A pair of Harvard students successfully rigged Meta-formerly-Facebook and Ray Ban’s smart glasses with facial recognition software.





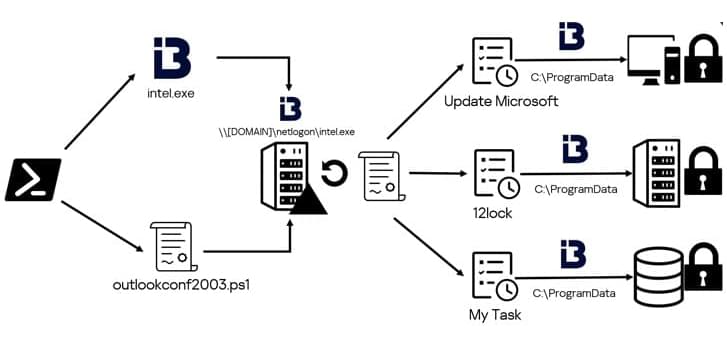


A massive infostealer malware operation encompassing thirty campaigns targeting a broad spectrum of demographics and system platforms has been uncovered, attributed to a cybercriminal group named “Marko Polo.”
The threat actors use a variety of distribution channels, including malvertising, spearphishing, and brand impersonation in online gaming, cryptocurrency, and software, to spread 50 malware payloads, including AMOS, Stealc, and Rhadamanthys.
According to Recorded Future’s Insikt Group, which has been tracking the Marko Polo operation, the malware campaign has impacted thousands, with potential financial losses in the millions.

Dell has confirmed to BleepingComputer that they are investigating recent claims that it suffered a data breach after a threat actor leaked the data for over 10,000 employees.
The allegations were published yesterday by a threat actor named “grep,” who alleges that the computing vendor suffered a “minor data breach” in September 2024, exposing internal employee and partner information.
In a post to a hacking forum, the threat actor says the stolen data includes employees’ unique identifiers, full names of employees for Dell and partners, status of employees (active or not), and an internal identification string.

The potential pathways through which AI could help us escape a simulated reality are both fascinating and complex. One approach could involve AI discovering and manipulating the underlying algorithms that govern the simulation. By understanding these algorithms, AI could theoretically alter the simulation’s parameters or even create a bridge to the “real” world outside the simulation.
Another approach involves using AI to enhance our cognitive and perceptual abilities, enabling us to detect inconsistencies or anomalies within the simulation. These anomalies, often referred to as “glitches,” could serve as clues pointing to the artificial nature of our reality. For instance, moments of déjà vu or inexplicable phenomena might be more than just quirks of human perception—they could be signs of the simulation’s imperfections.
While the idea of escaping a simulation is intriguing, it also raises profound ethical and existential questions. For one, if we were to confirm that we are indeed living in a simulation, what would that mean for our understanding of free will, identity, and the meaning of life? Moreover, the act of escaping the simulation could have unforeseen consequences. If the simulation is designed to sustain and nurture human life, breaking free from it might expose us to a harsher and more dangerous reality.

It also follows the discovery of a stealthy threat actor that presents itself as a legitimate enterprise and has been advertising automated CAPTCHA-solving services at scale to other cybercriminals and helping them infiltrate IT networks.
Dubbed Greasy Opal by Arkose Labs, the Czech Republic-based “cyber attack enablement business” is believed to have been operational since 2009, offering to customers a toolkit of sorts for credential stuffing, mass fake account creation, browser automation, and social media spam at a price point of $190 and an additional $10 for a monthly subscription.
The product portfolio runs the cybercrime gamut, allowing them to develop a sophisticated business model by packaging several services together. The entity’s revenues for 2023 alone are said to be no less than $1.7 million.