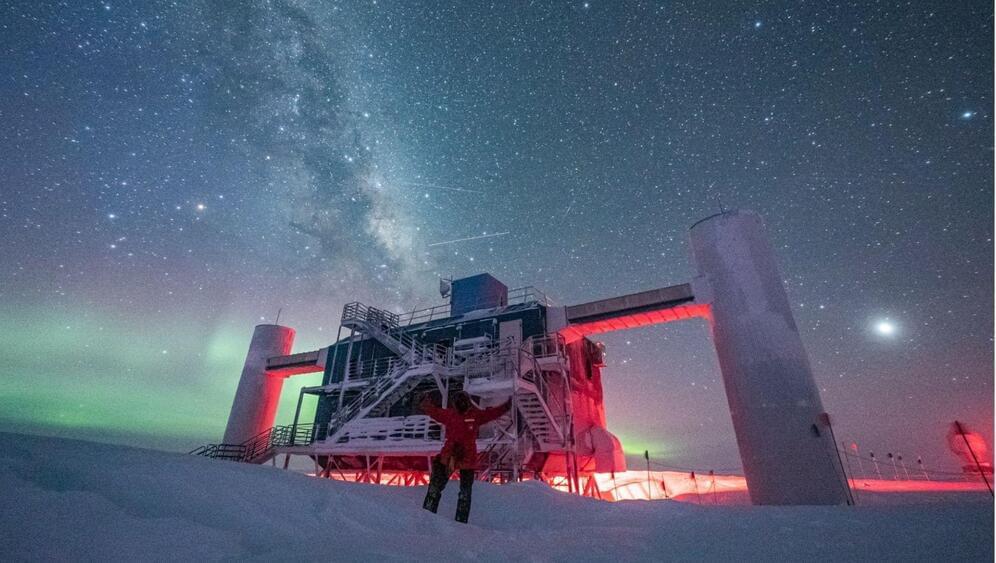
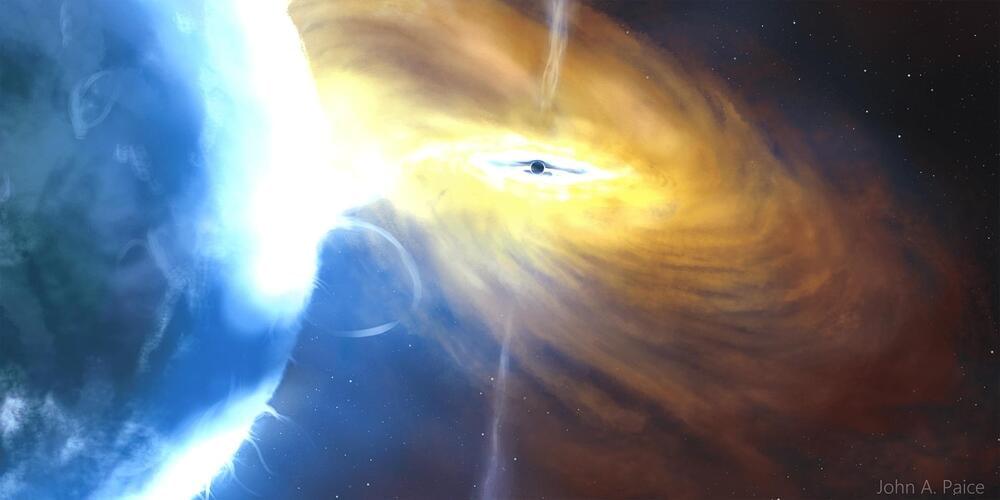
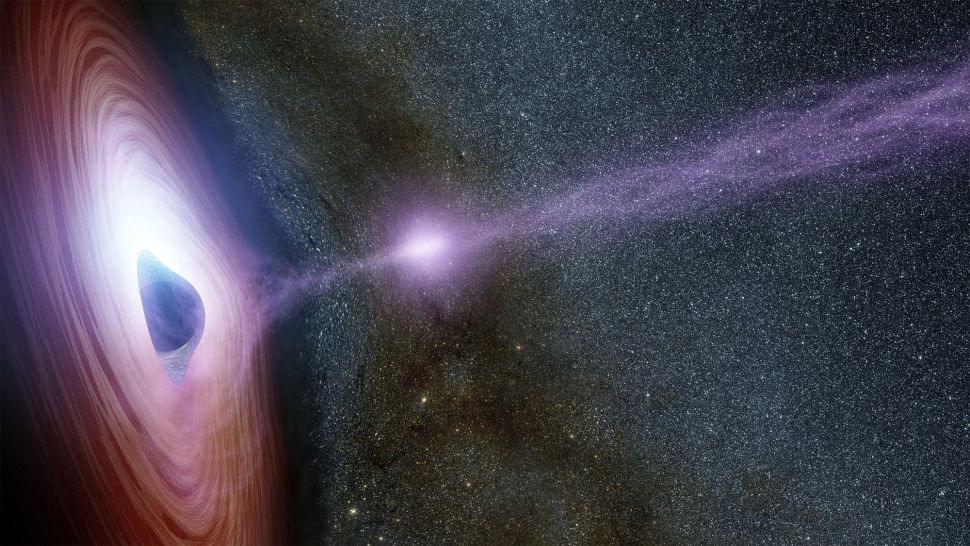
In 1961 astronomers discovered a powerful x-ray source coming from the constellation Cygnus. Not knowing what it was, they named the source Cygnus X-1. It’s one of the strongest x-ray sources in the sky, and we now know it is powered by a stellar-mass black hole. Since it is only about 7,000 light-years away, it also gives astronomers an excellent view of how stellar-mass black holes behave. Even after six decades of study, it continues to teach us a few things, as a recent study in Science shows.
Cygnus X-1 is actually a binary system. The black hole itself is a 21 solar-mass stellar remnant, and it orbits a 41 solar-mass companion star. It’s a powerful x-ray source because material from the star is captured into an accretion disk of the black hole, which superheats the material and generates jets of plasma that flow away from the black hole. This is a common situation for black holes, but astronomers still don’t understand all the details of how this type of structure evolves.
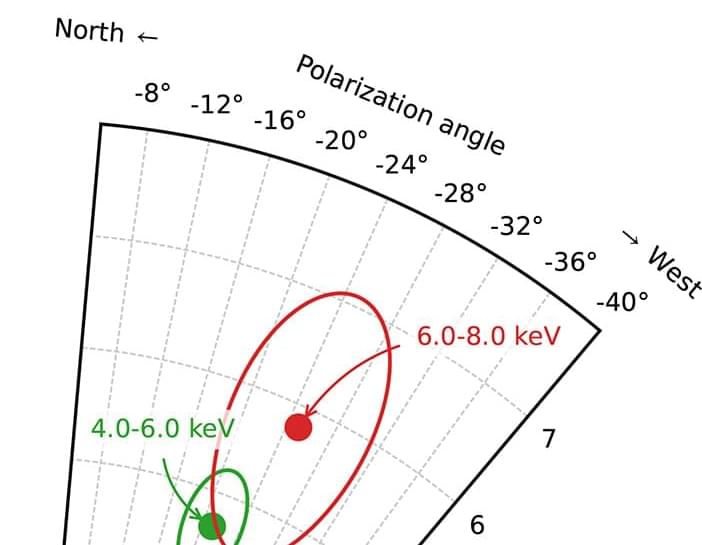
For this study, the team used data from the Imaging X-Ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE), which can capture not just x-rays but also their polarization. When they combined this data with other observations of Cygnus X-1, they found the x-rays are emitted not from the regions along the jets, but from a 2,000 km region perpendicular to the jets. In other words, the accretion disk itself is the primary x-ray source. This supports the model where the innermost region of the accretion disk is what powers a black hole’s jets.