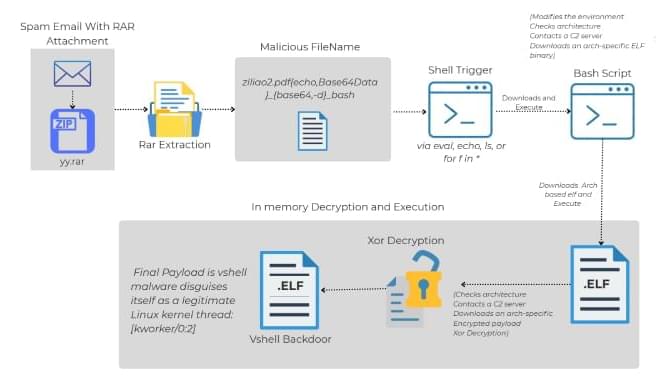
State-sponsored hackers linked to the Silk Typhoon activity cluster targeted diplomats by hijacking web traffic to redirect to a malware-serving website.
The hackers used an advanced adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) technique to hijack the captive portal of the network and send the target to the first-stage malware.
Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) tracks the threat actor as UNC6384 and, based on tooling, targeting, and infrastructure, believes it is associated with the Chinese threat actor TEMP.Hex, also known as Mustang Panda and Silk Typhoon.