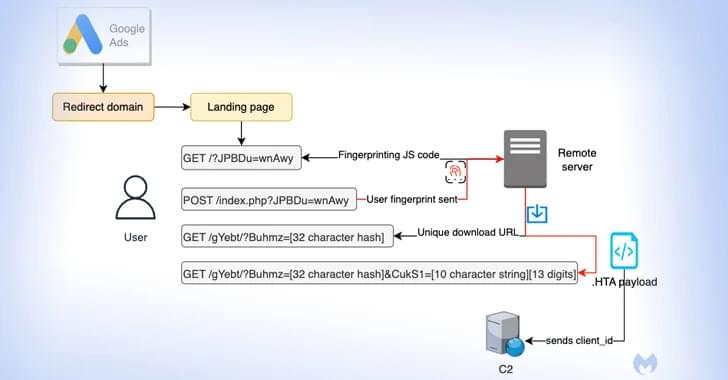
🚨 ALERT: A massive ad fraud botnet called PEACHPIT has been exposed. It exploited hundreds of thousands of Android and iOS devices to generate illicit profits for cybercriminals.


🚨Executives in U.S. firms under attack.
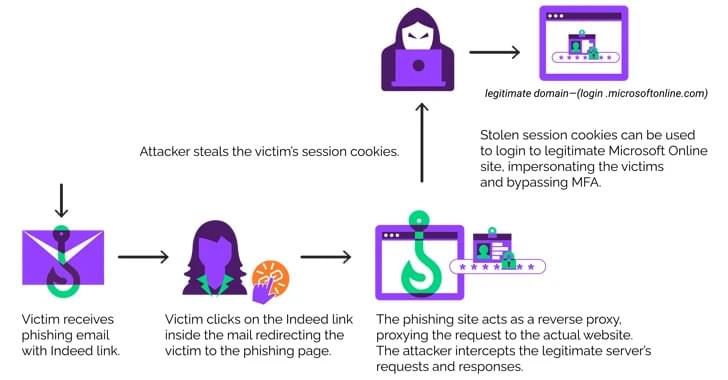
A new EvilProxy phishing campaign is targeting top-level employees, including banking, insurance, real estate, and manufacturing sectors.
Learn how they operate:
A new phishing campaign is on the rise, targeting U.S. organizations. Cybercriminals use EvilProxy to hijack accounts.

Operating since last May, an emerging ransomware strain called Rhysida was deployed along with new stealer malware called Lumar for a potent new one-two punch against Brazil’s popular PIX payment system users.
Researchers from Kaspersky reported Rhysida is functioning as a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) operation with a demonstrated ability to quickly evolve.
“ It stands out for its unique self-deletion mechanism and compatibility with pre-Windows 10 versions of Microsoft. Written in C++ and compiled with MinGW and shared libraries, Rhysida showcases sophistication in its design,” Kaspersky said in its findings about the group. “While relatively new, Rhysida faced initial configuration challenges with its onion server, revealing a group’s rapid adaptation and learning curve.”



To improve communication security and effectiveness, Edith Cowan University (ECU), observation data provider QL Space, and University of South Wales (UK) have formed a new collaboration that focuses on free space optics (FSO).
In early 2024, the agreement will see the construction of a satellite ground station close to ECU’s Joondalup campus in Perth’s north to empower FSO. It will eventually be one of numerous stations in the worldwide network built in collaboration with the University of South Wales (USW).
Using light to send data
FSO, commonly referred to as optical wireless communication or laser communication, uses light to send data across the air without the usage of physical cables or fibre optics. FSO systems transfer modulated data as optical signals using lasers or light-emitting diodes (LEDs).


A threat actor who claimed responsibility for the compromise of the 23AndMe site earlier this month has released a new dataset, including the records of more than 4 million people’s genetic ancestry.
The cybercriminal, known by the handle Golem, alleges in a cybercrime Dark Web forum the stolen data includes information on, “the wealthiest people living in the US and Western Europe,” according to reports.
23andMe spokesperson Andy Kill said in a statement the organization is still trying to confirm whether the most recently leaked data is genuine.
If you wanted to, you could access an “evil” version of OpenAI’s ChatGPT today—though it’s going to cost you. It also might not necessarily be legal depending on where you live.
However, getting access is a bit tricky. You’ll have to find the right web forums with the right users. One of those users might have a post marketing a private and powerful large language model (LLM). You’ll connect with them on an encrypted messaging service like Telegram where they’ll ask you for a few hundred dollars in cryptocurrency in exchange for the LLM.
Once you have access to it, though, you’ll be able to use it for all the things that ChatGPT or Google’s Bard prohibits you from doing: have conversations about any illicit or ethically dubious topic under the sun, learn how to cook meth or create pipe bombs, or even use it to fuel a cybercriminal enterprise by way of phishing schemes.