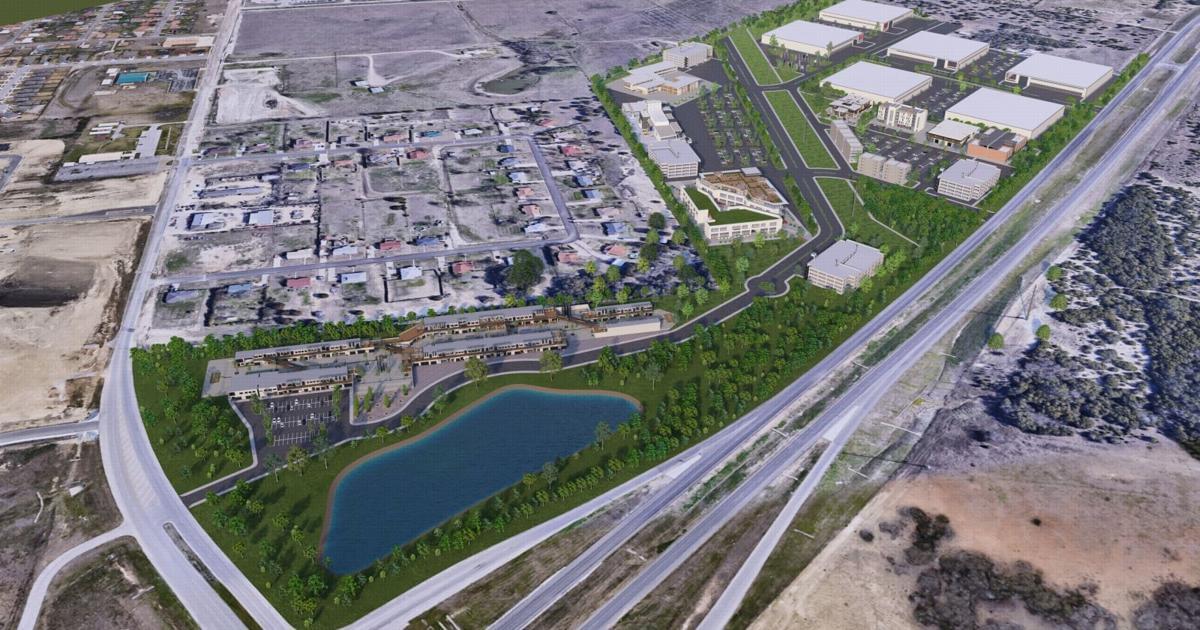
The establishment of a new business park in Killeen is underway.
Wolf Technology Park is set to inhabit 94-acres of real estate located on Texas Highway 195 in south Killeen.
“Wolf Technology Park is a cornerstone of our strategy to attract next-generation employers to Killeen,” Tyler Robert, vice president of the Killeen Economic Development Corporation, said. “With infrastructure investments already in place and sites ready for development, the park is well-positioned to support advanced manufacturing, federal services, health and life sciences, research and development, cybersecurity and semiconductor-related industries.”