It can wrap up any flat or three-dimensional structure, and, depending on the task, give it anti-reflective, antibacterial, and hydrophobic properties, including self-cleaning. The latter, for example, is a very important feature for expensive reusable overnight ortho-k lenses that correct the eyesight. Similar anti-reflective coatings are already known though created by more complex and costly methods. They are being used on the panels of computers, glasses, paintings in museums can be covered with them in order to exclude reflection and refraction of light.