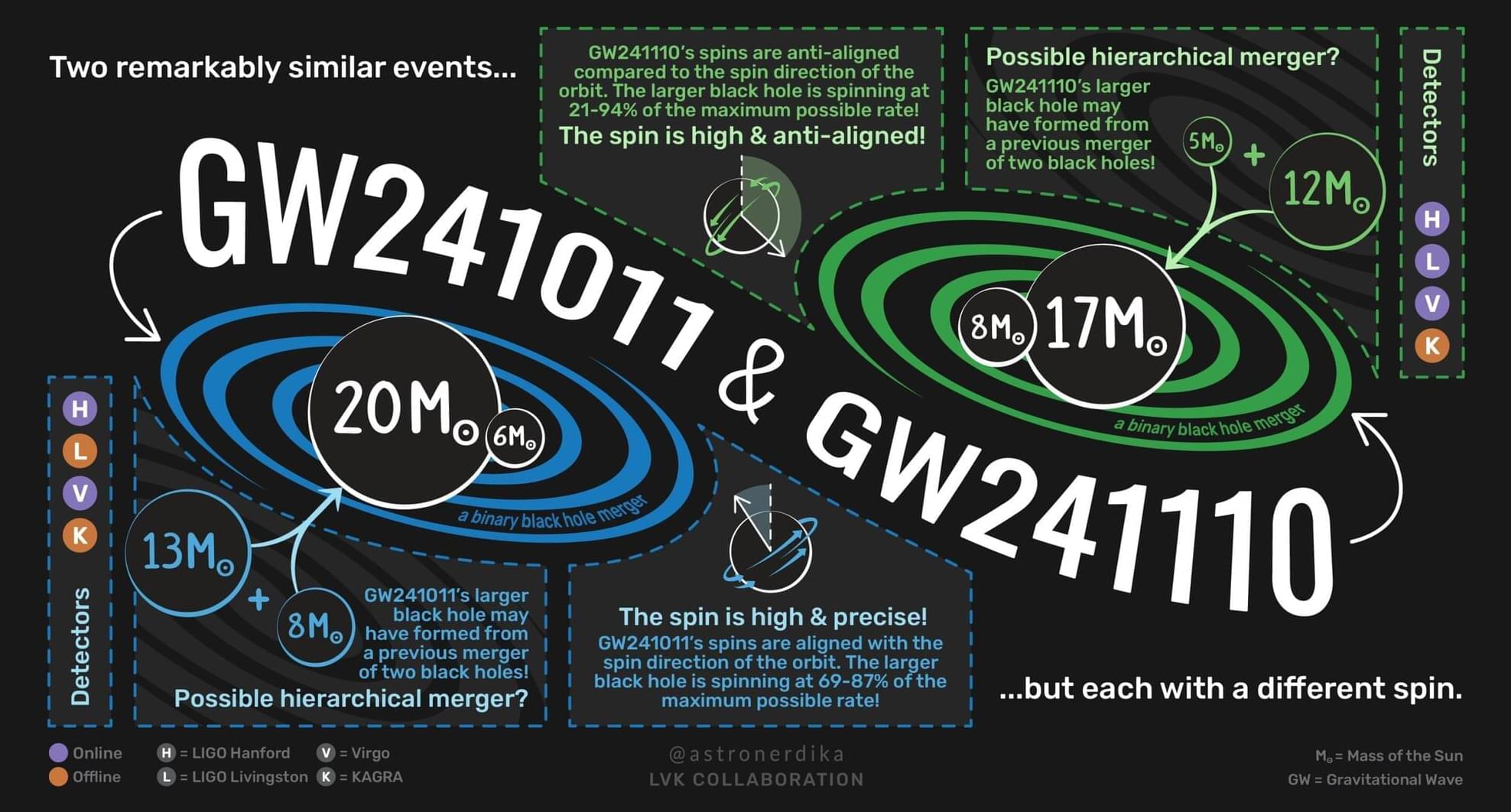
In a paper published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, the international LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA Collaboration reports on the detection of two gravitational wave events in October and November of 2024 with unusual black hole spins. This observation adds an important new piece to our understanding of the most elusive phenomena in the universe.
Gravitational waves are “ripples” in space-time that result from cataclysmic events in deep space, with the strongest waves produced by the collision of black holes.
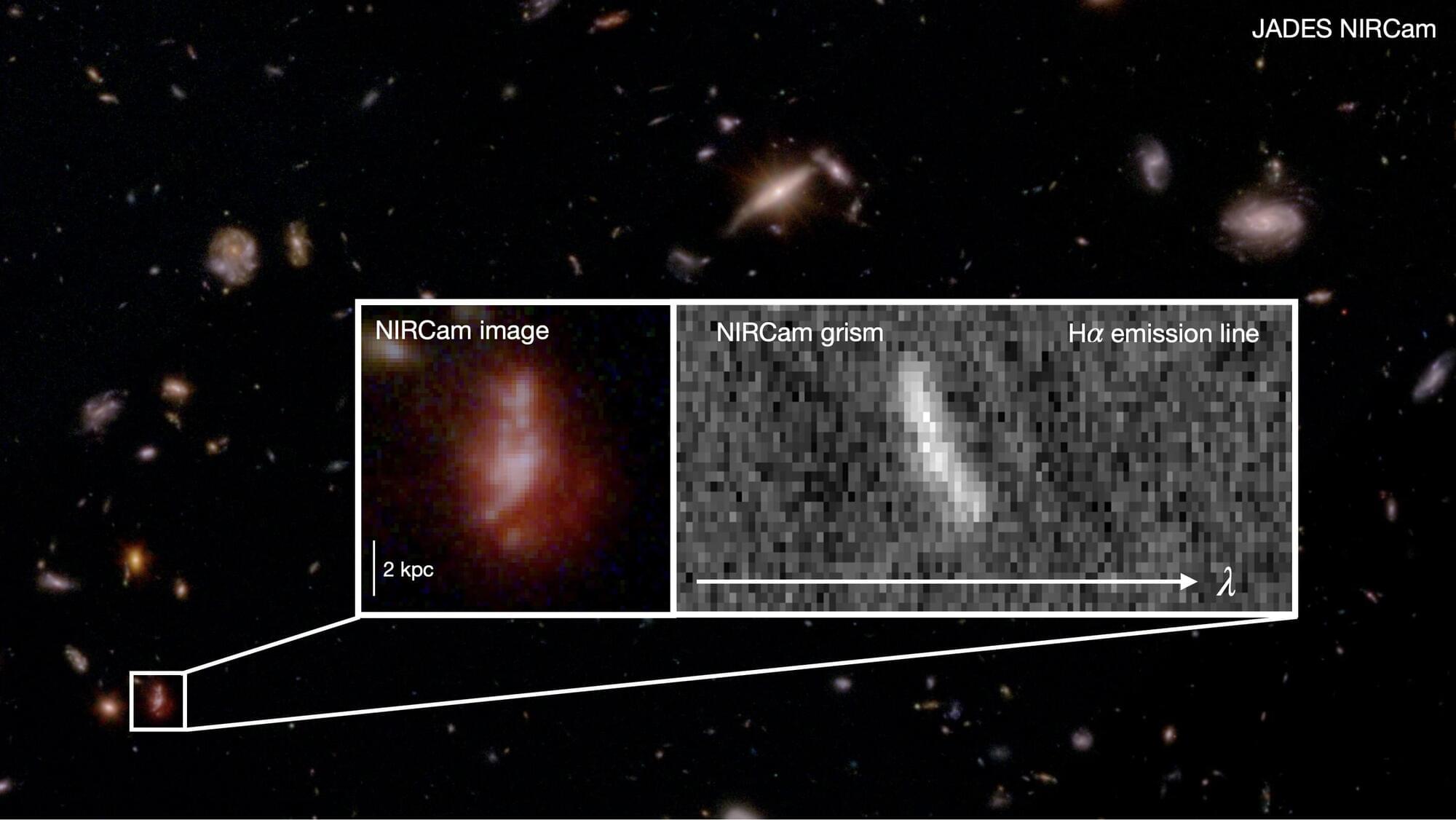
Using sophisticated algorithmic techniques and mathematical models, researchers are able to reconstruct many physical features of the detected black holes from the analysis of gravitational signals, such as their masses and the distance of the event from Earth, and even the speed and direction of their rotation around their axis, called spin.