Results from the XENON experiment in Italy hint at the possible discovery of long-sought axions.


The cosmos contains a Higgs field—similar to an electric field—generated by Higgs bosons in the vacuum. Particles interact with the field to gain energy and, through Albert Einstein’s iconic equation, E=mc2, mass. The Standard Model of particle physics, although successful at describing elementary particles and their interactions at low energies, does not include a viable and hotly debated dark-matter particle. The only possible candidates, neutrinos, do not have the right properties to explain the observed dark matter.
“One particularly interesting possibility is that these long-lived dark particles are coupled to the Higgs boson in some fashion—that the Higgs is actually a portal to the dark world. We know for sure there’s a dark world, and there’s more energy in it than there is in ours. It’s possible that the Higgs could actually decay into these long-lived particles,” said LianTao Wang, a University of Chicago physicist, in 2019, referring to the last holdout particle in physicists’ grand theory of how the universe works, discovered at the LHC in 2012, filling the last gap in the standard model of fundamental particles and forces. Since then, the standard model has stood up to every test, yielding no hints of new physics.
The dark world makes up more than 95 percent of the universe, but scientists only know it exists from its effects—” like a poltergeist you can only see when it pushes something off a shelf.” We know there’s dark matter because like the poltergeist, we can see gravity acting on it keeping galaxies from flying apart.
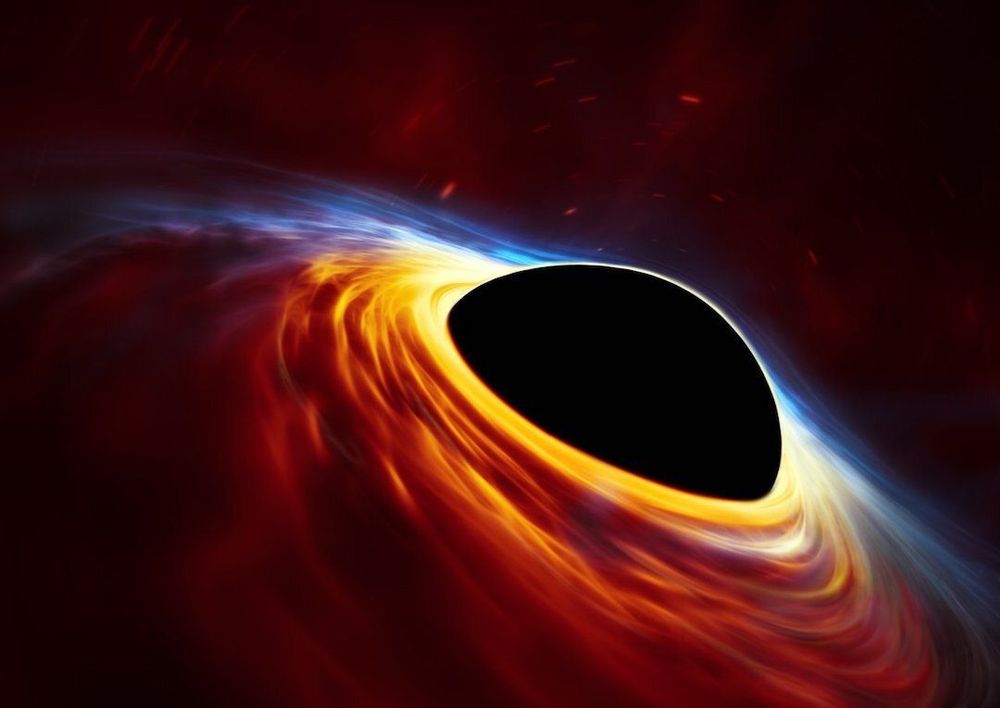

A black hole, at least in our current understanding, is characterized by having “no hair,” that is, it is so simple that it can be completely described by just three parameters, its mass, its spin and its electric charge. Even though it may have formed out of a complex mix of matter and energy, all other details are lost when the black hole forms. Its powerful gravitational field creates a surrounding surface, a “horizon,” and anything that crosses that horizon (even light) cannot escape. Hence the singularity appears black, and any details about the infalling material are also lost and digested into the three knowable parameters.
Astronomers are able to measure the masses of black holes in a relatively straightforward way: watching how matter moves in their vicinity (including other black holes), affected by the gravitational field. The charges of black holes are thought to be insignificant since positive and negative infalling charges are typically comparable in number. The spins of black holes are more difficult to determine, and both rely on interpreting the X-ray emission from the hot inner edge of the accretion disk around the black hole. One method models the shape of the X-ray continuum, and it relies on good estimates of the mass, distance, and viewing angle. The other models the X-ray spectrum, including observed atomic emission lines that are often seen in reflection from the hot gas. It does not depend on knowing as many other parameters. The two methods have in general yielded comparable results.
CfA astronomer James Steiner and his colleagues reanalyzed seven sets of spectra obtained by the Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer of an outburst from a stellar-mass black hole in our galaxy called 4U1543-47. Previous attempts to estimate the spin of the object using the continuum method resulted in disagreements between papers that were considerably larger than the formal uncertainties (the papers assumed a mass of 9.4 solar-masses and a distance of 24.7 thousand light-years). Using careful refitting of the spectra and updated modeling algorithms, the scientists report a spin intermediate in size to the previous ones, moderate in magnitude, and established at a 90% confidence level. Since there have been only a few dozen well confirmed black hole spins measured to date, the new result is an important addition.
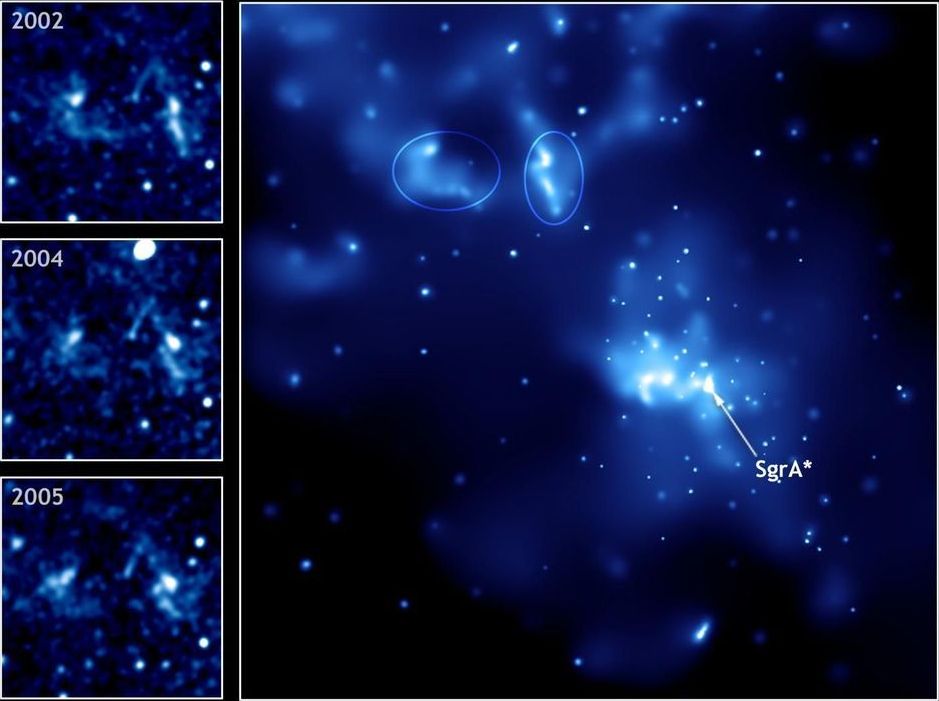

Like most galaxies, the Milky Way hosts a supermassive black hole at its center. Called Sagittarius A*, the object has captured astronomers’ curiosity for decades. And now there is an effort to image it directly.
Catching a good photo of the celestial beast will require a better understanding of what’s going on around it, which has proved challenging due to the vastly different scales involved. “That’s the biggest thing we had to overcome,” said Sean Ressler, a postdoctoral researcher at UC Santa Barbara’s Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics (KITP), who just published a paper in the Astrophysical Journal Letters, investigating the magnetic properties of the accretion disk surrounding Sagittarius A*.
In the study, Ressler, fellow KITP postdoc Chris White and their colleagues, Eliot Quataert of UC Berkeley and James Stone at the Institute for Advanced Study, sought to determine whether the black hole’s magnetic field, which is generated by in-falling matter, can build up to the point where it briefly chokes off this flow, a condition scientists call magnetically arrested. Answering this would require simulating the system all the way out to the closest orbiting stars.

A team of scientists, including Chief Investigator Ilya Mandel from the ARC Centre of Excellence for Gravitational Wave Discovery (OzGrav) at Monash University, recently studied what happens to rotating massive stars when they reach the end of their lives.
Stars produce energy by fusing lighter elements into heavier ones in their core: hydrogen into helium, then helium into carbon, oxygen, and so on, up to iron. The energy produced by this nuclear fusion also provides pressure support inside the star, which balances the force of gravity and allows the star to remain in equilibrium.
This process stops at iron. Beyond iron, energy is required to sustain fusion rather than being released by fusion. A heavy iron star core contracts under gravity, creating a neutron star, or if it is heavy enough, a black hole. Meanwhile, the outer layers of the star explode in a brilliant flash, observable as a supernova. However, some massive stars seem to completely disappear without any explosion. Theories suggest that these massive stars completely collapse into black holes, but is that possible?

Circa 2019 o,.0.
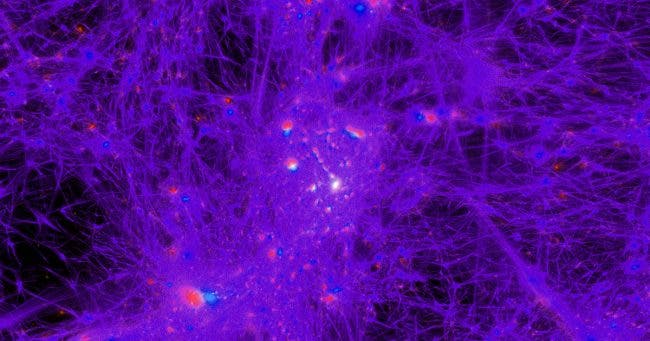
How did the universe evolve from a point of singularity, known as the Big Bang, into a massive structure whose boundaries seem limitless? New clues and insight into the evolution of the universe have recently been provided by an international team of physicists, who performed the most detailed large-scale simulation of the universe to date.
The researchers made their own universe in a box — a cube of space spanning more than 230 million light-years across. Previous cosmological simulations were either very detailed but spanned a small volume or less detailed across large volumes. The new simulation, known as TNG50, managed to combine the best of two worlds, producing a large-scale replica of the cosmos while, at the same time, allowing for unprecedented computational resolution.
The level of detail is incredible, matching what was once only possible to do in simulations of individual galaxies. TNG50, in fact, tracks 20 billion particles representing dark matter, stars, cosmic gas, magnetic fields, and supermassive black holes.

Black holes are the dark remnants of collapsed stars, regions of space cut off from the rest of the universe. If something falls into a black hole, it can never come back out. Not even light can escape, meaning black holes are invisible even with powerful telescopes. Yet physicists know black holes exist because they’re consistent with time-tested theories, and because astronomers have observed how matter behaves just outside a black hole.
Naturally, science fiction loves such an enigmatic entity. Black holes have played starring roles in popular books, movies and television shows, from “Star Trek” and “Doctor Who” to the 2014 blockbuster “Interstellar.”
But black holes aren’t quite as menacing as they are commonly portrayed. “They definitely do not suck,” says Daryl Haggard, an astrophysicist at McGill University in Montreal. “A black hole just sits there, passively. Things can fall onto it, just as meteors can fall to Earth, but it doesn’t pull stuff in.”

According to new research, black holes could be like a hologram, where all the information is amassed in a two-dimensional surface able to reproduce a three-dimensional image.
We can all picture that incredible image of a black hole that traveled around the world about a year ago. Yet, according to new research by SISSA, ICTP and INFN, black holes could be like a hologram, where all the information is amassed in a two-dimensional surface able to reproduce a three-dimensional image. In this way, these cosmic bodies, as affirmed by quantum theories, could be incredibly complex and concentrate an enormous amount of information inside themselves, as the largest hard disk that exists in nature, in two dimensions. This idea aligns with Einstein’s theory of relativity, which describes black holes as three dimensional, simple, spherical, and smooth, as they appear in that famous image. In short, black holes “appear” as three dimensional, just like holograms. The study which demonstrates it, and which unites two discordant theories, has recently been published in Physical Review X.
The mystery of black holes.
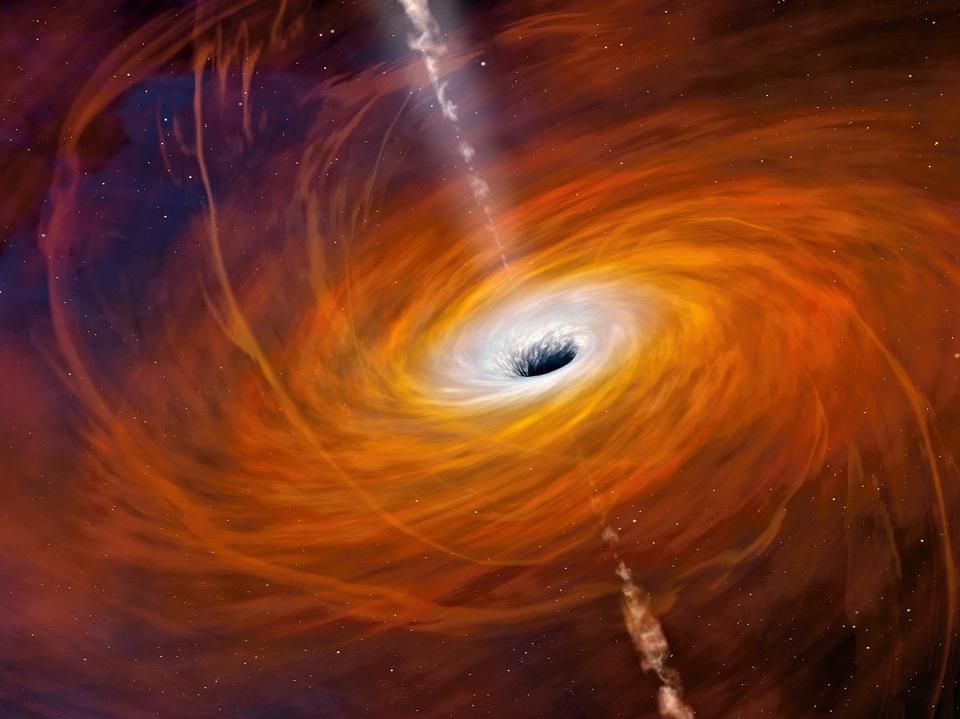


Warped Structure
When scientists say the universe is flat, it doesn’t necessarily mean it resembles an infinitely-expanding sheet of paper. More study, for instance, is needed to determine whether the universe could be bent into a torus — a donut-like shape still considered “flat” by cosmological models.
“This result shows the power of galaxy surveys to pin down the amount of dark energy and how it evolved over the last billion years,” Portsmouth cosmologist Seshadri Nadathur said in a press release. “We’re making really precise measurements now and the data is going to get even better with new surveys coming online very soon.”