The JWST provides an intriguing look at the early universe, but it’s not yet rewriting fundamental theories of the cosmos.
Category: cosmology – Page 289

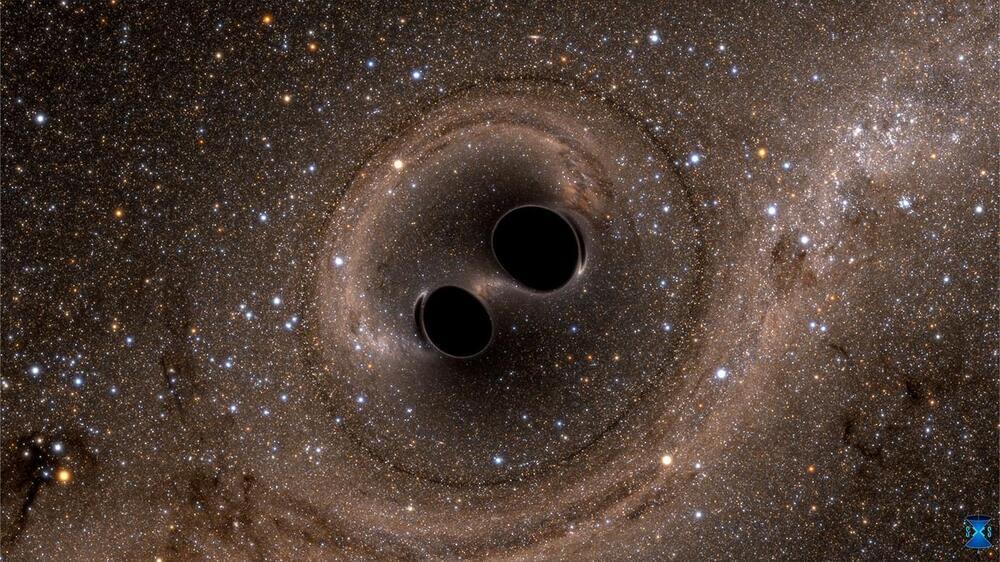
NASA have released the sound of a black hole and it’s terrifying
NASA has dropped a remix of what a black hole sounds like — and it’s exactly what you’d expect. The hole in question sits 200 million light-years away in the Perseus galaxy cluster — an 11 million-light-year-wide set of galaxies packed with hot gas. In the clip, you can hear rumbling and groaning which feels fit for an episode of Stranger Things, but it’s actually pressure waves rippling through the hot gas.




New underground lab to shed light on dark matter
Half a mile-deep lab is shielded with 100 tons of steel.
A gold mine located over half a mile (one km) underground in Victoria, Australia, has been converted into the Stawell Underground Physics Laboratory to study dark matter, a press release from Australia’s Nuclear Science and Technology Organization (ANSTO) said.
Scientists believe that dark matter, the invisible substance largely unknown to mankind, makes up 85 percent of our universe’s mass. To know more about it, scientists have been building dark matter detectors, and one of the “most sensitive” detectors delivered some significant results last month.
As with all things in science, one does not just stop with one data record.
A kilometre under the ground in Stawell, in the Northern Grampians in Victoria, a team of Australian scientists have put the final touches on an underground lab that will help us understand the nature of our universe.
Stage 1 of the Stawell Underground Physics Laboratory was officially opened today. It will be home to multi-disciplinary scientists from five research partners who are searching for evidence of dark matter.
Australia turns gold mine into physics lab to study dark matter
A gold mine located over half a mile (one km) underground in Victoria, Australia, has been converted into the Stawell Underground Physics Laboratory to study dark matter, a press release from Australia’s Nuclear Science and Technology Organization (ANSTO) said.
Scientists believe that dark matter, the invisible substance largely unknown to mankind, makes up 85 percent of our universe’s mass. To know more about it, scientists have been building dark matter detectors, and one of the “most sensitive” detectors delivered some significant results last month.
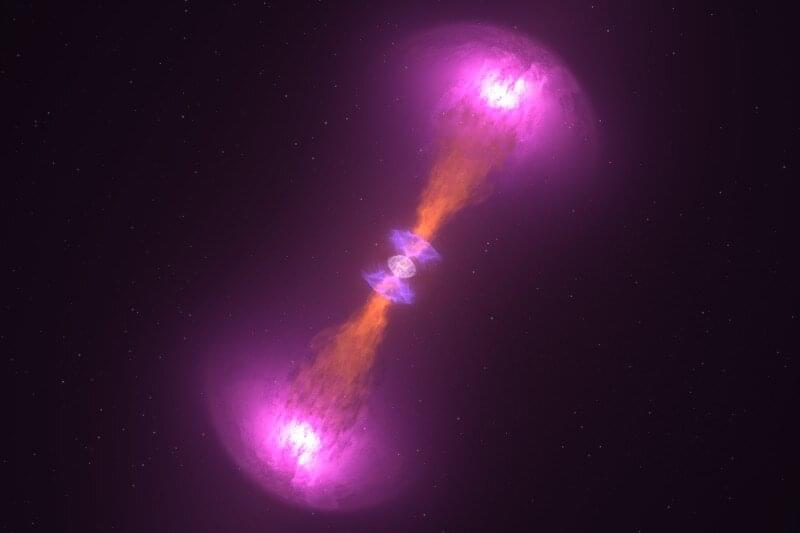
Looking inside a neutron star: New model will improve insights gleaned from gravitational waves
The oscillations in binary neutron stars before they merge could have big implications for the insights scientists can glean from gravitational wave detection.
Researchers at the University of Birmingham have demonstrated the way in which these unique vibrations, caused by the interactions between the two stars’ tidal fields as they get close together, affect gravitational-wave observations. The study is published in Physical Review Letters.
Taking these movements into account could make a huge difference to our understanding of the data taken by the Advanced LIGO and Virgo instruments, set up to detect gravitational waves —ripples in time and space—produced by the merging of black holes and neutron stars.

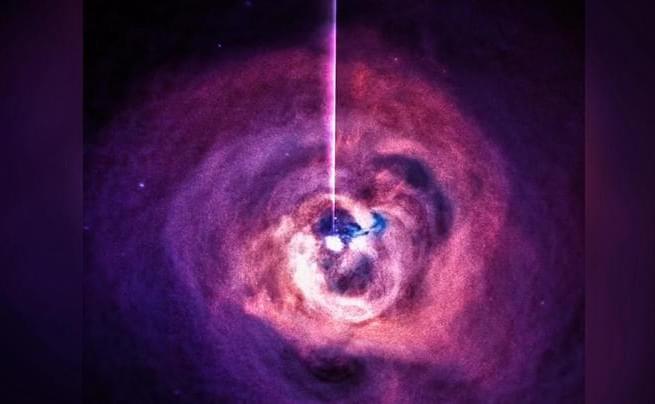
NASA — Saw Something Come Out Of A Black Hole For The First Time Ever… — Siamtoo
You don’t have to know a whole lot about science to know that black holes normally suck things in, not spew things out. But NASA detected something mighty bizarre at the supermassive black hole Markarian 335. Two of NASA’s space telescopes, including the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR), amazingly observed a black hole’s corona “launched” away from the supermassive black hole.
Then an enormous pulse of X-ray energy spewed out. This kind of phenomena has never been observed before.
