Multiverse Cosmology, Nobel Laureates, Theories Of Everything, And Much More! — Dr. Brian Keating Ph.D., Chancellor’s Distinguished Professor of Physics, UC San Diego.
Dr. Brian Keating, Ph.D. (https://briankeating.com/) is Chancellor’s Distinguished Professor of Physics, at the Center for Astrophysics & Space Sciences (CASS), in the Department of Physics, at the University of California, San Diego (https://bkeating.physics.ucsd.edu/).
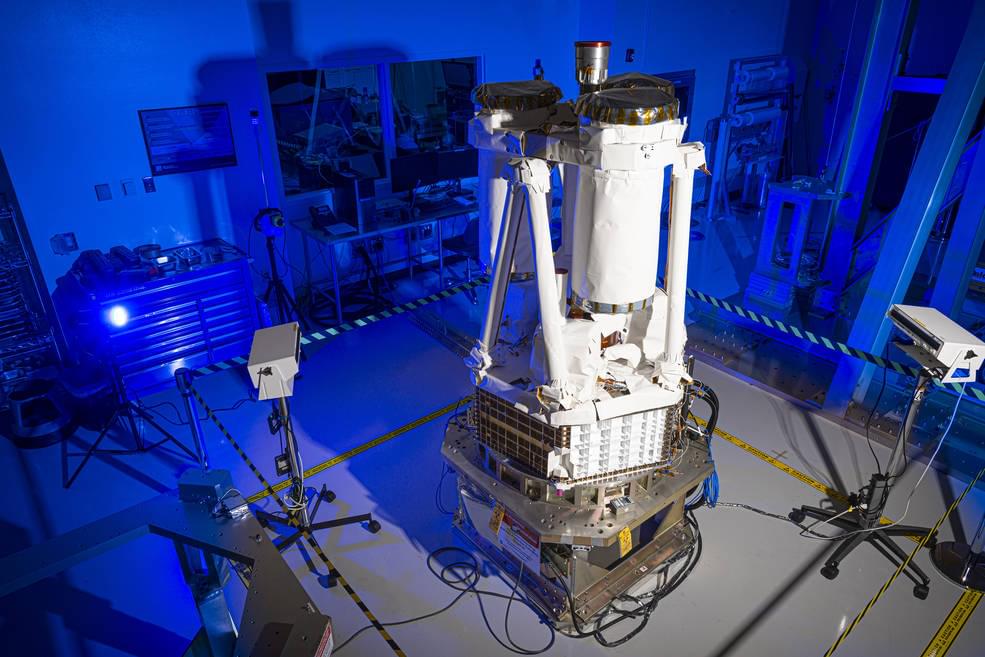
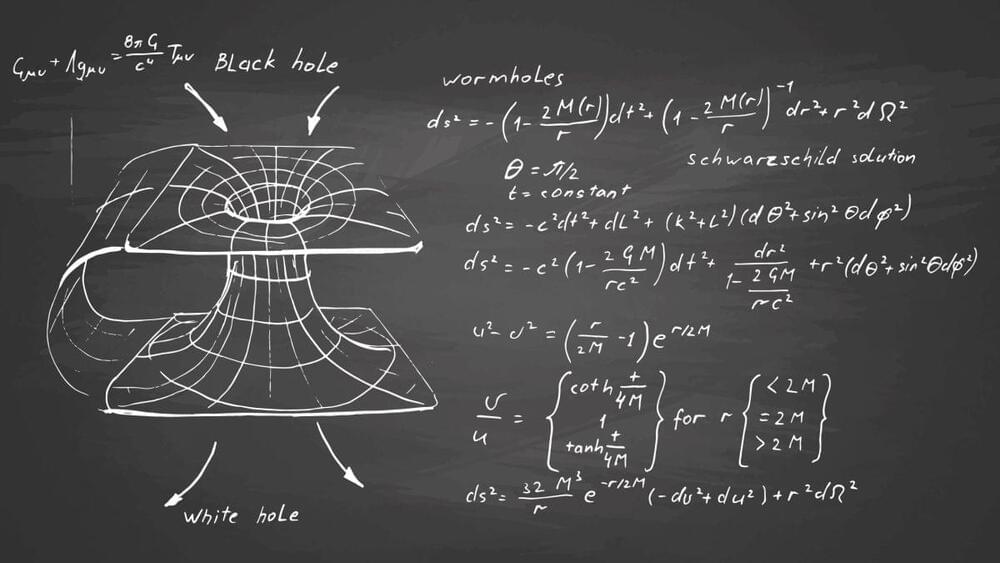
Dr. Keating is a public speaker, inventor, and an expert in the study of the universe’s oldest light, the cosmic microwave background (CMB), using it to learn not just about the origins and evolution of the universe, but to gain potential insights into an even bigger picture, that of the “multiverse”, a hypothetical group of multiple universes that comprise everything that exists: the entirety of space, time, matter, energy, information, and the physical laws and constants that describe them.
Dr. Keating is also a writer, the best-selling author of one of Amazon Editors’ Best Non-fiction Books of All Time, “Losing the Nobel Prize” (https://www.amazon.com/Losing-Nobel-Prize-Cosmology-Ambition…atfound-20 and his new book is entitled “Into The Impossible: Think Like A Nobel Prize Winner”.
Dr. Keating is also a prolific podcaster on the Into The Impossible podcast (https://briankeating.com/podcast.php).