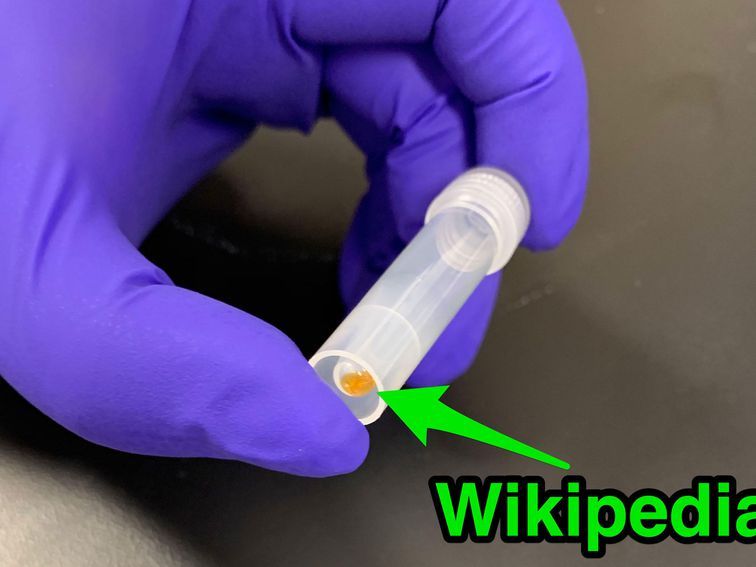
Biological molecules will last a lot longer than the latest computer storage technology, Catalog believes.



Conscious “free will” is problematic because brain mechanisms causing consciousness are unknown, measurable brain activity correlating with conscious perception apparently occurs too late for real-time conscious response, consciousness thus being considered “epiphenomenal illusion,” and determinism, i.e., our actions and the world around us seem algorithmic and inevitable. The Penrose–Hameroff theory of “orchestrated objective reduction (Orch OR)” identifies discrete conscious moments with quantum computations in microtubules inside brain neurons, e.g., 40/s in concert with gamma synchrony EEG. Microtubules organize neuronal interiors and regulate synapses. In Orch OR, microtubule quantum computations occur in integration phases in dendrites and cell bodies of integrate-and-fire brain neurons connected and synchronized by gap junctions, allowing entanglement of microtubules among many neurons. Quantum computations in entangled microtubules terminate by Penrose “objective reduction (OR),” a proposal for quantum state reduction and conscious moments linked to fundamental spacetime geometry. Each OR reduction selects microtubule states which can trigger axonal firings, and control behavior. The quantum computations are “orchestrated” by synaptic inputs and memory (thus “Orch OR”). If correct, Orch OR can account for conscious causal agency, resolving problem 1. Regarding problem 2, Orch OR can cause temporal non-locality, sending quantum information backward in classical time, enabling conscious control of behavior. Three lines of evidence for brain backward time effects are presented. Regarding problem 3, Penrose OR (and Orch OR) invokes non-computable influences from information embedded in spacetime geometry, potentially avoiding algorithmic determinism. In summary, Orch OR can account for real-time conscious causal agency, avoiding the need for consciousness to be seen as epiphenomenal illusion. Orch OR can rescue conscious free will.
Keywords: microtubules, free will, consciousness, Penrose-Hameroff Orch OR, volition, quantum computing, gap junctions, gamma synchrony.
We have the sense of conscious control of our voluntary behaviors, of free will, of our mental processes exerting causal actions in the physical world. But such control is difficult to scientifically explain for three reasons:
Hi all.
Up until now, chip-makers have been piggybacking on the renowned Moore’s Law for delivering successive generations of chips that have more compute capabilities and are less power hungry. Now, these advancements are slowly coming to a halt. Researchers around the world are proposing alternative architectures to continue producing systems which are faster and more energy efficient. This article discusses those alternatives and reasons why one of them might have an edge over others in averting the chip design industry from getting stymied.
Moore’s law, or to put it differently — savior of chip-makers worldwide — was coined by Dr. Gordon Moore, the founder of Intel Corp, in 1965. The law states that the number of transistors on a chip would double every 2 years. But why the savior of chip-makers? This law was so powerful during the semiconductor boom that “people would auto-buy the next latest and greatest computer chip, with full confidence that it would be better than what they’ve got”, said former Intel engineer Robert P. Colwell. Back in the day writing a program with bad performance was not an issue as the programmer knew that Moore’s law would ultimately save him.
Problem that we are facing today is, the law is nearly dead! Or to avert from offending Moore fans — as Henry Samueli, chief technology officer for Broadcom says.
Flashback to 2 years ago…
Scientists from Maastricht University have developed a method to look into the brain of a person and read out who has spoken to him or her and what was said. With the help of neuroimaging and data mining techniques the researchers mapped the brain activity associated with the recognition of speech sounds and voices.
In their Science article “‘Who’ is Saying ‘What’? Brain-Based Decoding of Human Voice and Speech,” the four authors demonstrate that speech sounds and voices can be identified by means of a unique ‘neural fingerprint’ in the listener’s brain. In the future this new knowledge could be used to improve computer systems for automatic speech and speaker recognition.
Seven study subjects listened to three different speech sounds (the vowels /a/, /i/ and /u/), spoken by three different people, while their brain activity was mapped using neuroimaging techniques (fMRI). With the help of data mining methods the researchers developed an algorithm to translate this brain activity into unique patterns that determine the identity of a speech sound or a voice. The various acoustic characteristics of vocal cord vibrations (neural patterns) were found to determine the brain activity.

Circa 2016
Diamond computer chips running at 100-GHz have been demonstrated by Akhan Semiconductor. They are currently using design rules in the 100s of nanometers.
Developers are focusing on power applications on 12-inch wafers. They hope to drive down the costs of production with higher volumes. Power devices are moving into pilot production at a fab. They are using the fab-lite model—that is produce small- to medium-sized runs themselves. They will then transfer their process to foundries when they ramp up into volume production.
They have some customers for diamond MEMS devices—specifically for capacitive switching arrays used to dynamically tune antenna in high-end smartphones.

Information and gravity may seem like completely different things, but one thing they have in common is that they can both be described in the framework of geometry. Building on this connection, a new paper suggests that the rules for optimal quantum computation are set by gravity.
Physicists Paweł Caputa at Kyoto University and Javier Magan at the Instituto Balseiro, Centro Atómico de Bariloche in Argentina have published their paper on the link between quantum computing and gravity in a recent issue of Physical Review Letters.
In the field of computational complexity, one of the main ideas is minimizing the cost (in terms of computational resources) to solve a problem. In 2006, Michael Nielsen demonstrated that, when viewed in the context of differential geometry, computational costs can be estimated by distances. This means that minimizing computational costs is equivalent to finding minimal “geodesics,” which are the shortest possible distances between two points on a curved surface.

Physicists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have teleported a computer circuit instruction known as a quantum logic operation between two separated ions (electrically charged atoms), showcasing how quantum computer programs could carry out tasks in future large-scale quantum networks.
Quantum teleportation transfers data from one quantum system (such as an ion) to another (such as a second ion), even if the two are completely isolated from each other, like two books in the basements of separate buildings. In this real-life form of teleportation, only quantum information, not matter, is transported, as opposed to the Star Trek version of “beaming” entire human beings from, say, a spaceship to a planet.
Teleportation of quantum data has been demonstrated previously with ions and a variety of other quantum systems. But the new work is the first to teleport a complete quantum logic operation using ions, a leading candidate for the architecture of future quantum computers. The experiments are described in the May 31 issue of Science.
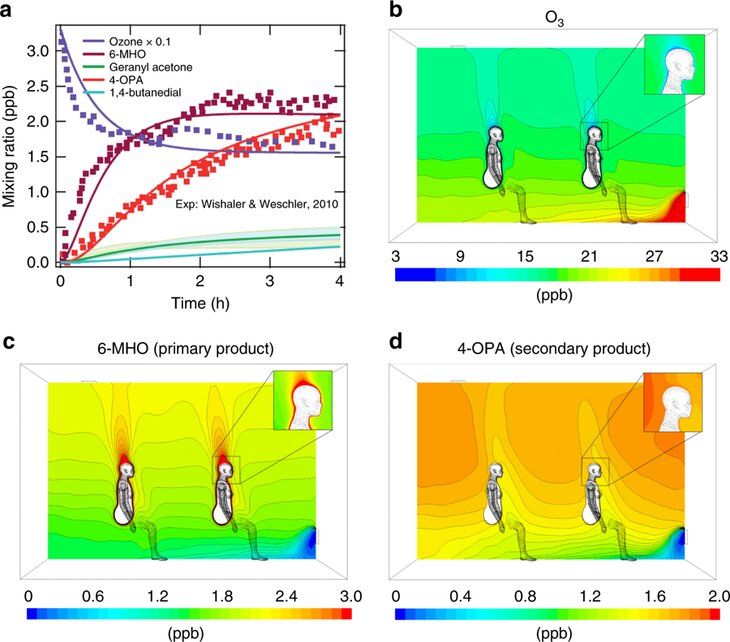
When ozone and skin oils meet, the resulting reaction may help remove ozone from an indoor environment, but it can also produce a personal cloud of pollutants that affects indoor air quality, according to a team of researchers.
In a computer model of indoor environments, the researchers show that a range of volatile and semi-volatile gases and substances are produced when ozone, a form of oxygen that can be toxic, reacts with skin oils carried by soiled clothes, a reaction that some researchers have likened to the less-than-tidy Peanuts comic strip character.
“When the ozone is depleted through human skin, we become the generator of the primary products, which can cause sensory irritations,” said Donghyun Rim, assistant professor of architectural engineering and an Institute for CyberScience associate, Penn State. “Some people call this higher concentration of pollutants around the human body the personal cloud, or we call it the ”Pig-Pen Effect.””.
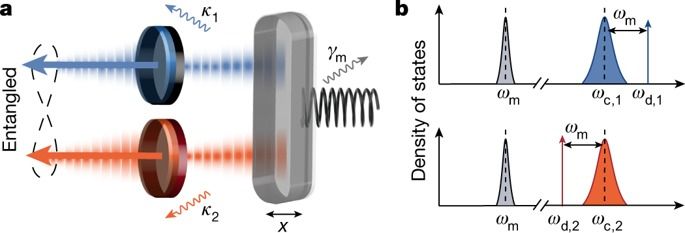
Mechanical systems facilitate the development of a hybrid quantum technology comprising electrical, optical, atomic and acoustic degrees of freedom, and entanglement is essential to realize quantum-enabled devices. Continuous-variable entangled fields—known as Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen (EPR) states—are spatially separated two-mode squeezed states that can be used for quantum teleportation and quantum communication. In the optical domain, EPR states are typically generated using nondegenerate optical amplifiers, and at microwave frequencies Josephson circuits can serve as a nonlinear medium4,5,6. An outstanding goal is to deterministically generate and distribute entangled states with a mechanical oscillator, which requires a carefully arranged balance between excitation, cooling and dissipation in an ultralow noise environment. Here we observe stationary emission of path-entangled microwave radiation from a parametrically driven 30-micrometre-long silicon nanostring oscillator, squeezing the joint field operators of two thermal modes by 3.40 decibels below the vacuum level. The motion of this micromechanical system correlates up to 50 photons per second per hertz, giving rise to a quantum discord that is robust with respect to microwave noise. Such generalized quantum correlations of separable states are important for quantum-enhanced detection and provide direct evidence of the non-classical nature of the mechanical oscillator without directly measuring its state. This noninvasive measurement scheme allows to infer information about otherwise inaccessible objects, with potential implications for sensing, open-system dynamics and fundamental tests of quantum gravity. In the future, similar on-chip devices could be used to entangle subsystems on very different energy scales, such as microwave and optical photons.